
Concept explainers
Draw structures of the following derivatives.
- a. the 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone of benzaldehyde
- b. the semicarbazone of cyclobutanone
- c. cyclopropanone oxime
- d. the ethylene acetal of hexan-3-one
- e. acetaldehyde dimethyl acetal
- f. the methyl hemiacetal of formaldehyde
- g. the (E) isomer of the ethyl imine of propiophenone
- h. the hemiacetal form of 5-hydroxypentanal
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure of the given derivative is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Ketones and aldehydes show different types of reactions which results to form many different products. The nucleophilic addition reactions are the common reactions, which form products like imines, diols, alcohols, cyanohydrins, and alkenes.
Answer to Problem 18.37SP
The structure of the given derivative is shown in Figure 1.
Explanation of Solution
The given derivative is 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone of benzaldehyde.
The 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine is treated with benzaldehyde to form a 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone derivative.
The structure of 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone of benzaldehyde is given as,
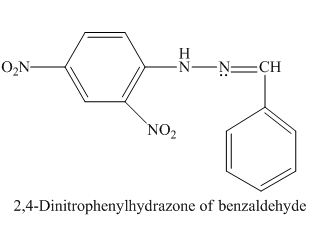
Figure 1
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure of the given derivative is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Ketones and aldehydes show different types of reactions which results to form many different products. The nucleophilic addition reactions are the common reactions, which form products like imines, diols, alcohols, cyanohydrins, and alkenes.
Answer to Problem 18.37SP
The structure of the given derivative is shown in Figure 2.
Explanation of Solution
The given derivative is semicarbazone of cyclobutanone.
The cyclobutanone is treated with semicarbazide to form a semicarbazone derivative.
The structure of semicarbazone of cyclobutanone is given as,
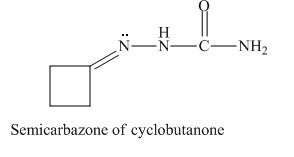
Figure 2
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure of the given derivative is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Ketones and aldehydes show different types of reactions which results to form many different products. The nucleophilic addition reactions are the common reactions, which form products like imines, diols, alcohols, cyanohydrins, and alkenes.
Answer to Problem 18.37SP
The structure of the given derivative is shown in Figure 3.
Explanation of Solution
The given derivative is cyclopropanone oxime.
The cyclopropanone is treated with hydroxylamine to form an oxime.
The structure of cyclopropanone oxime is given as,
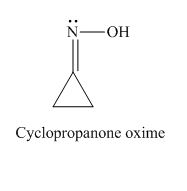
Figure 3
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure of the given derivative is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Ketones and aldehydes show different types of reactions which results to form many different products. The nucleophilic addition reactions are the common reactions, which form products like imines, diols, alcohols, cyanohydrins, and alkenes.
Answer to Problem 18.37SP
The structure of the given derivative is shown in Figure 4.
Explanation of Solution
The given derivative is ethylene acetal of hexan-3-one.
The ethylene glycol is treated with hexan-3-one to form ethylene acetal of hexan-3-one.
The structure of ethylene acetal of hexan-3-one is given as,
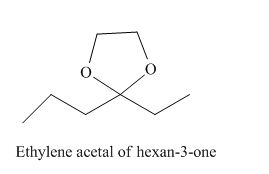
Figure 4
(e)
Interpretation:
The structure of the given derivative is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Ketones and aldehydes show different types of reactions which results to form many different products. The nucleophilic addition reactions are the common reactions, which form products like imines, diols, alcohols, cyanohydrins, and alkenes.
Answer to Problem 18.37SP
The structure of the given derivative is shown in Figure 5.
Explanation of Solution
The given derivative is acetaldehyde dimethyl acetal.
The acetaldehyde is treated with two moles of ethyl alcohol to form acetaldehyde dimethyl acetal.
The structure of acetaldehyde dimethyl acetal is given as,
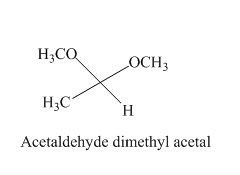
Figure 5
(f)
Interpretation:
The structure of the given derivative is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Ketones and aldehydes show different types of reactions which results to form many different products. The nucleophilic addition reactions are the common reactions, which form products like imines, diols, alcohols, cyanohydrins, and alkenes.
Answer to Problem 18.37SP
The structure of the given derivative is shown in Figure 6.
Explanation of Solution
The given derivative is methyl hemiacetal of formaldehyde.
The structure of hemiacetal of formaldehyde is given as,
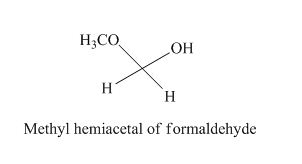
Figure 6
(g)
Interpretation:
The structure of the given derivative is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Ketones and aldehydes show different types of reactions which results to form many different products. The nucleophilic addition reactions are the common reactions, which form products like imines, diols, alcohols, cyanohydrins, and alkenes.
Answer to Problem 18.37SP
The structure of the given derivative is shown in Figure 7.
Explanation of Solution
The given derivative is (E)-isomer of the ethyl imine of propiophenone.
The propiophenone is treated with ethyl amine to form an ethyl imine derivative.
The structure of (E)-isomer of the ethyl imine of propiophenone is given as,
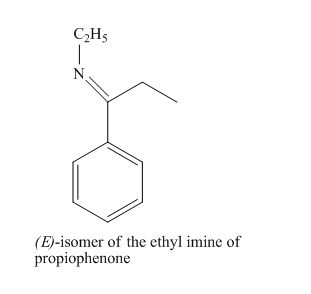
Figure 7
(h)
Interpretation:
The structure of the given derivative is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Ketones and aldehydes show different types of reactions which results to form many different products. The nucleophilic addition reactions are the common reactions, which form products like imines, diols, alcohols, cyanohydrins, and alkenes.
Answer to Problem 18.37SP
The structure of the given derivative is shown in Figure 8.
Explanation of Solution
The given derivative is hemiacetal of 5-hydroxypentanal.
The structure of hemiacetal of 5-hydroxypentanal is given as,
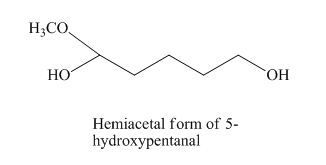
Figure 8
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Organic Chemistry (9th Edition)
- which has the greatest acidity? a. 2-hexanol b. valeric acid c. naphtol d. ethyl propionate which produces effervescence when dissolved in 10% sodium bicarbonate? a. 2-hexanol b. valeric acid c. napththol d. ethyl propionatearrow_forward1. An alkene reacts with water with an acid catalyst results into a formation of: A. Aldehyde B. Ketone C. Alcohol D. Ester 2. 3-Methylhexanal with K2Cr2O7 will yield: A. 3-Methyl-1-hexanol B. 3-Methylhexanoic acid C. 3-Methyl-1-hexanone D. 3-Methyl-1-hexanethiol 3. This is a reverse process of Hydration reaction: A. Oxidation reaction B. Reduction reaction C. Dehydration reaction D. Hydration reaction 4. Acetic acid reacts with a strong base forms: A. Salt B. Water C. Salt and Water D. No reaction 5. Ketones can be further oxidized with benedict's solution into: A. Alcohol B. Aldehyde C. Catalysts D. No reactionarrow_forwardCyclopentanone is treated with chlorine (Cl2) in the presence of acid (H*). What product is formed? A. Chlorocyclopentane B. 1-chloro-1-hydroxycyclopentane C. 2-chlorocyclopentanone D. 3-chlorocyclopentanonearrow_forward
- Draw the structure of the ff. aldehydes and ketones. a. 3-chlorobutanal 6. 8,8-dibromo -4-cthylcyclo hexanone C. 2,4-dimetnylpontanone • Draw the structure of the ff. compounds. a. oyclobutanecarboxylic acid b. 3,8-dimcthylpontancdioic acid C. 4-aminopcntanoic acid d. 2-mothylcycloheranecarooxylic acid m- chlorobėnzoic acidarrow_forwardWhat reagents would you use to convert methyl propanoate to the following compounds? a. isopropyl propanoate b. sodium propanoate c. N-ethylpropanamide d. propanoic acidarrow_forwardReagents a. C6H5CHO b. NaOH, ethanol h. BrCH2CH=CH2 i. Na* OEt, ethanol j. Br2, H* k. K* t-BuO c. Pyrrolidine, cat. H* d. H2C=CHCN e. H3O* f. I. CH2(CO2ET)2 -CH2CH2CN LDA m. heat g. ELOC(=0)CO2ET Select reagents from the table to synthesize this compound from cyclopentanone. Enter the letters of the chosen reagents, in the order that you wish to use them, without spaces or punctuation (i.e. geda).arrow_forward
- 1. Which carbonyl group of the given compound is most reactive for nucleophilic addition reaction? a. All have equal reactivity b. Carbonyl Group 1 c. Carbonyl Group 2 d. Carbonyl Group 2. An aldehyde commonly exhibits a nucleophilic addition type of reaction. When a nucleophile attacks a carbonyl carbon, what happens to the oxygen atom in the structure? Refer to the structure below. ~ a. Oxygen atom becomes more electronegative. b. Oxygen atom obtains a net negative charge. c. Oxygen atom transforms to an alkoxide group. d. Oxygen atom acts as the new electrophile. 3. Assign the trivial name of the structure below. a. Diphenylketone b. Benzyl phenylketone c. Diphenyl aldehyde d. Benzyl phenyl aldehydearrow_forwardFLAVORANTS: Identify the aldehyde and ketone-containing flavoring compound from each following sources. Choose your best answer from the choices below A. 2-Octanone B. Citral C. Benzaldehyde D. Vanillin E. Cinnamaldehyde F. a-Damascone 1. Вerry 2. Mushroom 3. Lemongrass 4. Cinnamon 5. Almonds Idchyde or ketone formed froarrow_forwardpyridine reacts with 1-bromobutane to give?arrow_forward
- COOH ? CH2 CH2 H3C H3C Reagents a. HBr e. PBг3 b. Mg, ether f. NaCN then H3O+ c. CO2, ether then H3O+ g. NBS, CC14 d. BH3, THF then H2O2, OH h. CrO3, H2SO4arrow_forwardThere are THREE parts. Please circle the final answer! Which reagent would not react with a carboxylic acid? O a. LIAIH4 b. NaOH C. KMN04 d. ВНЗ/THF An aldehyde cannot be made directly from this type of compound a. carboxylic acid O b. alcohol C. ester O d. acid chloridearrow_forwardWhat is the product of the following reaction? a. b. c. d. مر Br 1)LDA, -780 2)EtBrarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





