
Organic Chemistry (9th Edition)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9780321971371
Author: Leroy G. Wade, Jan W. Simek
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 2.50SP
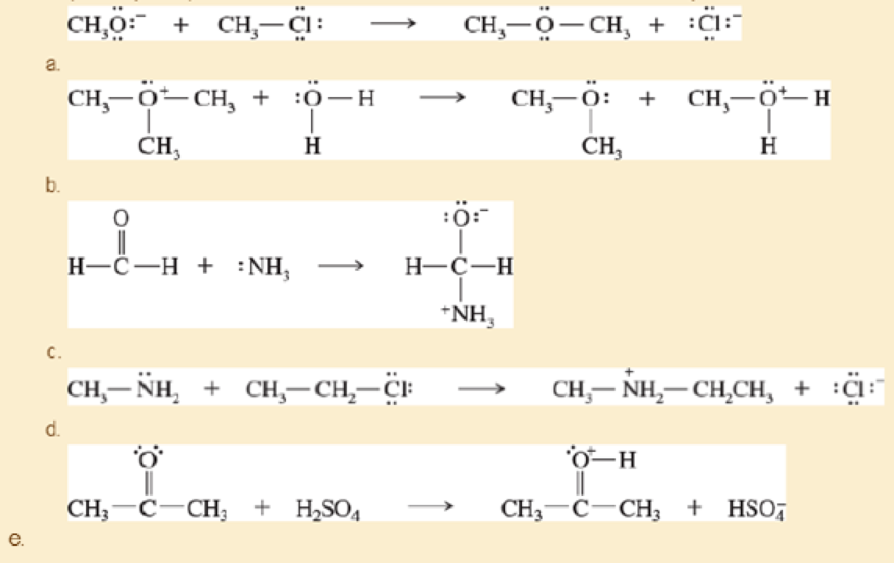
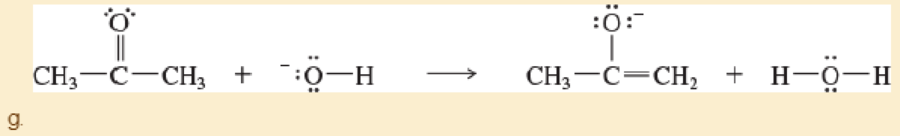
Label the reactants in these acid-base reactions as Lewis acids (electrophiles) or Lewis bases (nucleophiles). Use curved arrows to show the movement of electron pairs in the reactions.
- f. (CH3)3CCl + AlCl3 → (CH3)3C+ + −AlCl4
- h. CH2=CH2+BF3→BF–3—CH2—C+H2
- i. BF–3—CH2—C+H2+CH2=CH2→BF–3—CH2—CH2—CH2—CH+2
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
achieve.macmillanlearning.com
Canvas
EA eac
h Hulu
YouTube
G 3 methyl cyclobutanol - Google Search
Ranking Phenol Acidity
Course -236 - Organic Chemistry - Mac...
←
Assessment
Completed 10 of 22 Questions
1 +
Netflix
paramount plus
chem hw
Galdehyde reaction with grignard reagent...
b My Questions | bartleby
M Inbox - chenteislegit@gmail.com - Gmail
Due: Fri, Jan 31
Resources
Solution
Penalized
? Hint
Submit Answer
Use retrosynthetic analysis to suggest two paths to synthesize 2-methyl-3-hexanol using the Grignard reaction. (Click and drag
the appropriate image to the correct position in the reactions.)
Route 1
Aldehyde 1
or
+98
Aldehyde 2
Route 2
Q6
+100
Solved in 1 attempt
Q7
+95
Solved in 2 attempts
Q8
+98
Unlimited attempts
possible
+
+
Grignard 1
OH
H3O+
Grignard 2
Answer Bank
Q9
+90
MgBr
Unlimited attempts
possible
CH3CH2CH2MgBr
Q10
Unlimited attempts
Q11
?
?
+100
in 1 attempt
2-methyl-3-hexanol
CH3CH2MgBr
H
H
о
H
Attempt 3
2) (4 pt) After the reaction was completed, the student collected the following data. Crude
product data is the data collected after the reaction is finished, but before the product
is purified. "Pure" product data is the data collected after attempted purification using
recrystallization.
Student B's data:
Crude product data
"Pure"
product data
after
recrystallization
Crude mass: 0.93 g grey solid
Crude mp: 96-106 °C
Crude % yield:
Pure mass: 0.39 g white solid
Pure mp: 111-113 °C
Pure % yield:
a) Calculate the crude and pure percent yields for the student's reaction.
b) Summarize what is indicated by the crude and pure melting points.
Don't used hand raiting
Chapter 2 Solutions
Organic Chemistry (9th Edition)
Ch. 2.1A - Prob. 2.1PCh. 2.1B - The NF bond is more polar than the NH bond: but...Ch. 2.1B - For each of the following compounds 1. Draw the...Ch. 2.1B - Two isomers of 1,2-dichloroethene are known One...Ch. 2.2C - Prob. 2.5PCh. 2.2C - Prob. 2.6PCh. 2.3 - Prob. 2.7PCh. 2.4 - Calculate the pH of the following solutions a....Ch. 2.6A - Ammonia appears in Table 2-2 as both an acid and a...Ch. 2.7 - Write equations for the following acid-base...
Ch. 2.7 - Ethanol, methylamine. and acetic acid are all...Ch. 2.8 - Prob. 2.12PCh. 2.10 - Write equations for the following acid-base...Ch. 2.10 - Rank the following acids in decreasing order of...Ch. 2.11 - Prob. 2.15PCh. 2.11 - Prob. 2.16PCh. 2.11 - Consider each pair of bases and explain which one...Ch. 2.12 - Which is a stronger base ethoxide ion or acetate...Ch. 2.12 - Prob. 2.19PCh. 2.12 - Prob. 2.20PCh. 2.12 - Prob. 2.21PCh. 2.12 - Choose the more basic member of each pair of...Ch. 2.14 - Prob. 2.23PCh. 2.15D - Classify the following hydrocarbons and draw a...Ch. 2.16D - Prob. 2.25PCh. 2.17C - Draw a Lewis structure and classify each of the...Ch. 2.17C - Circle the functional groups in the following...Ch. 2 - The CN triple bond in acetonitrile has a dipole...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.29SPCh. 2 - Sulfur dioxide has a dipole moment of 1.60 D....Ch. 2 - Which of the following pure compounds can form...Ch. 2 - Predict which member of each pair is more soluble...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.33SPCh. 2 - Prob. 2.34SPCh. 2 - Predict which compound in each pair has the higher...Ch. 2 - All of the following compounds can react as acids...Ch. 2 - Rank the following species in order of increasing...Ch. 2 - Rank the following species in order of increasing...Ch. 2 - The Ka of phenylacetic acid is 5 2 105, and the...Ch. 2 - The following compound can become protonated on...Ch. 2 - The following compounds are listed in increasing...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.42SPCh. 2 - Prob. 2.43SPCh. 2 - Compare the relative acidity of 1-molar aqueous...Ch. 2 - The following compounds can all react as acids. a....Ch. 2 - The following compounds can all react as bases. a....Ch. 2 - The following compounds can all react as acids. a....Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.48SPCh. 2 - Methyllithium (CH3Li) is often used as a base in...Ch. 2 - Label the reactants in these acid-base reactions...Ch. 2 - In each reaction, label the reactants as Lewis...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.52SPCh. 2 - Each of these compounds can react as a nucleophile...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.54SPCh. 2 - Give a definition and an example for each class of...Ch. 2 - Circle the functional groups in the following...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.57SP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A DEPT NMR spectrum is shown for a molecule with the molecular formula of C5H12O. Draw the structure that best fits this data. 200 180 160 140 120 100 一盆 00 40 8- 20 ppm 0 Qarrow_forwardDon't used hand raitingarrow_forwardShown below is the major resonance structure for a molecule. Draw the second best resonance structure of the molecule. Include all non-zero formal charges. H. H. +N=C H H H Cl: Click and drag to start drawing a structure. : ? g B S olo Ar B Karrow_forward
- Don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardS Shown below is the major resonance structure for a molecule. Draw the second best resonance structure of the molecule. Include all non-zero formal charges. H H = HIN: H C. :0 H /\ H H Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ×arrow_forwardPlease help me figure out these calculation and what should be plotted. These are notes for my chemistry class.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399425
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry | Acids & Bases; Author: Ninja Nerd;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AOr_5tbgfQ0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY