
Essential University Physics (3rd Edition)
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9780134202709
Author: Richard Wolfson
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 18, Problem 20E
An ideal gas expands from the state (p1, V1) to the state (p2, V2), where p2 = 2p1 and V2 = 2V1. The expansion proceeds along the diagonal path AB in Fig. 18.19. Find an expression for the work done by the gas during this process.
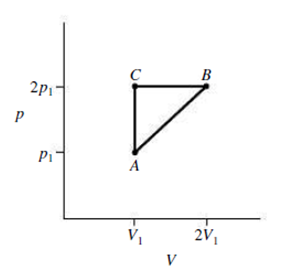
FIGURE 18.19 Exercises 20, 21 and Problem 75
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A square metal sheet 2.5 cm on a side and of negligible thickness is attached to a balance and inserted into a container of fluid. The contact angle is found to be zero, as shown in Figure a, and the
balance to which the metal sheet is attached reads 0.42 N. A thin veneer of oil is then spread over the sheet, and the contact angle becomes 180°, as shown in Figure b. The balance now reads
0.41 N. What is the surface tension of the fluid?
N/m
a
Sucrose is allowed to diffuse along a 12.0-cm length of tubing filled with water. The tube is 6.1 cm² in cross-sectional area. The diffusion coefficient is equal to 5.0 × 10-10 m²/s, and 8.0 × 10−14
x
transported along the tube in 18 s. What is the difference in the concentration levels of sucrose at the two ends of the tube?
.00567
kg is
need help part a and b
Chapter 18 Solutions
Essential University Physics (3rd Edition)
Ch. 18.2 - Two identical gas-cylinder systems are taken from...Ch. 18.2 - Name the basic thermodynamic process involved when...Ch. 18.3 - The same amount of heat flows into equal volumes...Ch. 18 - Prob. 1FTDCh. 18 - Prob. 2FTDCh. 18 - Prob. 3FTDCh. 18 - Why cant an irreversible process be described by a...Ch. 18 - Are the initial and final equilibrium states of an...Ch. 18 - Does the first law of thermodynamics apply to...Ch. 18 - Prob. 7FTD
Ch. 18 - Figure 18.18 shows two processes, A and B. that...Ch. 18 - When you let air out of a tire, the air seems...Ch. 18 - Blow on the back of your hand with your mouth wide...Ch. 18 - You boil water in an open pan. Of which of the...Ch. 18 - Three identical gas-cylinder systems are...Ch. 18 - Prob. 13FTDCh. 18 - In what sense can a gas of diatomic molecules be...Ch. 18 - Prob. 15ECh. 18 - Prob. 16ECh. 18 - A 40-W heat source is applied to a gas sample for...Ch. 18 - Find the rate of heat flow into a system whose...Ch. 18 - In a certain automobile engine, 17% of the total...Ch. 18 - An ideal gas expands from the state (p1, V1) to...Ch. 18 - Repeat Exercise 20 for a process that follows the...Ch. 18 - A balloon contains 0.30 mol of helium. It rises,...Ch. 18 - The balloon of Exercise 22 starts at 100 kPa...Ch. 18 - How much work does it take to compress 2.5 mol of...Ch. 18 - By what factor must the volume of a gas with =...Ch. 18 - Prob. 26ECh. 18 - A carbon-sequestration scheme calls for...Ch. 18 - A gas mixture contains 2.5 mol of O2 and 3.0 mol...Ch. 18 - A mixture of monatomic and diatomic gases has...Ch. 18 - What should be the approximate specific-heat ratio...Ch. 18 - Prob. 31ECh. 18 - An ideal gas expands to 10 times its original...Ch. 18 - During cycling, the human body typically releases...Ch. 18 - A 0.25-mol sample of ideal gas initially occupies...Ch. 18 - As the heart beats, blood pressure in an artery...Ch. 18 - It takes 1.5 kJ to compress a gas isothermally to...Ch. 18 - A gas undergoes an adiabatic compression during...Ch. 18 - A gas with = 1.40 occupies 6.25 L when its at...Ch. 18 - A gas sample undergoes the cyclic process ABCA...Ch. 18 - Prob. 40PCh. 18 - A gasoline engine has compression ratio 8.5 (sec...Ch. 18 - By what factor must the volume of a gas with =...Ch. 18 - Volvos B5340 engine, used in the V70 series cars,...Ch. 18 - A research balloon is prepared for launch by...Ch. 18 - Prob. 45PCh. 18 - By what factor does the internal energy of an...Ch. 18 - An ideal monatomic gas is compressed to half its...Ch. 18 - A gas expands isothermally from state A to state...Ch. 18 - A 3.50-mol sample of ideal gas with molar specific...Ch. 18 - Prove that the slope of an adiabat at a given...Ch. 18 - An ideal gas with = 1.67 starts at point A in...Ch. 18 - The gas of Example 18.4 starts at state A in Fig....Ch. 18 - The gas of Example 18.4 starts at state A in Fig....Ch. 18 - A 25-L sample of ideal gas with = 1.67 is at 250...Ch. 18 - Prob. 55PCh. 18 - A 25-L sample of ideal gas with = 1.67 is at 250...Ch. 18 - Youre the product safety officer for a company...Ch. 18 - Figure 18.22 shows data and a fit curve from an...Ch. 18 - External forces compress 21 mol of ideal monatomic...Ch. 18 - A gas with = 7/5 is at 273 K when its compressed...Ch. 18 - An ideal gas with = 1.3 is initially at 273 K and...Ch. 18 - The curved path in Fig. 18.23 lies on the 350-K...Ch. 18 - Repeat part (a) of Problem 62 for the path ACDA in...Ch. 18 - A gas mixture contains monatomic argon and...Ch. 18 - How much of a triatomic gas with Cv = 3R would you...Ch. 18 - An 8.5-kg rock at 0C is dropped into a...Ch. 18 - A piston-cylinder arrangement containing 0.30 mol...Ch. 18 - Experimental studies show that the pV curve for a...Ch. 18 - Show that the application of Equation 18.3 to an...Ch. 18 - A horizontal piston-cylinder system containing n...Ch. 18 - Prob. 71PCh. 18 - The table below shows measured values of pressure...Ch. 18 - In a reversible process, a volume of air V0= 17 m3...Ch. 18 - A real gas is more accurately described using the...Ch. 18 - Repeat Exercise 20 for an expansion along the path...Ch. 18 - The adiabatic lapse rate is the rate at which air...Ch. 18 - The nuclear power plant at which youre the public...Ch. 18 - Prob. 78PCh. 18 - One scheme for reducing greenhouse-gas emissions...Ch. 18 - Warm winds called Chinooks (a Native-American term...Ch. 18 - Warm winds called Chinooks (a Native-American term...Ch. 18 - Warm winds called Chinooks (a Native-American term...Ch. 18 - Warm winds called Chinooks (a Native-American term...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Distinguish between microevolution, speciation, and macroevolution.
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Microphylls are found in which plant group? (A) lycophytes (B) liverworts (C) ferns (D) hornworts
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
All of the following processes are involved in the carbon cycle except: a. photosynthesis b. cell respiration c...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Choose the best answer to etch of the following. Explain your reasoning. What two pieces of information would y...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
41. Humans vary in many ways from one another. Among many minor phenotypic differences are the following five i...
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Fill in the blanks: a. The wrist is also known as the _________ region. b. The arm is also known as the _______...
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Complete the table below for spherical mirrors indicate if it is convex or concave. Draw the ray diagrams S1 10 30 S1' -20 20 f 15 -5 Marrow_forwardA particle with a charge of − 5.20 nC is moving in a uniform magnetic field of (B→=−( 1.22 T )k^. The magnetic force on the particle is measured to be(F→=−( 3.50×10−7 N )i^+( 7.60×10−7 N )j^. Calculate the scalar product v→F→. Work the problem out symbolically first, then plug in numbers after you've simplified the symbolic expression.arrow_forwardNeed help wity equilibrium qestionarrow_forward
- need answer asap please thanks youarrow_forwardA man slides two boxes up a slope. The two boxes A and B have a mass of 75 kg and 50 kg, respectively. (a) Draw the free body diagram (FBD) of the two crates. (b) Determine the tension in the cable that the man must exert to cause imminent movement from rest of the two boxes. Static friction coefficient USA = 0.25 HSB = 0.35 Kinetic friction coefficient HkA = 0.20 HkB = 0.25 M₁ = 75 kg MB = 50 kg P 35° Figure 3 B 200arrow_forwardA golf ball is struck with a velocity of 20 m/s at point A as shown below (Figure 4). (a) Determine the distance "d" and the time of flight from A to B; (b) Determine the magnitude and the direction of the speed at which the ball strikes the ground at B. 10° V₁ = 20m/s 35º Figure 4 d Barrow_forward
- The rectangular loop of wire shown in the figure (Figure 1) has a mass of 0.18 g per centimeter of length and is pivoted about side ab on a frictionless axis. The current in the wire is 8.5 A in the direction shown. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field parallel to the y-axis that will cause the loop to swing up until its plane makes an angle of 30.0 ∘ with the yz-plane. Find the direction of the magnetic field parallel to the y-axis that will cause the loop to swing up until its plane makes an angle of 30.0 ∘ with the yz-plane.arrow_forwardA particle with a charge of − 5.20 nC is moving in a uniform magnetic field of (B→=−( 1.22 T )k^. The magnetic force on the particle is measured to be (F→=−( 3.50×10−7 N )i^+( 7.60×10−7 N )j^. Calculate the y and z component of the velocity of the particle.arrow_forwardneed answer asap please thank youarrow_forward
- 3. a. Determine the potential difference between points A and B. b. Why does point A have a higher potential energy? Q = +1.0 C 3.2 cm 4.8 cm Aarrow_forwardPls help ASAParrow_forward1. Explain the difference between electrical field, potential difference, and electrical potential differencearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Thermodynamics: Crash Course Physics #23; Author: Crash Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4i1MUWJoI0U;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY