Concept explainers
A person gets in an elevator on the ground floor and rides it to the top floor of a building. Sketch a velocity-versus-time graph for this motion.
To draw: The velocity-versus-time graph.
Answer to Problem 1CQ
The velocity-versus-time graph is drawn.
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
A person gets in an elevator on the ground floor and rides it to the top floor of a building.
Explanation:
Normally when the elevator starts to function, initially the speed or velocity will be low and then gradually increases its speed. In the middle period of the elevator functioning, the speed becomes constant and at end period speed slows down and comes to rest.
The velocity-versus-time graph for the above scenario is shown in Figure 1.
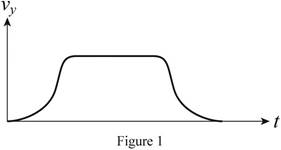
Initially graph starts from zero, gradually increases. During middle period velocity remains constant showing horizontal line in the graph. During end period there will be gradual decrease and end at zero in the graph.
Conclusion:
Hence, the velocity-versus-time graph is drawn.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
- Shown below is a graph of velocity versus time for a moving object. The object starts at position x = 0 m at t = 0 s. What is the displacement in meters, from t = 0 s to t = 3.0 s?arrow_forwardAn object is moving with constant non-zero velocity in the + x direction. The position versus time graph of this object is a horizontal straight line. a vertical straight line. a straight line making an angle with the time axis. a parabolic curve.arrow_forwardA woman backs her van out of her parking space with a constant acceleration of 1.8 m/s2. Assume that her initial motion is in the positive direction. Part A: How long does it take her to reach a speed of 2.1 m/s in seconds? Part B: If she then brakes to a stop in 0.65 s, what is her acceleration in meters per square second?arrow_forward
- Basam is standing on the edge of a cliff and tosses her physics book upward with a speed of 22.0 m/s. It hits the ground at the base of the cliff 6.0 s later. Create a VELOCITY-TIME graph that represents this scenario. You may assume that the acceleration of the textbook is -9.81 m/s². Use the graph to determine a) the height of the cliff. b) the speed of the book when it impacts the ground. DO NOT use kinematics formulas to solve this problem. This task is assessing your understanding of GRAPHING to represent accelerate motion.arrow_forwardA train starts from rest and accelerates uniformly, until it has traveled 2.5 km and acquired a velocity of 24 m/s. The train then moves at a constant velocity of 24 m/s for 400 s. The train then slows down uniformly at 0.065 m/s2, until it is brought to a halt. What is the total time traveled by the train?arrow_forwardA man drives his car down a straight road at 5.2 km at 40 kph at which point he minutes. What is the average velocity of the driver from the time that the car started to the time that the driver arrived at the gas station?arrow_forward
- A commuter backs her car out of her garage with a constant acceleration of 1.9 m/s2. Assume that her initial motion is in the positive direction. How long does it take her to reach a speed of 2.35 m/s in seconds? If she then brakes to a stop in 0.65 s, what is her acceleration in meters per square second?arrow_forwardStarting at x = - 17 m at time t = 0 s, an object takes 17 s to travel 55 m in the +x direction at a constant velocity. On a sheet of paper, make a position vs. time graph of the object's motion. What is its velocity?arrow_forwardAn astronaut has left an orbiting space shuttle to test a new personal maneuvering unit. As she moves along a straight line, her partner on board the shuttle measures her velocity every 2.0s starting at 2. time t=1.0s as follows: t 1.0s 0.8m/s 1.2m/s 1.8m/s 3.0s 5.0s Find the average acceleration for each time interval: a) 1s to 3s and b) 3s to 5sarrow_forward
- A car is moving at a velocity of 20 m/s. The car then accelerates uniformly at 1.8 m/s2. The car continues at the same acceleration until it reaches a velocity of 25 m/s, which is the legal speed limit. What is the distance the car travels in while accelerating?arrow_forwardI am having trouble with an average speed problem. The problem states that a person walks at 4.5 meters per second from point a to b. Then walks back from point b to a at a speed of 3.2 m/s. I know that average speed is displacement/time. However I am not sure how to calculate time or displacement from the two givens. The problem also gives that the average velocity is 0.arrow_forward41. Average velocity. In t seconds, an object dropped from a certain height will fall s(t) feet, where s(t) = 161?. a) Find s(5) – s(3). b) What is the average rate of change of distance with respect to time during the period from 3 to 5 sec? This is known as average velocity, or speed.arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
