
(a)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
Nitration is a process in which an
Answer to Problem 18.69AP
The reaction of benzene and chlorine gas in the presence of iron chloride followed by nitration forms
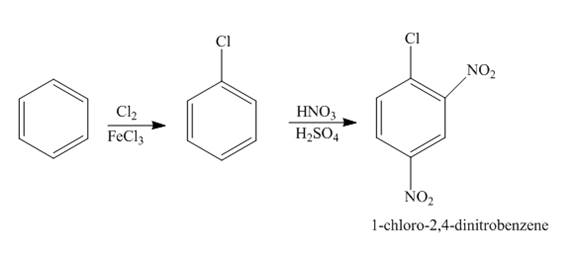
Explanation of Solution
The chlorination of benzene using chlorine gas in the presence of iron chloride forms chlorobenzene which further reacts with nitric acid in the presence of sulphuric acid to give
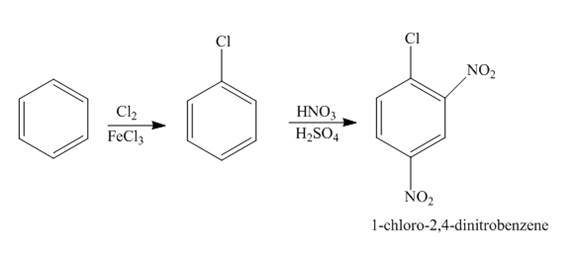
Figure 1
The reaction of benzene and chlorine gas in the presence of iron chloride followed by nitration forms
(b)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
Nitration is a process in which an aromatic compound is nitrated by electrophilic substitution in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid and concentrated nitric acid. Electron donating groups substituted on the aromatic ring are those which donate electron to the aromatic ring. Electron donating groups are ortho and para-directing.
Answer to Problem 18.69AP
The reaction of benzene and nitric acid in the presence of sulphuric acid followed by the treatment with
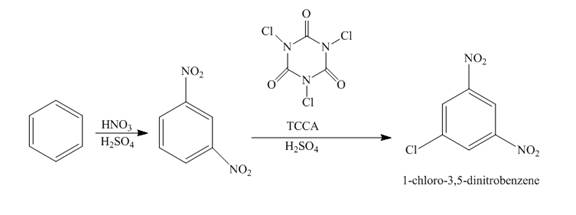
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of benzene and nitric acid in the presence of sulphuric acid forms

Figure 2
The reaction of benzene and nitric acid in the presence of sulphuric acid followed by the treatment with
(c)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of diphenylacetylene from
Concept introduction:
The addition of a bromine atom in a compound is known as bromination. Bromination occurs through electrophilic substitution reaction. Bromine atom acts as an electrophile which causes the formation of sigma bond in the reaction.
Answer to Problem 18.69AP
The reaction of
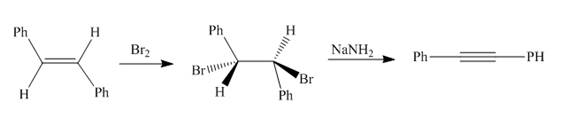
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of

Figure 3
The reaction of
(d)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one
Answer to Problem 18.69AP
The reaction of chlorobenzene and acetyl chloride in the presence of
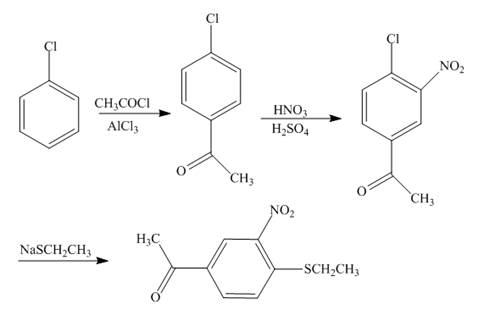
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of chlorobenzene and acetyl chloride in the presence of
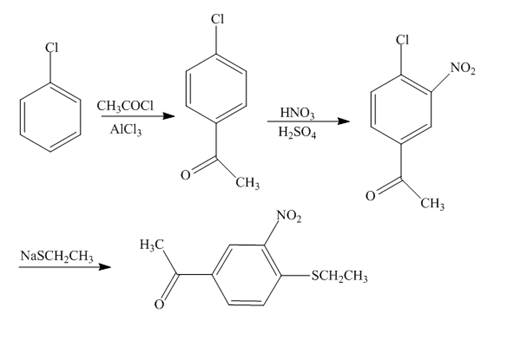
Figure 4
The reaction of chlorobenzene and acetyl chloride in the presence of
(e)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
Nitration is a process in which an aromatic compound is nitrated by electrophilic substitution in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid and concentrated nitric acid. Electron donating groups substituted on the aromatic ring are those which donate electron to the aromatic ring. Electron donating groups are ortho and para-directing.
Answer to Problem 18.69AP
The reaction of chlorobenzene undergoes nitration followed by the addition of a base which further oxidizes with the help of
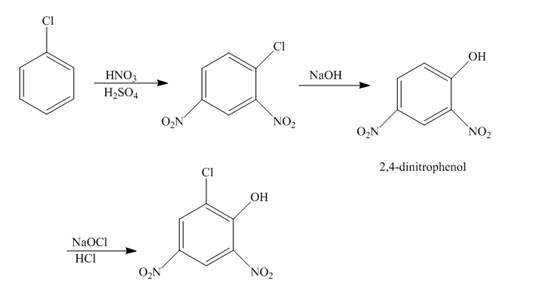
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of chlorobenzene and nitric acid in the presence of sulphuric acid undergoes nitration forms
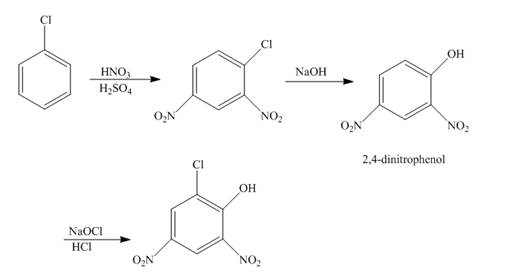
Figure 5
The reaction of chlorobenzene undergoes nitration followed by the addition of a base which further oxidizes with the help of
(f)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) from
Concept introduction:
A chemical reaction that involves the removal of a water molecule from the reacting molecule is known as a dehydration reaction. It takes place in the presence of a strong acid. The percentage of product formed is determined by Saytzeff’s rule.
Answer to Problem 18.69AP
The reaction of
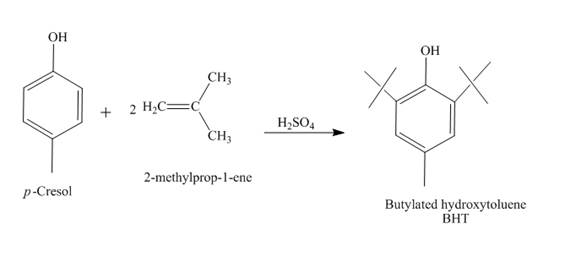
Explanation of Solution
The reaction between

Figure 6
The reaction of
(g)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of the given product from catechol and other reagents is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
A chemical reaction that involves the removal of a water molecule from the reacting molecule is known as a dehydration reaction. It takes place in the presence of a strong acid. The percentage of product formed is determined by Saytzeff’s rule.
Answer to Problem 18.69AP
The reaction of catechol and
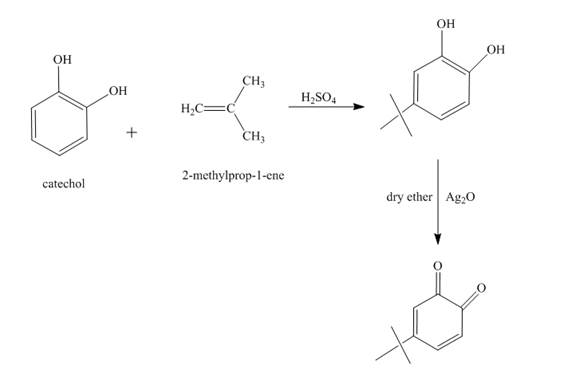
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of catechol and

Figure 7
The reaction of catechol and
(h)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
Grignard reagents are
Answer to Problem 18.69AP
The reaction of bromobenzene with Grignard reagent and ethylene oxide forms
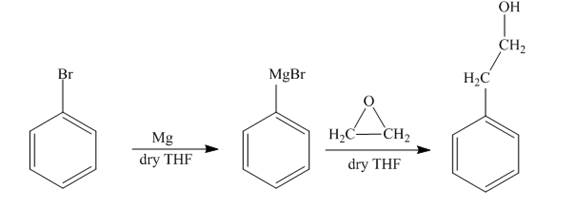
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of bromobenzene with magnesium in the presence of dry
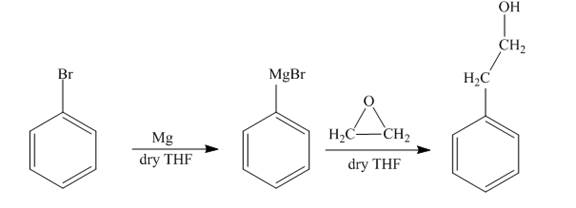
Figure 8
The synthesis of
(i)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of given product from
Concept introduction:
Nitration is a process in which an aromatic compound is nitrated by electrophilic substitution in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid and concentrated nitric acid. Electron donating groups substituted on the aromatic ring are those which donate electron to the aromatic ring. Electron donating groups are ortho and para-directing.
Answer to Problem 18.69AP
The reaction of fluorobenzene undergoes nitration followed by the addition of
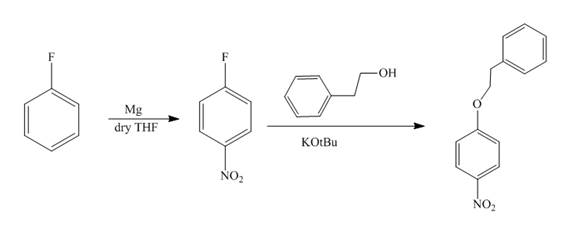
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of fluorobenzene with nitric acid in the presence of sulphuric acid forms

Figure 9
The reaction of fluorobenzene undergoes nitration followed by the addition of
(j)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of the given product from benzene, ethylene group and other reagents is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Nitration is a process in which an aromatic compound is nitrated by electrophilic substitution in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid and concentrated nitric acid. Electron donating groups substituted on the aromatic ring are those which donate electron to the aromatic ring. Electron donating groups are ortho and para-directing.
Answer to Problem 18.69AP
The synthesis of the desired product from benzene and ethylene group is shown below.
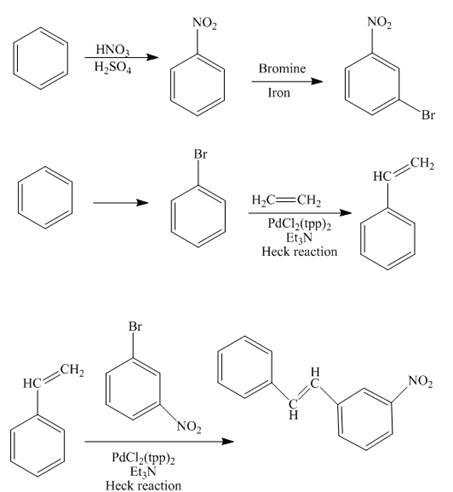
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of benzene with nitric acid in the presence of sulphuric acid forms nitrobenzene which further reacts with bromine to form
The styrene is prepared by the bromination of benzene followed by the addition of ethane in the presence of
In the final step, the compound
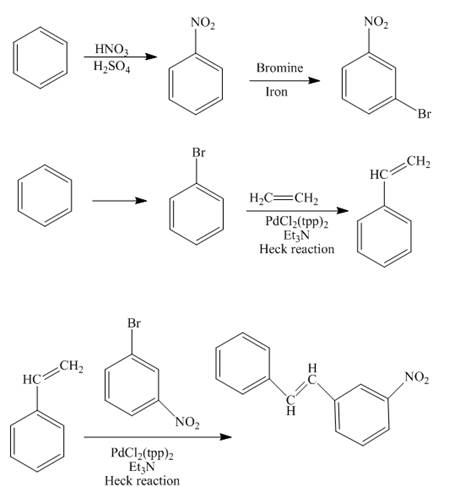
Figure 10
The synthesis of the desired product from benzene and ethylene group as shown in Figure 10.
(k)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of the given product from
Concept introduction:
The treatment of unsaturated halide with an alkene in the presence of a base and a
Answer to Problem 18.69AP
The reaction of
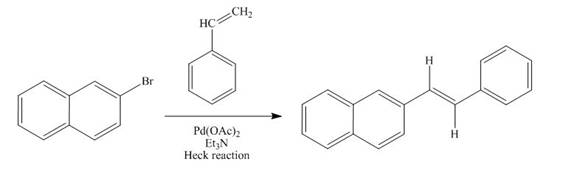
Explanation of Solution
The

Figure 11
The reaction of
(l)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of the given product from bromobenzene, ethylene group and other reagents is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Nitration is a process in which an aromatic compound is nitrated by electrophilic substitution in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid and concentrated nitric acid.
Answer to Problem 18.69AP
The reaction of bromobenzene with nitric acid in the presence of sulphuric acid followed by coupling reaction with allyl alcohol to form the desired product is shown below.
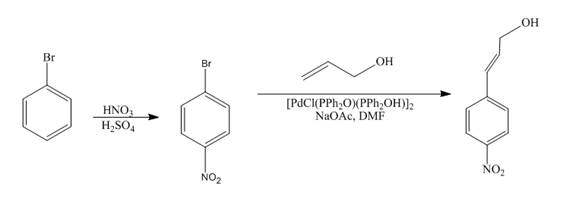
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of bromobenzene with nitric acid in the presence of sulphuric acid forms

Figure 12
The reaction of bromobenzene with nitric acid in the presence of sulphuric acid followed by coupling reaction with allyl alcohol to form the desired product as shown in Figure 12.
(m)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of the given product from
Concept introduction:
The hydroxide ions acts as a poor leaving groups as well as strong bases. The tosyl chloride reacts with hydroxide ions in the presence of weak base like pyridine to convert in a good leaving groups.
Answer to Problem 18.69AP
The reaction of
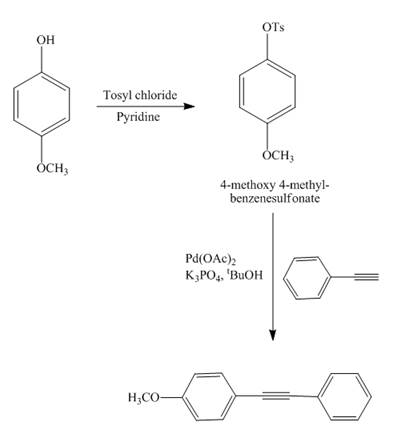
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
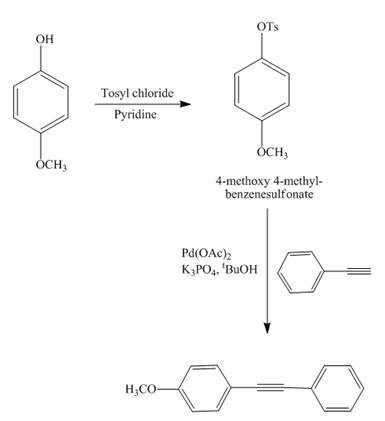
Figure 13
The reaction of
(n)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of the given product from
Concept introduction:
Sonogashira coupling is used to form carbon-carbon bond in the chemical reaction.
The addition of bromine atom in a compound is known as bromination. Bromination is occurs through elctrophilic substitution reaction. Bromine atom acts as a electrophile which causes the formation of sigma bond in the reaction.
Answer to Problem 18.69AP
The synthesis of the desired product from
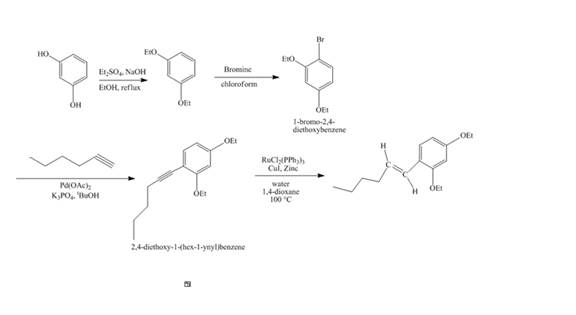
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of recorcinol with

Figure 14
The synthesis of the desired product from
(o)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of the given product from iodobenzene and other reagents is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
The coupling reactions used to connect two compounds with the help of a metal catalyst like palladium. Sonogashira coupling is used to form a carbon-carbon bond in the chemical reaction.
Answer to Problem 18.69AP
The synthesis of the desired product from iodobenzene and cyclohexene is shown below.
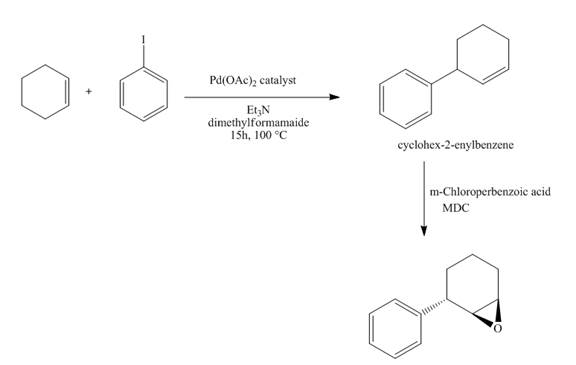
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of iodobenzene with cyclohexene in the presence of
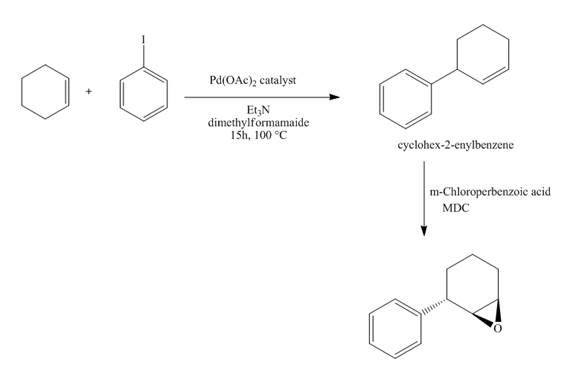
Figure 15
The synthesis of the desired epoxide compound from iodobenzene and cyclohexene is shown below in Figure 15.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- (b) A student wanted to synthesize methyl tert-butyl ether. He attempted the synthesis by adding sodium methoxide to tert-butyl chloride, but he obtained none of the desired product (1) (ii) Use an equation to show the product formed in this reaction Propose a suitable William ether synthetic route for methyl tert-butyl ether tach l.arrow_forwardGive detailed Solution with explanation neededarrow_forward(a) Given and Scara were given a task of synthesising (2-methylprop-1- enyl)cyclohexane 2 (A potential TB drug). After a brief discussion with each other, Given proposed Method A to synthesise 2 from cyclohexanecarbaldehyde 1 while Scara proposed Method B that started from hydroxymethylcyclohexane 3. When designing a synthetic route for drug molecule, you have to make sure the synthetic process is as efficient as possible (e.g. few synthetic steps, mostly making one product and more). THF A Ph Ph Ph B 3 1. PCC 2. isopropyl magnesium vromide 3. H₂SO4 100 °C OH Method B is not preferred synthetic route due to the number of steps involve (3 steps vs 1 step for Method A). What else is making method A unfavorable synthetic method? Use curly arrows to explain this effect. (Ctrl) -arrow_forward
- Provide the reagents and solvents (where appropriate) needed to bring about the following transformations. (a) CI (b)arrow_forwardGive detailed Solution with explanation neededarrow_forwardGive the reagents suitable for effecting each of the following reactions, and write the principal products. If an ortho, para mixture is expected, show both. If the meta isomer is the expected major product, wrote only that isomer. Nitration of benzene Nitration of the product of (a) Bromination of toluene Bromination of (trifluoromethyl)benzene Sulfonation of anisole Sulfonation of acetanilide (C6H5NHCOCH3) Chlorination of bromobenzene Friedel-Crafts alkylation of anisole with benzyl chloride Friedel-Crafts acylation of benzene with benzoyl chloride Nitration of the product of (i) Clemmensen reduction of product from (i) Wolff-Kishner reduction of product from (i)arrow_forward
- Show how to synthesize each of the following trisubstituted benzenes from a unsubstituted benzene.arrow_forward(b) acid, HNO3 to produce compound L. The reaction of compound L with bromine, Br2 in the presence of iron tribromide, FeBr3 produced compound M. Benzene also undergoes Fridel-crafts alkylation reaction with chloroethane, CH;CH2CI using catalyst N to produce compound P. Benzene, CeHe undergoes substitution reaction with concentrated nitric Benzena, CsHe menjalani tindak balas penukargantian dengan asid nitrik, HNO, pekat untuk menghasilkan sebatian L. Tindak balas sebatian L dengan bromin, Brz dengan kehadiran ferum tribromida, FeBrs menghasilkan sebatian M. Benzena juga menjalani tindak balas alkilasi Fridel-crafts dengan kloroetana, CH3CH2CI dengan menggunakan pemangkin N untuk menghasilkan sebatian P. (i) Draw the structural formula of L, M and P. Lukiskan formula struktur bagi sebatian L, M dan P. (ii) State catalyst N. Nyatakan pemangkin N. (iii) Show the formation of electrophile that will be reacted with benzene for the formation of compound P.arrow_forwardV) Outline a synthesis of the following compound from benzene and other appropriate organic or inorganic reagents. ? CH3 ? CO2H Excess ?arrow_forward
- Show all working explaining detailly each step. Answer should be type written using a comuter Keyboard!arrow_forward(a) benzene can potentially react with Lewis acid to form new carbon-carbon bond. Propose the starting material and stepwise mechanism to produce new chemical structure which consists of a formula molecule of C11H16.arrow_forward- Rank the following substances in order of increasing acidity: (a) Phenol, p-methylphenol, p-(trifluoromethyl)phenol (b) Benzyl alcohol, phenol, p-hydroxybenzoic acidarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





