
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure for the eight constitutional isomers of molecular formula C4H11N should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
There are three types of
Answer to Problem 18.48P
The structures for the eight constitutional isomers of molecular formula C4H11N are represented as follows:

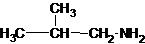
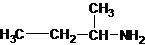
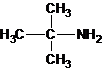
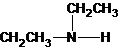
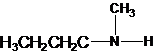
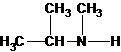
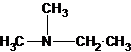
Explanation of Solution
Four structures of primary amines can be drawn with the formula C4H11N.

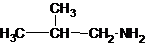
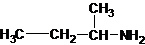
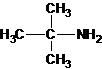
Three structures of secondary amines can also be drawn.
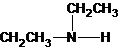
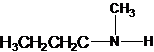
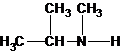
A tertiary structure can also be drawn as follows:
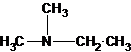
(b)
Interpretation:
The systematic name for each amine should be given.
Concept Introduction:
In nomenclature of primary amine, the longest carbon chain bonded to nitrogen is determined and the −e ending of the parent
Answer to Problem 18.48P
The name of amines are as follows:

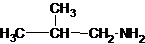
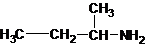
1-butanamine 2-methylpropan-1-amine butan-2-amine
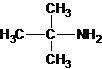
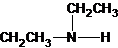
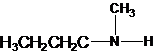
2-methylpropan-2-amine N-ethylethanamine N-methylpropan-1-amine
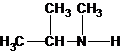
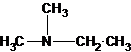
N-methylpropan-2-amine N,N-dimethylethanamine
Explanation of Solution

The longest carbon chain has four carbons. So the alkane name is butane. N is attached to C-1. Therefore, the systematic name of the amine is butanamine.
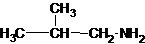
The longest carbon chain has three carbons. There is a methyl group at C-2. So the parent name is 2-methylpropanamine. The N atom is bonded to C-1. Therefore, the name become 2-methylpropan-1-amine.
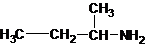
The longest carbon chain bonded to amine group has four carbons. The parent name is butanamine. The N atom is bonded to C-2. Therefore, the systematic name of the amine is butan-2-amine.
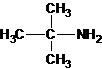
The longest carbon chain bonded to amine group has three carbons. There is a methyl group at C-2. The parent name is 2-methylpropanamine. The N atom is bonded to C-2. Therefore, the systematic name of the amine is 2-methylpropan-2-amine.
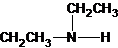
The secondary amine has the longest carbon chain with 2 carbons. So, the parent name is ethanamine. The N atom has bonded to C-1 and has 1 ethyl group as a substituent. Therefore, the systematic name become N-ethylethanamine.
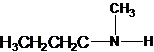
The secondary amine has the longest carbon chain with 3 carbons. So, the parent name is propanamine. The N atom has bonded to C-1 and has 1 methyl group as a substituent. Therefore, the systematic name become N-methylpropan-1-amine.
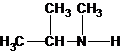
The secondary amine has the longest carbon chain with 3 carbons. So, the parent name is propanamine. The N atom has bonded to C-2 and has 1 methyl group as a substituent. Therefore, the systematic name become N-methylpropan-2-amine.
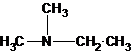
The tertiary amine has the longest carbon chain with 2 carbons. So the parent name is ethanamine. N atom has bonded to C-1 and has two methyl groups and 1 ethyl group as substituents. So, the systematic name of the amine is N,N-dimethylethanamine.
(c)
Interpretation:
The chirality center present in one of the amines should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
An atom that has four different groups bonded to it is referred to as chirality center. A chiral molecule has a non-superimposable mirror image.
Answer to Problem 18.48P
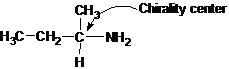
Explanation of Solution
Butan-2-amine has long carbon chain with 4 carbons and amine group is bonded to C-2. This C-2 carbon has four different groups bonded to it as 1 ethyl group, 1 methyl group, 1 amine group and a hydrogen. So, C-2 carbon is a chirality center.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
ALEKS 360 ACCESS CARD F/GEN. ORG.CHEM
- Indicate whether each statement is true or false: (a) Fat molecules contain amide bonds. (b) Phosphoplipids can be zwitterions. (c) Phospholipids form bilayers in water in order to have their long hydrophobic tails interact favorably with each other, leaving their polar heads to the aqueous environment.arrow_forwardDraw and name compounds that meet these descriptions:(a) Three different amides with the formula C5H11NO(b) Three different esters with the formula C6H12O2arrow_forward(a) Compound Z is a tertiary aromatic amine with the formula, C8H11N. Provide a chemical structure for compound Z. (b)nDraw the structure of the product formed exclusively when nitrous acid reacts with Z.arrow_forward
- Draw a structural formula for each amine. (a) 2-Butanamine (b) 1-Octanamine (c)2,2-Dimethyl-1-propanaminearrow_forwardDraw the structures for the four amines of molecular formula C 3H 9N. Give the systematic name for each amine.arrow_forwardBecause amines are basic, they can often accept a proton. Draw the protonated structure of n-propylamine.arrow_forward
- Draw the condensed formula or skeletal structural formula for the following compounds: (a) 2,3-dimethylpentanoic acid (b) Ethyl pentanoate (c) N,N-dimethyl-1-propanaminearrow_forwardGiven that C6H11COOH has a pKa = 4.8 and C6H11N+H3 has a pKa = 10.7, (a) What pH would you make the water layer to cause the carboxylic acid to dissolve in the water layer and the amine to dissolve in the ether layer? (b) What pH would you make the water layer to cause the carboxylic acid to dissolve in the ether layer and the amine to dissolve in the water layer?arrow_forwardClassify each compound (a)–(f) as one of the following: (i) amide, (ii) ester, or(iii) carboxylic acid. (a) CH3COOCH3 (b) RCONHR (c) C6H5COOHarrow_forward
- (i) Draw the structure of any amine and give the IUPAC name of that amine. (1) Classify the amine in your answer provided in (i) above (iii) Draw the structure of ethyl butanoate and name the functional group. (iv) Give the IUPAC name of the following compound and name the functional group:arrow_forwardDraw a structural formula for each amine. (a) 2-Butanamine (b) 1-Octanamine (c) 2,2-Dimethyl-1-propanamine (d) 1,5-Pentanediamine (e) 2-Bromoaniline (f) Tributylaminearrow_forwardDraw the structure of a compound of molecular formula C 9H 11NO that contains a benzene ring and a: (a) 1 ° amide; (b) 2 ° amide; (c) 3 ° amide.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
