
(a)
Interpretation:
The way by which alkylation or acylation of an enamine can be used to convert acetophenone into the given compound has to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Enamine:
An enamine is a compound where the lone pair of electrons in the nitrogen atom of
It is formed by the reaction of a
Hydrolysis of enamine: Under acidic conditions, enamine reacts with water to give corresponding ketone and secondary amine.
Here, the bond between nitrogen and the
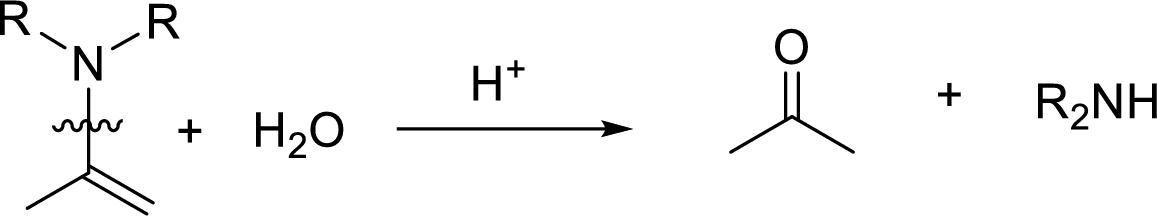
(b)
Concept introduction:
Enamine:
An enamine is a compound where the lone pair of electrons in the nitrogen atom of
It is formed by the reaction of a ketone or aldehyde and a secondary amine under acidic conditions with the elimination of water molecule.
Hydrolysis of enamine: Under acidic conditions, enamine reacts with water to give corresponding ketone and secondary amine.
Here, the bond between nitrogen and the
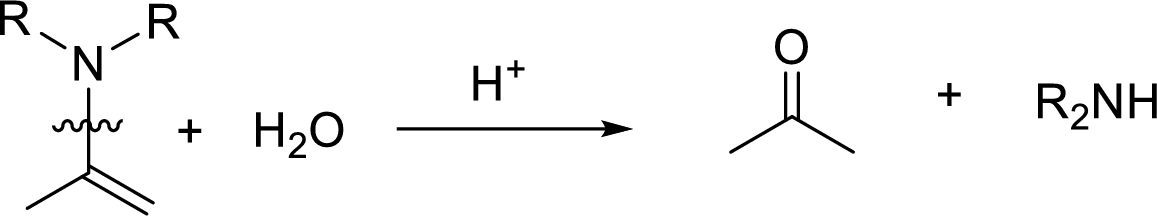
(c)
Concept introduction:
Enamine:
An enamine is a compound where the lone pair of electrons in the nitrogen atom of
It is formed by the reaction of a ketone or aldehyde and a secondary amine under acidic conditions with the elimination of water molecule.
Hydrolysis of enamine: Under acidic conditions, enamine reacts with water to give corresponding ketone and secondary amine.
Here, the bond between nitrogen and the
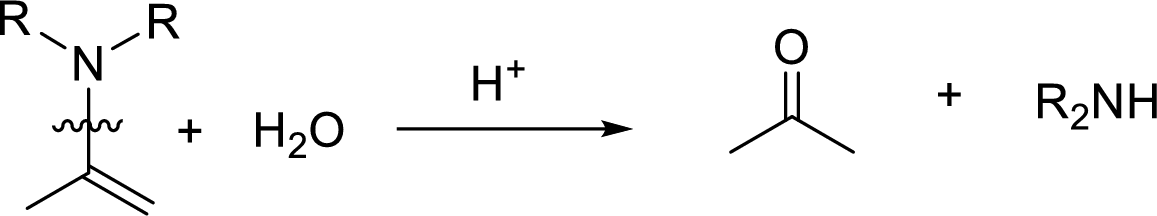
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 19 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Loose-leaf Version
- Aldehydes and ketones react with thiols to yield thioacetals just as they react with alcohols to yield acetals. Predict the product of the following reaction, and propose a mechanism:arrow_forwardPredict the products formed when cyclohexanone reacts with the following reagents. h) sodium acetylide, then mild H3O+arrow_forwardHow to synthesize 5-nitro-2-hydroxyacetophenone from 2-hydroxyacetophenone?arrow_forward
- Propose a mechanism for the reaction of benzyl acetate with methylamine. Label theattacking nucleophile and the leaving group, and draw the transition state in which theleaving group leaves.arrow_forwardDraw out the reaction mechanism for cyclohexanol to cyclohexanone. Sodium hypochlorite oxidation of an alcohol to a ketone with the product being cyclohexanone.arrow_forwardShow how alkylation and acylation of enamines and lithium enolates are usedsynthetically. Give mechanisms for these reactions.arrow_forward
- Bisphenol A is made on a large scale by a condensation of phenol with acetone. Suggest an appropriate catalyst, and propose a mechanism for this reaction.arrow_forwardHow to synthesize cyclohexylbenze from cyclohexanone?arrow_forwardBenzene + nitration, followed by bromination, then reduction of the nitro group to an amine, followed by diazonization, addition of copper I cyanide to the reaction and the product is O benzoyl nitrile O ortho-bromoaniline O para-bromo-nitrobenzene O 3,5-dibromnobenzonitrile O para-bromobenzyl bromidearrow_forward
- Acetic acid has been mixed with isoamyl alcohol to produce isoamyl acetate giving off a banana smell. Propose a reaction mechanism for this reaction.arrow_forwardShow how you would synthesize octanal from each compound. You may use any necessary reagents.ethyl octanoatearrow_forwardThe mechanism for acidic hydrolysis of a nitrile resembles the basic hydrolysis, exceptthat the nitrile is first protonated, activating it toward attack by a weak nucleophile (water).Under acidic conditions, the proton transfer (tautomerism) involves protonation on nitrogen followed by deprotonation on oxygen. Propose a mechanism for the acid-catalyzedhydrolysis of benzonitrile to benzamide.arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

