
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Whether the fatty acid
Concept introduction:
A fatty acid having a long aliphatic chain with no double bond is called saturated fatty acid and a fatty acid that contains at least one double bond within the fatty acid chain is called unsaturated fatty acid. Due to the presence of a long alkyl side chain in saturated fatty acids, their packing efficiency is more than those of unsaturated fatty acids. As a result, unsaturated fatty acids possess lower melting point than saturated fatty acids. Thus, most of the saturated fatty acids are solid at room temperature.
Answer to Problem 18.9E
The fatty acid
Explanation of Solution
The structural formula of fatty acid
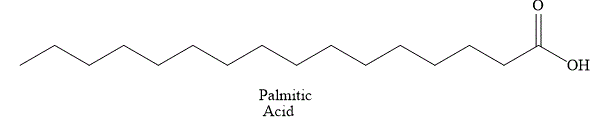
Figure 1
The general name of the above fatty acid is palmitic acid. Palmitic acid has a long aliphatic chain of
The fatty acid shown in Figure 1 is a saturated fatty acid and it is solid at room temperature.
(b)
Interpretation:
Whether the fatty acid
Concept introduction:
A fatty acid having a long aliphatic chain with no double bond is called saturated fatty acid and a fatty acid that contains at least one double bond within the fatty acid chain is called unsaturated fatty acid. Due to the presence of a long alkyl side chain in saturated fatty acids, their packing efficiency is more than those of unsaturated fatty acids. As a result, unsaturated fatty acids possess lower melting point than saturated fatty acids. Thus, most of the saturated fatty acids are solid at room temperature.
Answer to Problem 18.9E
The fatty acid
Explanation of Solution
The structural formula of fatty acid

Figure 2
The general name of the above fatty acid is lenoleic acid. The structural formula of lenoleic acid shows that there are two double bonds in the carbon chain. Therefore, lenoleic acid is an unsaturated fatty acid. The side chain in unsaturated fatty acids possess less van der Waal’s interactions between side chains of adjacent molecule. Therefore, the unsaturated fatty acid is a liquid at room temperature.
The fatty acid shown in Figure 2 is an unsaturated fatty acid and it is a liquid at room temperature.
(c)
Interpretation:
Whether the fatty acid
Concept introduction:
A fatty acid having a long aliphatic chain with no double bond is called saturated fatty acid and a fatty acid that contains at least one double bond within the fatty acid chain is called unsaturated fatty acid. Due to the presence of a long alkyl side chain in saturated fatty acids, their packing efficiency is more than those of unsaturated fatty acids. As a result, unsaturated fatty acids possess lower melting point than saturated fatty acids. Thus, most of the saturated fatty acids are solid at room temperature.
Answer to Problem 18.9E
The fatty acid
Explanation of Solution
The structural formula of fatty acid
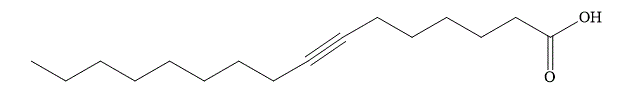
Figure 3
The general name of the above fatty acid is palmitolic acid. The structural formula of palmitolic acid contains double bonds within the fatty acid chain. Therefore, palmitolic acid is an unsaturated fatty acid. The side chain in unsaturated fatty acids possess less van der Waal’s interactions between side chains of adjacent molecule. Therefore, the unsaturated fatty acid is a liquid at room temperature.
The fatty acid shown in Figure 3 is an unsaturated fatty acid and it is a liquid at room temperature.
(d)
Interpretation:
Whether the fatty acid
Concept introduction:
A fatty acid having a long aliphatic chain with no double bond is called saturated fatty acid and a fatty acid that contains at least one double bond within the fatty acid chain is called unsaturated fatty acid. Due to the presence of a long alkyl side chain in saturated fatty acids, their packing efficiency is more than those of unsaturated fatty acids. As a result, unsaturated fatty acids possess lower melting point than saturated fatty acids. Thus, most of the saturated fatty acids are solid at room temperature.
Answer to Problem 18.9E
The fatty acid
Explanation of Solution
The structural formula of fatty acid
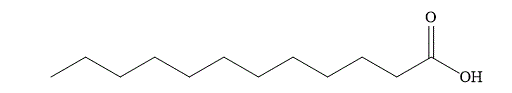
Figure 4
The general name of the above fatty acid is lauric acid. Lauric acid has a long aliphatic chain of
The fatty acid shown in Figure 4 is a saturated fatty acid and it is a solid at room temperature.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Biochemistry
- Pleasssssseeee solve this question in cheeemsirty, thankss sirarrow_forwardThe Ksp for lead iodide ( Pbl₂) is 1.4 × 10-8. Calculate the solubility of lead iodide in each of the following. a. water Solubility = mol/L b. 0.17 M Pb(NO3)2 Solubility = c. 0.017 M NaI mol/L Solubility = mol/Larrow_forwardPleasssssseeee solve this question in cheeemsirty, thankss sirarrow_forward
 Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





