
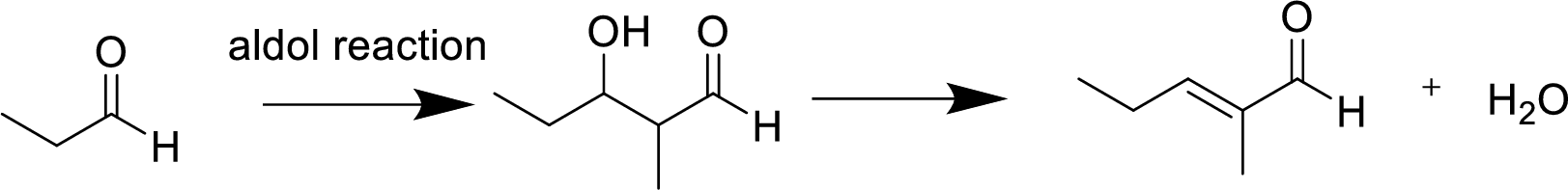
(a)
Interpretation:
The product of the aldol reaction of the given compound and the
Concept introduction:
Aldol reaction is an addition reaction of
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The aldol reaction product for the given compound has to be drawn.
The aldol reaction yield a
Base abstracts a proton from the
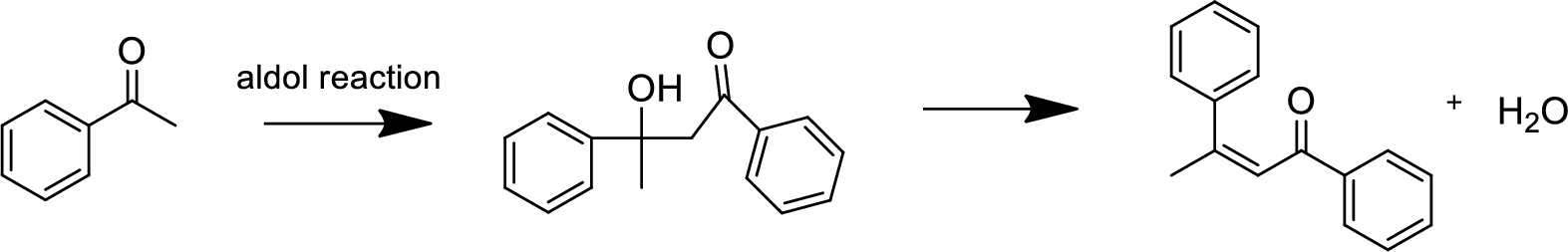
(b)
Interpretation:
The product of the aldol reaction of the given compound and the
Concept introduction:
Aldol reaction is an addition reaction of aldehydes and ketones. Aldol reaction is a reversible reaction and occurs in the presence of a strong base like sodium hydroxide. One molecule (aldehyde or ketone) acts a nucleophile and attacks the electrophilic carbon center of the other molecule to give the addition product. The product is named
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The aldol reaction product for the given compound has to be drawn.
The aldol reaction yield a
Base abstracts a proton from the
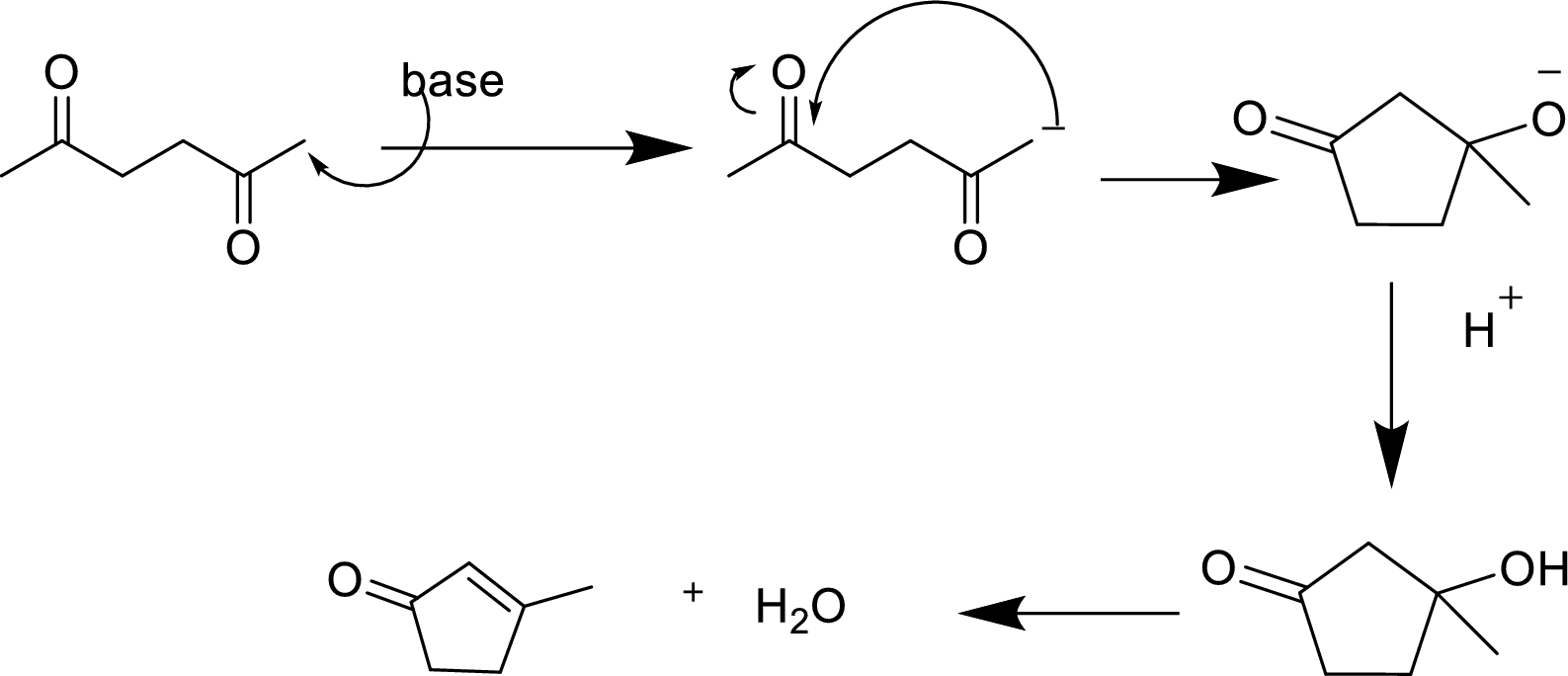
(c)
Interpretation:
The product of the aldol reaction of the given compound and the
Concept introduction:
Aldol reaction is an addition reaction of aldehydes and ketones. Aldol reaction is a reversible reaction and occurs in the presence of a strong base like sodium hydroxide. One molecule (aldehyde or ketone) acts a nucleophile and attacks the electrophilic carbon center of the other molecule to give the addition product. The product is named
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The aldol reaction product for the given compound has to be drawn.
The aldol reaction yield a
Base abstracts a proton from the
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Loose-leaf Version
- Draw a structural formula for the product of crossed aldol reaction and for the compound formed by dehydration of aldol productarrow_forwardDraw the product formed when each organometallic reagent is treated with H2O.arrow_forwardDraw a structural formula for the product of crossed aldol reaction and for the compound formed by dehydration of aldol productarrow_forward
- What is the general name for the reaction product formed in an aldol addition reaction? O y-Hydroxy carbonyl compound a,B-Hydroxy carbonyl compound O a-Hydroxy carbonyl compound O B-Hydroxy carbonyl compoundarrow_forwardGive the IUPAC name of the reactants that would give the following aldol condensation product.arrow_forwardbase 2 H3C H H3C OH heat H H3C + H₂O H The aldol reaction is a carbonyl condensation reaction between two carbonyl partners and involves a combination of nucleophilic addition and a-substitution steps. One partner is converted into an enolate ion nucleophile and adds to the electrophilic carbonyl group of the second partner. In the classic aldol reaction, the carbonyl partners are aldehydes or ketones, although aldehydes are more reactive. The product is a ẞ-hydroxy carbonyl compound. Under reaction conditions slightly more vigorous than those employed for the aldol reaction, the ẞ-hydroxyl group is eliminated in an E1CB dehydration to give an a,ẞ-unsaturated carbonyl compound. Draw curved arrows to show the movement of electrons in this step of the mechanism. Arrow-pushing Instructions X :OH H₂O: а کی H₂C H H₂C H Harrow_forward
- The following molecule is formed in an intramolecular aldol condensation reaction. Draw the organic starting material needed to form the given α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound.arrow_forwardDraw the product formed when each organometallic reagent is treated with H2O.arrow_forwardAnswer the following questions about curcumin, a yellow pigment isolated from turmeric, a tropical perennial in the ginger family and a principal ingredient in curry powder.a.In Chapter 11, we learned that most enols, compounds that contain a hydroxy group bonded to a C=C, are unstable and tautomerize to carbonyl groups. Draw the keto form of the enol of curcumin, and explain why the enol is more stable than many other enols. b.Explain why the enol O—H proton is more acidic than an alcohol O—H proton. c. Why is curcumin colored? d.Explain why curcumin is an antioxidant.arrow_forward
- Drawing an Enol and a Ketone Formed by Hydration of an Alkyne Draw the enol intermediate and the ketone product formed in the following reaction.arrow_forward2-Pentylcinnamaldehyde, commonly called flosal, is a perfume ingredient with a jasmine-like odor. Flosal is an α,β-unsaturated aldehyde made by a crossed aldol reaction between benzaldehyde (C6H5CHO) and heptanal (CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CHO), followed by dehydration. Draw a stepwise mechanism for the following reaction that prepares flosal.arrow_forwardDraw out the reaction mechanism for cyclohexanol to cyclohexanone. Sodium hypochlorite oxidation of an alcohol to a ketone with the product being cyclohexanone.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

