
Control Systems Engineering
7th Edition
ISBN: 9781118170519
Author: Norman S. Nise
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 63P
A muscle hanging from a beam is shown in Figure P2.37(a) (Lessard, 2009). The a-motor neuron can be used to electrically stimulate the muscle to contract and pull the mass, m, which under static conditions causes the muscle to stretch. An equivalent
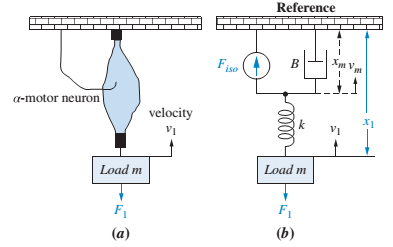
FIGURE P2.37 a. Motor neuron stimulating a muscle;17 b. equivalent circuit18
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
1
An object of mass 125 kg is released from rest from a boat into the water and allowed to sink. While gravity is pulling the object down, a buoyancy force of
times the weight of the object is pushing the object up (weight = mg). If we assume that water
40
resistance exerts a force on the object that is proportional to the velocity of the object, with proportionality constant 10 N-sec/m, find the equation of motion of the object. After how many seconds will the velocity of the object be 90 m/sec? Assume that the
acceleration due to gravity is 9.81 m/ sec2.
Find the equation of motion of the object.
X(t) =
%3D
Figure Q3 shows one cart with a mass that is separated from two walls by two springs and a
dashpot, where kı, k2 and ka are the first, second spring and dashpot coefficients, respectively.
The mass, m could represent an automobile system. An external force is also shown as F(t).
Only horizontal motion and forces are considered. F(t) is input and x2(t) is output.
(a)
Derive all equations related to the system
(b)
Construct the block diagram from equation in (a)
(c)
Obtain the transfer function of the system
(a) A body of mass m, controlled by an elastic system, is given a displacement x.
Derive an expression for the periodic frequency, n, of linear motion of the elastic
system
1
n =
Hz
1
Hz
where ő is the static deflection in metres under the load, mg.
(b) Figure TQ3.3 shows a suspended pendulum from a fixed pivot at O. The pendulum
consists of a bar B, of mass 1kg, and block C of mass 6kg. The centre of gravity G1 and
G2 of B and C are at distance 150mm and 375mm from 0. The radius of gyration of B
and C, each about its own centre of gravity, are respectively 100mm and 25mm. A light
spring is attached to the pendulum at point P, 200mm from 0, and is anchored at a fixed
point, Q.
When the Pendulum is in equilibrium, the line OG,PG2 is at 45° from the vertical and
the angle OPQ is 90°. The spring has a stiffness of 700N/m.
Calculate the natural frequency of the pendulum for small oscillations about the
equilibrium position.
45°
0-150
0-20
Ig N
G2
f0-3750
Y6g N
Figure TQ3.3
Chapter 2 Solutions
Control Systems Engineering
Ch. 2 - Prob. 1RQCh. 2 - Prob. 2RQCh. 2 - Prob. 3RQCh. 2 - Define the transfer function.Ch. 2 - Prob. 5RQCh. 2 - What do we call the mechanical equations written...Ch. 2 - If we understand the form the mechanical equations...Ch. 2 - Why do transfer functions for mechanical networks...Ch. 2 - What function do gears perform?Ch. 2 - What are the component parts of the mechanical...
Ch. 2 - The motor’s transfer function relates armature...Ch. 2 - Summarize the steps taken to linearize a nonlinear...Ch. 2 - Prob. 1PCh. 2 - Prob. 2PCh. 2 - Prob. 3PCh. 2 - Prob. 4PCh. 2 - Prob. 5PCh. 2 - Prob. 6PCh. 2 - Prob. 7PCh. 2 - A system is described by the following...Ch. 2 - For each of the following transfer functions,...Ch. 2 - Write the differential equation for the system...Ch. 2 - Write the differential equation that is...Ch. 2 - Prob. 12PCh. 2 - Use MATLAB to generate the MATLAB ML transfer...Ch. 2 - Repeat Problem 13 for the MATLAB following...Ch. 2 - Use MATLAB to generate the partial fraction...Ch. 2 - Use MATLAB and the Symbolic Math Symbolic Math...Ch. 2 - Prob. 17PCh. 2 - Prob. 18PCh. 2 - Prob. 19PCh. 2 - Repeat Problem 19 using nodal equations. [Section:...Ch. 2 - Prob. 22PCh. 2 - Prob. 23PCh. 2 - Prob. 24PCh. 2 - Prob. 25PCh. 2 - Prob. 26PCh. 2 - Prob. 27PCh. 2 - Prob. 28PCh. 2 - Prob. 29PCh. 2 - Write, but do not solve, the equations of motion...Ch. 2 - For the unexcited (no external force applied)...Ch. 2 - For each of the rotational mechanical systems...Ch. 2 - For the rotational mechanical system shown in...Ch. 2 - Find the transfer function, 1sTs , for the system...Ch. 2 - For the rotational mechanical system with gears...Ch. 2 - For the rotational system shown in Figure P2.21,...Ch. 2 - Prob. 37PCh. 2 - Find the transfer function, Gs=4s/Ts , for the...Ch. 2 - For the rotational system shown in Figure P2.24,...Ch. 2 - Prob. 40PCh. 2 - Given the rotational system shown in Figure P226,...Ch. 2 - In the system shown in Figure P2.27, the inertia,...Ch. 2 - Prob. 43PCh. 2 - Given the combined translational and rotational...Ch. 2 - Prob. 45PCh. 2 - The motor whose torque-speed characteristics are...Ch. 2 - A dc motor develops 55 N-m of torque at a speed of...Ch. 2 - 48. In this chapter, we derived the transfer...Ch. 2 - Prob. 49PCh. 2 - Find the series and parallel analogs for the...Ch. 2 - Find the series and parallel analogs for the...Ch. 2 - A system’s output, c, is related to the system’s...Ch. 2 - Prob. 53PCh. 2 - Consider the differential equation...Ch. 2 - 55. Many systems are piecewise linear. That is,...Ch. 2 - For the translational mechanical system with a...Ch. 2 - 57. Enzymes are large proteins that biological...Ch. 2 - Prob. 58PCh. 2 - Figure P2.36 shows a crane hoisting a load....Ch. 2 - 60. In 1978, Malthus developed a model for human...Ch. 2 - 61. In order to design an underwater vehicle that...Ch. 2 - 62. The Gompertz growth model is commonly used to...Ch. 2 - A muscle hanging from a beam is shown in Figure...Ch. 2 - A three-phase ac/dc converter supplies dc to a...Ch. 2 - Prob. 65P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 2. A kilogram mass is attached to the end of the spring with spring constant 2 N/m. Find the equation of motion if the mass is initially released (set in motion) from rest from a point 1 meter above equilibrium position. (Use the convention that displacements measured below the equilibrium position are positive.) (a) Write the initial-value problem which describes the position of the mass. (b) Find the solution to your initial-value problem from part (a). (c) Graph the solution found in (b) on (0arrow_forwardFor the mechanical system shown below, find the equation of motions and the system matrix. Where (x = X ewt)arrow_forwardQ5/ A beam with a length L is attached to the wall with a cable as shown. A load W = 400 lb. is attached to the beam. The tension force, T, k in the cable is given by: T = WL√h²+x² hx For a beam with L= 120 in. and h = 50 in. calculate T for x = 10, 30, 50, 70, 90, and 110 in. MATLAB D Warrow_forwardThree springs with different spring constants are connected as shown below. You are going to use spring elements to simulate this system. Suppose that the spring constants of the first, second and third elements are k1=3,410 N/m, k2=3,160 N/m and k3=3,380 N/m, respectively. Two horizontal forces are applied to the system (as shown) at nodes. 2 and 3. Find the displacement of node 3 and write your answer in mm (millimetre). Hint: Write your answer with 5 decimal places. For example if you calculated the value 1.2345678, then rounding off to 5 decimal places yields 1.23457 and that is the value you need to type in the answer box. U₁=0 (1) F₂ = 2N U₂ = ? F3 = -1N (2) M U3 = ? (3) U4 = 0arrow_forwarda) A vehicle circulates on a road as shown in Figure Q2a. The road profile can be modelled as the input u(t). The vehicle is modelled as a quarter car of mass m, and the suspension has a spring stiffness coefficient k = 2 Nm and a damper of coefficient c = 2 Nm s. Find the position of the mass, y(t) and any time t if the road profile is a unit step. m 一 Road Figure Q2a b) In Figure Q2b, a disk flywheel J of mass m 32 kg and radius r = 0.5 m is driven by an electric motor that when it is working produces an oscillating torque of Tin = 10sin(wt) N- m. The shaft bearings may be modelled as viscous rotary dampers with a damping coefficient of BR = 0.4 N-m-s/rad and stiffness coefficient KR = 2 Nm If the flywheel is at rest at t 0 and the power is suddenly applied to the motor, do the following [Hint:J = mr²/2]: (i) Find the natural frequency of oscillation of the disk expressed in Hz. (ii) Find the damping ratio for this system. (iii) Describe in no more than 3-4 lines the behaviour of the…arrow_forward2. Duffing's equation is a model for a dynamic system that includes a damping term and a nonlinear stiffness term. It most notably describes dynamics of electrical systems, but it has a simple analog as a nonlinear vibrations problem. Derive the non-homogeneous Duffings equation below using Hamilton's Principle. Start from the definition of the kinetic energy of a unit mass, and the virtual work of the springs and damper. Note, the spring force terms are both derivable from an energy function. x+cx+kx+vx³ = F sin sin(at)arrow_forwardA mass of 2 kilograms is on a spring with spring constant k newtons per meter with no damping. Suppose the system is at rest and at time t = 0 the mass is kicked and starts traveling at 2 meters per second. How large does k have to be to so that the mass does not go further than 3 meters from the rest position? use 2nd order differential equations to solve (mechanical vibrations)arrow_forwardQ)(a) A spring and mass system is shown in Figure P1.8. Assume that the rotation is small so that the spring deflects horizontally and ignore mass of the rod. Determine the frequency of vibration. (b) If total mass of the rod is m0 , how it will affect the frequency of vibration?arrow_forward4. The pitch (angular motion) and bounce (up-down linear motion) of a motor vehicle is shown in Figure Q4. Write down the two equations of motion of the vehicle and hence find its frequency equation. (a) (b) Assume that the mass of the vehicle is 1,000 kg, radius of gyration is 0.9 m, spring stiffnesses kr = 18 kN/m and kr = 22 kN/m, distances Iı = 1.0 m and l2 = 1.5 m, determine the two natural frequencies and mode shapes of the system. Bounce Pitch C.G.I Figure Q4arrow_forwardA machine weighing 2000 N rests on a support as illustrated in Figure P2.37. The support deflects about 5 cm as a result of the weight of the machine. The floor under the support is somewhat flexible and moves, because of the motion of a nearby machine, harmonically near resonance (r=1) with an amplitude of 0.2 cm. Model the floor as base motion, and assume a damping ratio of = 0.01, and calculate the transmitted force and the amplitude of the transmitted displacement. 2.37 Machine of mass m Rubber mount modeled as a A = static deflection stiffness k and a damper c Flexible floor y(t) Figure P2.37arrow_forwardFind the transfer function 8,(s) / T(s) of the given mechanical network below. Show your complete solution on a clean sheet of paper. I should see the following • List of torques exerted in tabular form ( • Clearly stated equations ( • Solution on how to find the transfer function from these equations IN-m/rad T) 02(1) for f I kg-m2 IN-m-s/rad I N-m-s/rad I N-m-s/radarrow_forwardGet the equation of motion by drawing the free body diagram of the given systems. a) Get the system's transfer function and find the unit digit answer. Show all decals in detail. m = 1 kg b= 20 Ns/m k = 125 N/m F ww k b) get the transfer function of the system. X(s)/Pg(s) =? Show all decals in detail. resistance R k Pg massless piston area (A) capacitancearrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Mechanical SPRING DESIGN Strategy and Restrictions in Under 15 Minutes!; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dsWQrzfQt3s;License: Standard Youtube License