
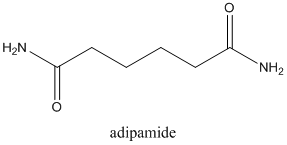
(a)
Interpretation:
The
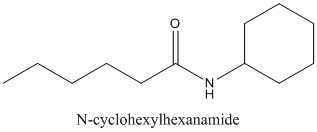
Concept Introduction:
Amides are formed by a reaction with a carboxylic acid and an amine which are the
The mechanism for formation of an amide is as follows taking example of propanoic acid and ethylamine:
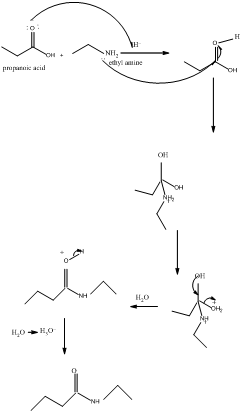
The hydrolysis of amide so formed can give back the carboxylic acid and amine.
(b)
Interpretation:
The carboxylic acid and amine or ammonia needs to be identified from which each amide be synthesized.
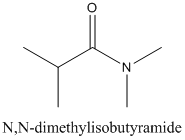
Concept Introduction:
Amides are formed by a reaction with a carboxylic acid and an amine which are the functional groups. This results in the formation of amide bond, in which OH group of carboxylic acid reacts with one of the H in amine group and CO-NH bond is formed. This bond is known as an amide bond.
The mechanism for formation of an amide is as follows taking example of propanoic acid and ethylamine:
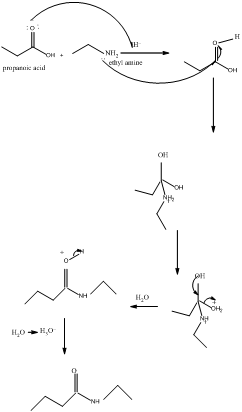
The hydrolysis of amide so formed can give back the carboxylic acid and amine.
(c)
Interpretation:
The carboxylic acid and amine or ammonia needs to be identified from which each amide be synthesized.
Concept Introduction:
Amides are formed by a reaction with a carboxylic acid and an amine which are the functional groups. This results in the formation of amide bond, in which OH group of carboxylic acid reacts with one of the H in amine group and CO-NH bond is formed. This bond is known as an amide bond.
The mechanism for formation of an amide is as follows taking example of propanoic acid and ethylamine:
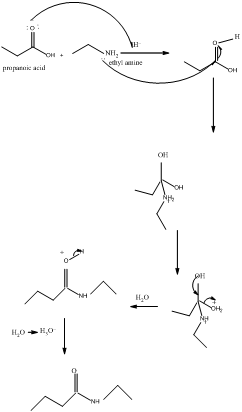
The hydrolysis of amide so formed can give back the carboxylic acid and amine.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 19 Solutions
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning


