
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS & ENGINEERS
5th Edition
ISBN: 9780134296074
Author: GIANCOLI
Publisher: VST
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 19Q
Describe in words the motion of the object graphed in Fig. 2–37.
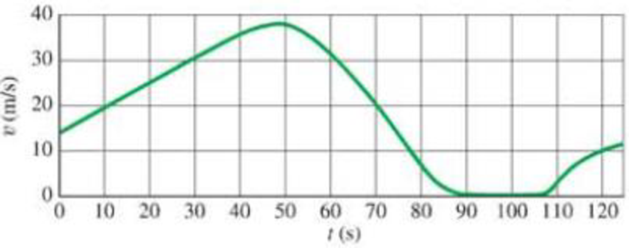
FIGURE 2–37 Question 19, Problem 23.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A person driving her car at 35 km/h approaches an inter-
section just as the traffic light turns yellow. She knows that
the yellow light lasts only 2.0s before turning to red, and
she is 28 m away from the near side of the intersection
(Fig. 2–49). Should she try to stop, or should she speed up
to cross the intersection before the light turns red? The
intersection is 15 m wide. Her car's maximum deceleration
is -5.8 m/s?, whereas it can accelerate from 45 km/h to
65 km/h in 6.0 s. Ignore the length of her car and her
reaction time.
– 28 m -
-15 m→
FIGURE 2-49 Problem 73.
In putting, the force with which a golfer strikes a ball is
planned so that the ball will stop within some small distance
of the cup, say 1.0m long or short, in case the putt is missed.
Accomplishing this from an uphill lie (that is, putting the
ball downhill, see Fig. 2–47) is more difficult than from a
downhill lie. To see why, assume that on a particular green
the ball decelerates constantly at 1.8 m/s² going downhill,
and constantly at 2.6 m/s² going uphill. Suppose we have an
uphill lie 7.0 m from the cup. Calculate the allowable range
of initial velocities we may impart to the ball so that it stops
in the range 1.0 m short to 1.0 m long of the cup. Do the
same for a downhill lie 7.0 m from the cup. What in your
results suggests that the downhill putt is more difficult?
Uphill
lie
Downhill
7.0 m
lie
- 7.0 m
FIGURE 2-47 Problem 70.
Figure 2-42 shows a simple device for measuring your reaction time. It consists of a cardboard strip marked with a scale and two large dots. A friend holds the strip vertically, with thumb and forefinger at the dot on the right in Fig. 2-42. You then position your thumb and forefinger at the other dot (on the left in Fig. 2-42), being careful not to touch the strip. Your friend releases the strip, and you try to pinch it as soon as possible after you see it begin to fall. The mark at the place where you pinch the strip gives your reaction time. (a) How far from the lower dot should you place the 50.0 ms mark? How much higher should you place the marks for (b) 100, (c) 150, (d) 200, and (e) 250 ms? (For example, should the 100 ms marker be 2 times as far from the dot as the 50 ms marker? If so, give an answer of 2 times. Can you find any pattern in the answers?)
Chapter 2 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS & ENGINEERS
Ch. 2.1 - An ant starts at x = 20cm on a piece of graph...Ch. 2.3 - What is your speed at the instant you turn around...Ch. 2.4 - A powerful car is advertised to go from zero to 60...Ch. 2.4 - A car moves along the x axis. What is the sign of...Ch. 2.4 - The position of a particle is given by the...Ch. 2.5 - Prob. 1FECh. 2.7 - Prob. 1GECh. 2.7 - Prob. 1HECh. 2 - Does a car speedmeter measure speed, velocity, or...Ch. 2 - Can an object have a varying speed if its velocity...
Ch. 2 - When an object moves with constant velocity, does...Ch. 2 - If one object has a greater speed than a second...Ch. 2 - Compare the acceleration of a motorcycle that...Ch. 2 - Can an object have a northward velocity and a...Ch. 2 - Can the velocity of an object be negative when its...Ch. 2 - Give an example where both the velocity and...Ch. 2 - Two cars emerge side by side from a tunnel. Car A...Ch. 2 - Can an object be increasing in speed as its...Ch. 2 - A baseball player hits a ball straight up into the...Ch. 2 - As a freely falling object speeds up, what is...Ch. 2 - You travel from point A to point B in a car moving...Ch. 2 - Can an object have zr velocity and nonzero...Ch. 2 - Can an object have zero acceleration and nonzero...Ch. 2 - Which of these motions is not at constant...Ch. 2 - Prob. 17QCh. 2 - Describe in words the motion plotted in Fig. 236...Ch. 2 - Describe in words the motion of the object graphed...Ch. 2 - Prob. 1MCQCh. 2 - Prob. 2MCQCh. 2 - Prob. 4MCQCh. 2 - Prob. 5MCQCh. 2 - Prob. 6MCQCh. 2 - Prob. 7MCQCh. 2 - Prob. 9MCQCh. 2 - Prob. 11MCQCh. 2 - (I) If you are driving 110 km/h along a straight...Ch. 2 - What must your cars average speed be in order to...Ch. 2 - (I) A particle at t1 = 2.0 s is at x1 = 4.3 cm and...Ch. 2 - (II) According to a rule-of-thumb, every five...Ch. 2 - Prob. 5PCh. 2 - Prob. 6PCh. 2 - Prob. 7PCh. 2 - Prob. 8PCh. 2 - Prob. 9PCh. 2 - Prob. 10PCh. 2 - Prob. 11PCh. 2 - Prob. 12PCh. 2 - Prob. 13PCh. 2 - Prob. 14PCh. 2 - Prob. 15PCh. 2 - Prob. 16PCh. 2 - Prob. 17PCh. 2 - Prob. 18PCh. 2 - Prob. 19PCh. 2 - Prob. 20PCh. 2 - Prob. 21PCh. 2 - Prob. 22PCh. 2 - Prob. 24PCh. 2 - (II) A car moving in a straight line starts at x =...Ch. 2 - Prob. 26PCh. 2 - Prob. 27PCh. 2 - (II) The position of a racing car, which starts...Ch. 2 - Prob. 29PCh. 2 - Prob. 30PCh. 2 - Prob. 31PCh. 2 - Prob. 32PCh. 2 - Prob. 33PCh. 2 - Prob. 34PCh. 2 - Prob. 35PCh. 2 - Prob. 36PCh. 2 - Prob. 37PCh. 2 - Prob. 38PCh. 2 - Prob. 39PCh. 2 - Prob. 40PCh. 2 - (II) A car traveling 85 km/h slows down at a...Ch. 2 - Prob. 42PCh. 2 - Prob. 43PCh. 2 - Prob. 45PCh. 2 - Prob. 46PCh. 2 - Prob. 47PCh. 2 - Prob. 48PCh. 2 - Prob. 49PCh. 2 - Prob. 50PCh. 2 - Prob. 52PCh. 2 - Prob. 53PCh. 2 - Prob. 54PCh. 2 - Prob. 55PCh. 2 - Prob. 56PCh. 2 - Prob. 57PCh. 2 - (II) The best rebounders in basketball have a...Ch. 2 - Prob. 59PCh. 2 - Prob. 60PCh. 2 - Prob. 61PCh. 2 - Prob. 62PCh. 2 - Prob. 63PCh. 2 - Prob. 64PCh. 2 - Prob. 65PCh. 2 - Prob. 66PCh. 2 - Prob. 67PCh. 2 - Prob. 69PCh. 2 - (III) A toy rocket moving vertically upward passes...Ch. 2 - Prob. 71PCh. 2 - Prob. 72PCh. 2 - Prob. 73PCh. 2 - (III) Air resistance acting on a falling body can...Ch. 2 - Prob. 75GPCh. 2 - A person jumps from a fourth-story window 15.0 m...Ch. 2 - Prob. 77GPCh. 2 - Prob. 78GPCh. 2 - Prob. 79GPCh. 2 - Prob. 80GPCh. 2 - Consider the street pattern shown in Fig. 247....Ch. 2 - Prob. 82GPCh. 2 - Prob. 83GPCh. 2 - Prob. 84GPCh. 2 - Prob. 86GPCh. 2 - Prob. 87GPCh. 2 - In putting, the force with which a golfer strikes...Ch. 2 - Prob. 89GPCh. 2 - Prob. 91GPCh. 2 - Prob. 92GPCh. 2 - Prob. 93GPCh. 2 - Prob. 94GPCh. 2 - Prob. 95GPCh. 2 - Prob. 96GPCh. 2 - Prob. 97GPCh. 2 - Prob. 98GPCh. 2 - Prob. 99GPCh. 2 - Prob. 100GPCh. 2 - Prob. 101GPCh. 2 - Prob. 102GPCh. 2 - You are traveling at a constant speed vM, and...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
A flock of geese is attempting to migrate due south, but the wind is blowing from the west at 5.1 m/s. If the b...
Essential University Physics (3rd Edition)
44. ǁ The drivers of two cars having equal speeds hit their brakes at the same time, but car A has three times ...
College Physics (10th Edition)
The weight of the bowling ball.
Physics (5th Edition)
16. On the Apollo 14 mission to the moon, astronaut Alan Shepard hit a golf ball with a 6 iron. The free-fall a...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Does the acceleration change as the ball rolls up the track? Would the acceleration vector you obtain differ if...
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
14. FIGURE Q4.14 shows four rotating wheels. For each, determine the signs (+ or -) of w and a.
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics (4th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A stone is thrown vertically upward with a speed of 15.5 m/s from the edge of a cliff 75.0 m high (Fig. 2–48). (a) How much later does it reach the bottom of the cliff? (b) What is its speed just before hitting? (c) What total distance -y = 0 did it travel? FIGURE 2-48 Ey= -75 m Problem 71.arrow_forward65. Consider the street pattern shown in Fig. 2–46. Each inter- section has a traffic signal, and the speed limit is 40 km/h. Suppose you are driving from the west at the speed limit. When you are 10.0 m from the first intersection, all the lights turn green. The lights are green for 13.0 s each. (a) Calculate the time needed to reach the third stoplight. Can you make it through all three lights without stopping? (b) Another car was stopped at the first light when all the lights turned green. It can accelerate at the rate of 2.00 m/s² to the speed limit. Can the second car make it through all three lights without stopping? By how many seconds would it make it, or not make it? West O East 0000 Speed limit 40 km/h Your 10 m 50 m 70 m car 15 m 15 m 15 m FIGURE 2-46 Problem 65.arrow_forwardA sports car accelerates approximately as shown in the velocity-time graph of Fig. 2-43. (The short flat spots in the curve represent manual shifting of the gears.) Estimate the car's average acceleration in (a) second gear and (b) fourth gear. Plot the graph for this problem.arrow_forward
- (III) A stone is thrown vertically upward with a speed of 12.0 m/s from the edge of a cliff 70.0 m high (Fig. 2-34). (a) How much later does it reach the bottom of the cliff? (b) What is its speed just before hitting? (c) What total distance did it travel?arrow_forward· (III) A falling stone takes 0.31 s to travel past a window 2.2 m tall (Fig. 2-41). From what height above the top of the window did the stone fall? To travel this - distance took 0.31s 2.2 m FIGURE 2-41 Problem 53.arrow_forward(III) An automobile traveling 95 km/h overtakes a 1.30-km- long train traveling in the same direction on a track parallel to the road. If the train's speed is 75 km/h, how long does it take the car to pass it, and how far will the car have traveled in this time? See Fig. 2–36. What are the results if the car and train are traveling in opposite directions? -1.30 km- v = 75 km/h sdesla sia i de das das v = 95 km/h vir FIGURE 2–36 Problem 16.arrow_forward
- (II) In Fig. 2–44, (a) during what time periods, if any, is the velocity constant? (b) At what time is the velocity greatest? (c) At what time, if any, is the velocity zero? (d) Does the object move in one direction or in both directions during the time shown?arrow_forwardT a half marathon is 13.1 miles ,how long will it take Complete the distance runing at rate of 5 minutes and 30 seconds per kilometer ? for a runner to an average mile = 1.61 kilometers:)arrow_forwardDescribe in words the motion plotted in Fig. 2-32 in terms of velocity, acceleration, etc. [Hint: First try to dupli- cate the motion plotted by walking or moving your hand.] * 10 10 20 30 40 50 t (s) FIGURE 2-32 Question 16. 20 (u) xarrow_forward
- A person jumps out a fourth-story window 18.0 m above a firefighter's safety net. The survivor stretches the net 1.0 m before coming to rest, Fig. 2–45. (a) What was the average deceleration experienced by the survivor when she was slowed to rest by the net? (b) What would you do to make it "safer" (that is, to generate a smaller deceleration): would you stiffen or loosen the net? Explain. 18.0 m 1.0 m FIGURE 2-45 Problem 62.arrow_forward(I) A particle at is at and at t1=-2.0 s is at x1=4.8cm and at t2=4.5 s is at x2 = 8.5 cm. What is its average velocity over this time interval? Can you calculate its average speed from these data?Why or why not?arrow_forward12–6. The position of a particle along a straight line is given by s = (1.5t ³ – 13.5t2 + 22.5t) ft, where t is in seconds. Determine the position of the particle when t= 6 s and the total distance it travels during the 6-s time interval. Hint: Plot the path to determine the total distance traveled.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Position/Velocity/Acceleration Part 1: Definitions; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4dCrkp8qgLU;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY