Concept explainers
a.
Explain whether the interconnection of ideal sources in the circuit in Figure P2.1 in the textbook is valid or not.
a.
Answer to Problem 1P
The interconnection of ideal sources in the given circuit is valid.
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Refer to Figure P2.1 in the textbook for required data.
Description:
All the sources in the given circuit are independent sources. The independent voltage source can carry any current that required by the connection and the independent current source can support any voltage that required by the connection.
As the given circuit consists of all ideal independent sources and the Kirchhoff’s law is not violated, the interconnection of ideal sources in the given circuit is valid.
Conclusion:
Thus, the interconnection of ideal sources in the given circuit is valid.
b.
Identify the power developing sources and power absorbed sources in the given circuit.
b.
Answer to Problem 1P
The power developing sources are 15 V voltage source and 5 A current source, and the power absorbing source is 20 V voltage source.
Explanation of Solution
Formula used:
Write the expression for power developed or absorbed by the source (voltage or current) as follows:
Here,
Calculation:
If the current enters from the negative terminal and leaves from the positive terminal of a voltage source then the source delivers the power. The delivering power is obtained with negative sign.
If the current enters from the positive terminal and leaves from the negative terminal of a voltage source then the source absorbs the power. The absorbing power is obtained with positive sign.
From the given circuit, current of 5 A enters from the positive terminal of 20 V source. Therefore, 20 V voltage source absorbs the power.
Rewrite the expression in Equation (1) to find the power absorbed by the 20 V voltage source as follows:
From given circuit, the values of
Therefore, the power absorbed by the 20 V voltage source is 100 W.
From the given circuit, current of 5 A enters from the negative terminal of 15 V source. Therefore, 15 V voltage source develops the power.
Rewrite the expression in Equation (1) to find the power developed by the 15 V voltage source as follows:
From given circuit, the values of
Therefore, the power developed by the 15 V voltage source is
From the given circuit, the voltage drop across 5 A current source is calculated by using KVL to the circuit as follows:
Therefore, the voltage drop across 5 A current source is
Rewrite the expression in Equation (1) to find the power developed by the 5 A current source as follows:
From given circuit, the values of
The negative sign indicates the developed power by the source. Therefore, the power developed by the 5 A current source is 25 W.
Conclusion:
Thus, the power developing sources are 15 V voltage source and 5 A current source, and the power absorbing source is 20 V voltage source.
c.
Verify the power absorbed in the circuit is equal to the power developed in the circuit.
c.
Answer to Problem 1P
The power absorbed in the circuit is equal to the power developed in the circuit.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
From Part (b), write the expression for power absorbed in the circuit as follows:
Substitute 100 W for
From Part (b), the power developed in the circuit as follows:
Substitute 75 W for
From the calculation, it is clear that the power absorbed in the circuit is equal to the power developed in the circuit.
Conclusion:
Thus, the power absorbed in the circuit is equal to the power developed in the circuit.
d.
Explain whether the interconnection of ideal sources in the modified circuit is valid or not and identify the power developing and absorbing sources in the modified circuit. Verify the power absorbed in the modified circuit is equal to the power delivered in the circuit.
d.
Answer to Problem 1P
The interconnection of ideal sources in the modified circuit is valid, voltage source of 20 V and voltage source of 15 V are power developing sources and 5 A current source is a power absorbing source. The power absorbed in the modified circuit is equal to the power developed in the circuit.
Explanation of Solution
Description:
Redraw the circuit by reversing the polarity of 20 V voltage source as shown in Figure 1.
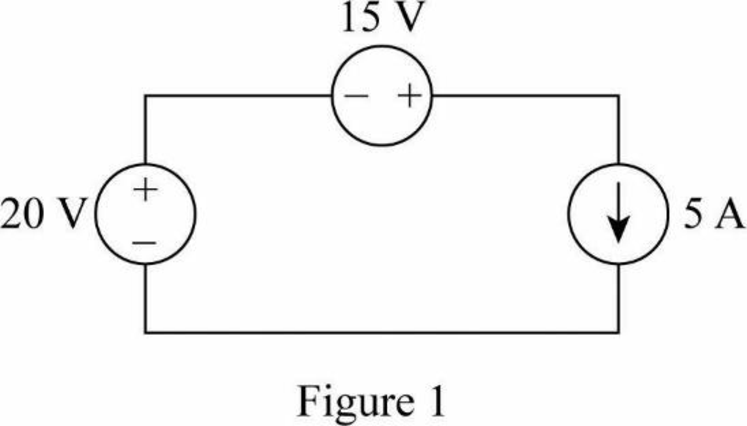
As the modified circuit in Figure 1 consists of all ideal independent sources, the interconnection of ideal sources in the modified circuit is valid.
From Figure 1, current of 5 A enters from the negative terminal of 20 V source. Therefore, 20 V voltage source develops the power.
Rewrite the expression in Equation (1) to find the power developed by the 20 V voltage source as follows:
From given circuit, the values of
Therefore, the power delivered by the 20 V voltage source is 100 W.
From the given circuit, current of 5 A enters from the negative terminal of 15 V source. Therefore, 15 V voltage source develops the power.
Rewrite the expression in Equation (1) to find the power developed by the 15 V voltage source as follows:
From given circuit, the values of
Therefore, the power developed by the 15 V voltage source is 75 W.
From the given circuit, the voltage drop across 5 A current source is calculated by using KVL to the circuit as follows:
Therefore, the voltage drop across 5 A current source is 35 V. That is, current 5 A enters the positive terminal and leaves from the negative terminal of 35 V voltage drop. Therefore, 5 A current source absorbs the power.
Rewrite the expression in Equation (1) to find the power absorbed by the 5 A current source as follows:
From given circuit, the values of
Therefore, the power absorbed by the 5 A current source is 175 W.
From the calculation, write the expression for power absorbed in the circuit as follows:
Substitute 175 W for
From the calculation, the power developed in the circuit as follows.
Substitute 100 W for
From the calculation, it is clear that the power absorbed in the circuit is equal to the power developed in the circuit.
Conclusion:
Thus, the interconnection of ideal sources in the modified circuit is valid, voltage source of 20 V and voltage source of 15 V are power developing sources and 5 A current source is a power absorbing source. The power absorbed in the modified circuit is equal to the power developed in the circuit.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Electric Circuits (10th Edition)
- They are one quearrow_forwardO Draw the four possible negative feedback contigurations of an op-amp. Write the input and output impedances of these configurations in ideal cases. 5arrow_forwardE9.6 Determine the average power absorbed by the 4-2 and 3-2 resistors in Fig. E9.6. 302 j20 Figure E9.3 4Ω ww Figure E9.6 12/0° V j30 -j2 N 13/10° A (+60° V (OEFarrow_forward
- -160 For the P-channel JFET given in the following figure, the IDSS = 2MA a) Determine IDQ and VSDQ b) Determine the source-follower circuit transistor parameters are: Vp = +1,75 V, and λ=0. Small-signal voltage gain, Av = So VDD = 10V R₁ = 90kr Rs =5k CC1 WW R₂ = 110kn 50 C02 BL = 10 kr GNDarrow_forwardNeed a solarrow_forwardI need a drawing on how to connect the function generator, oscilliscope, and both multimeters. It is hard for me to follow text instructions. The function generator has a postive,common and negative. The oscilliscope has chanell A and B, both channels have a postive and a negative. I know you can provide text instruction but a little sketch would be very helpful thank you.arrow_forward
- Don't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forwardQ1/ A three phase, 500 kVA, 6600 V, 50 Hz, 6 pole, star connected synchronous motor has synchronous impedance of J 70 ohm per phase at its normal rating, the motor is excited to give unity power factor at the input terminals. Find a) The rated current and power factor. b) The emf behind the synchronous impedance. c) The developed torque. d) The pull out torque. e) The increase in excitation which will just permit an increase of 30% of rated torque before pulling out of synchronism. (45 M.)arrow_forwardcan you fin Vds and Vgs of all transistors and specify te operating region off all transistors and prove it. 58V 5.8 V 1.8V M2 0.9V 22222 と A 4852 m 3 01 A Voy = 0.2 V V4)=0.SV λ=0.1 V-1arrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





