
Concept explainers
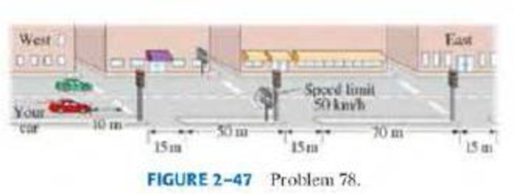
Consider the street pattern shown in Fig. 2–47. Each intersection has a traffic signal, and the speed limit is 50 km/ h. Suppose you are driving from the west at the speed limit. When you are 10.0m from the first intersection, all the lights turn green. The lights are green for 13.0 s each. (a) Calculate the time needed to reach the third stoplight. Can you make it through all three lights without stopping? (b) Another car was stopped at the first light when all the lights turned green. It can accelerate at the rate of 2.00 m/s2 to the speed limit. Can the second car make it through all three lights without stopping? By how many seconds would it make it or not?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 2 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS & ENGINEERS
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
- (1) If you are driving 110 km/h along a straight road and you look to the side for 2.0 s, how far do you travel during this inattentive period?arrow_forwardPerson A jogs east at a speed of 5 meters per second for 3 minutes, then turns north and jogs at 4 meters per second for 5 minutes. (1) what is the jogging speed of person A for the whole duration?arrow_forwardThere are two trains. The Rabbit heads north on the expressway at 45 kph. Exacty 12 minutes after, the Panther follows at a steady speed of 54 kph. How long does it take the Panther to overtake the Rabbit?arrow_forward
- A truck is traveling east at 82 km/h. At an intersection 34 km ahead, a car is traveling north at 60 km/h. (a) How long (in minutes) after this moment will the vehicles be closest to each other? b) How far apart will they be at that point (in km)?arrow_forwardDo highway speed limit signs refer to average speeds or to instantaneous speeds? Explain.arrow_forwardIs it possible for speed to be constant while acceleration is not zero?arrow_forward
- If a car is traveling eastward, can its acceleration be westward? Explain.arrow_forwardThe minimum distance required to stop a car moving at 35.0 mi/h is 40.0 ft. What is the minimum stopping distance for the same car moving at 70.0 mi/h, assuming the same rate of acceleration?arrow_forwardA stone is thrown vertically upward with a speed of 15.5 m/s from the edge of a cliff 75.0 m high (Fig. 2–48). (a) How much later does it reach the bottom of the cliff? (b) What is its speed just before hitting? (c) What total distance -y = 0 did it travel? FIGURE 2-48 Ey= -75 m Problem 71.arrow_forward
- b) If the fastest you can safely drive is 65 mi/h, what is the longest time you can stop for a dinner if you must travel 235 mi in 4.5 h total?arrow_forward(III) Sketch the v vs. t graph for the object whose displacement as a function of time is given by Fig. 2–44arrow_forwardAn airplane travels 2100 km at a speed of 720 km/h and then encounters a tailwind that boosts its speed to 990 km/h for the next 2800 km. What was the total time for the trip? What was the average speed of the plane for this trip?[Hint: Does Eq. 2–11d apply?arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University



