
(a)
Interpretation:
The validation corresponding to the fact that aspartame is chiral is to be stated. If aspartame is chiral, then the possible number of stereoisomers for aspartame is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
A compound that contains a chiral carbon is known as chiral compound. Carbon atom that contains all the four different atoms or group of atoms attached to it is referred as the chiral atom. This carbon is also known as stereocenter.
The possible number of stereoisomers is calculated by the expression
Answer to Problem 10P
Aspartame is a chiral compound. The possible number of stereoisomers for aspartame is
Explanation of Solution
The aspartame is a chiral compound. The structure of aspartame which contains chiral carbon atoms is shown as,
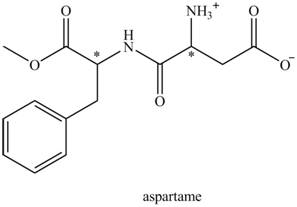
There are two chiral carbon atoms present in aspartame which are marked with asterisk sign. In the structure of aspartame, one carbon atom is directly bonded to
Thus, the possible number of stereoisomers in aspartame is,
Where,
- is the number of stereocenter.
Thus, the possible stereoisomers of aspartame is
(b)
Interpretation:
The name of each functional group present in aspartame is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
An atom or a group of atoms that shows characteristic physical and chemical properties are collectively known as
Answer to Problem 10P
The name of each functional group present in aspartame is ester group
Explanation of Solution
According to the structure of aspartame shown in Figure 1, there are four functional groups present in the structure of aspartame.
The name of all the functional group of aspartame is ester group
(c)
Interpretation:
The net charge on aspartame molecule in an aqueous solution at
Concept Introduction:
The negative logarithm of hydrogen ion concentration of the solution is known as
Answer to Problem 10P
The net charge on aspartame molecule in an aqueous solution at
Explanation of Solution
In an aqueous solution of
Hence, there is no change of charge takes place in aspartame and it possesses zero net charge.
(d)
Interpretation:
The validation corresponding to the fact that aspartame is whether soluble in water or not is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
According to the concept of solubility, it is mentioned that like dissolves like. Generally, polar compound can only be dissolved in polar solvents and non-polar or weakly polar compounds can only be dissolved in non-polar solvents or weakly polar solvents.
Answer to Problem 10P
Aspartame is soluble in water.
Explanation of Solution
The given structure of asparatame is present in zwitterion form which suggests that it is a polar molecule. According to the concept of like dissolves like, aspartame is soluble in water because water is also a polar molecule.
(e)
Interpretation:
The structural formulas for the products that are obtained by the complete hydrolysis of aspartame in aqueous
Concept Introduction:
An atom or a group of atoms that shows characteristic physical and chemical properties are collectively known as functional groups. The functional group is the most reactive part present in the molecule. The main functional groups are
The addition of water molecule to the compound is known as hydrolysis that compound.
Answer to Problem 10P
The structural formulas for the products that are obtained by the complete hydrolysis of aspartame in aqueous
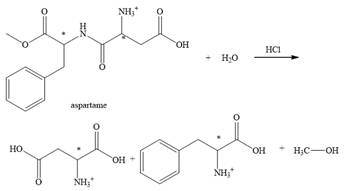
Explanation of Solution
The hydrolysis of aspartame in the presence of aqueous
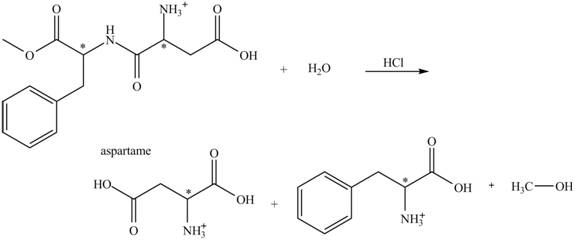
Figure 2.
The reaction of aspartame with aqueous
(f)
Interpretation:
The structural formulas for the products that are obtained by the complete hydrolysis of aspartame in aqueous
Concept Introduction:
An atom or a group of atoms that shows characteristic physical and chemical properties are collectively known as functional groups. The functional group is the most reactive part present in the molecule. The main functional groups are
The addition of water molecule to the compound is known as hydrolysis that compound.
Answer to Problem 10P
The structural formulas for the products that are obtained by the complete hydrolysis of aspartame in aqueous
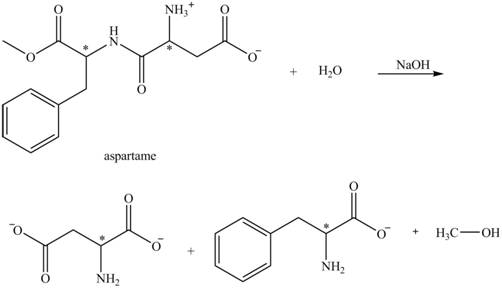
Explanation of Solution
The hydrolysis of aspartame in the presence of aqueous
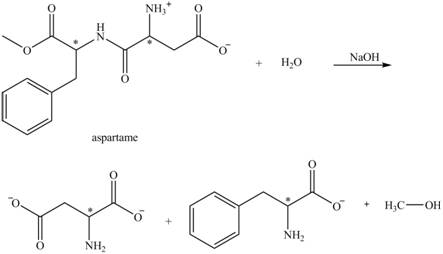
Figure 3.
The reaction of aspartame with aqueous
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
- (a) The following synthesis of the molecule shown in the circle has a major problem. What is this problem? (2 pts) 1) HBr (no peroxides) 2) H- NaNH2 Br 3) NaNH, 4) CH3Br 5) H2, Pd (b) Starting with the molecule shown below and any other materials with two carbons or less, write out an alternate synthesis of the circled molecule. More than one step is needed. Indicate the reagent(s) and the major product in all the steps in your synthesis. (5 pts) 2024 Fall Term (1) Organic Chemistry 1 (Lec) CHEM 22204 02[6386] (Hunter College) (c) Using the same starting material as in part (b) and any other materials win two carpons or less, write out syntheses of the circled molecules shown below. More than one step is needed in each case. Indicate the reagent(s) and the major product in all the steps in your synthesis. You may use reactions and products from your synthesis in part (b). (5 pts)arrow_forwardalt ons for Free Response Questions FRQ 1: 0/5 To spectrophotometrically determine the mass percent of cobalt in an ore containing cobalt and some inert materials, solutions with known [Co?) are prepared and absorbance of each of the solutions is measured at the wavelength of optimum absorbance. The data are used to create a calibration plot, shown below. 0.90- 0.80- 0.70 0.60 0.50 0.40- 0.30 0.20- 0.10- 0.00- 0.005 0.010 Concentration (M) 0.015 A 0.630 g sample of the ore is completely dissolved in concentrated HNO3(aq). The mixture is diluted with water to a final volume of 50.00 ml. Assume that all the cobalt in the ore sample is converted to Co2+(aq). a. What is the [Co2] in the solution if the absorbance of a sample of the solution is 0.74? 13 ✗ b. Calculate the number of moles of Co2+(aq) in the 50.00 mL solution. 0.008 mols Coarrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forward
- Closo-boranes and arachno-boranes are structures that exhibit B-B, B-H-B, and B-H bonds. Correct?arrow_forwardIndicate why boron hydrides cannot form large linear or planar structures.arrow_forwardNido-boranes are structures with the molecular formula BnHn+4 that exhibit B-B, B-H-B and B-H bonds. Correct?arrow_forward
- 8:07 AM Wed Dec 18 Final Exam 2024 copy Home Insert Draw Page Layout Formulas Data Review AA 田 General A G fx Alexis Cozort ☑ ⚫ 61% A B D E F H K M N P R S T U 3+ 10 125 mM that yielded peak heights of Aa = 9 1-(a)A sample solution was examined under XRF to quantify the analyte Ce³+. Find the response factor F, when standardized concentration of analyte [Ce³+]A = concentration of internal standard S i.e. [In³*]s = 151 mM was spiked with standardized 1600 and As = 3015 respectively? 11 12 (i)Define F, F = Aa As [A] [S] + X 13 (*Define with variables) 4000 14 15 (ii)Calculate F, F = numeral (You will use the F value in part 1-(b) below) As 16 (*Calculate with numerals) 17 18 1-(b)To determine the unknown conc of analyte [Ce³+], a volume of 15 mL of internal standard S having a concentration [In³+]s = 0.264 M 19 20 was added to 45 mL of unknown, and the mixture was diluted to 100 mL in a volumetric flask. XRF analysis yielded a spectrum, Figure-1, where peak heights A and As are…arrow_forwardAll structural types of Boron hydrides exhibit B-B, B-H-B and B-H bonds. Correct?arrow_forwardN-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) is a suspected carcinogen that can form via reactions between dimethylamine (DMA) and monochloramine (NH2Cl). The relevant elementary reactions and the corresponding rate constants are as shown below. Reaction Rate constant (M¹s¹) DMA + NH2Cl = DMCA + NH3 k =1.4×10-1, kr = 5.83×10-3 1.28×10-3 DMA + NH2Cl → UDMH UDMH + NH2Cl → NDMA -> 1.11×10-1 If the initial concentrations of DMA and NH2Cl are given, you should be able to predict the concentrations of all species at any given reaction time. Please write down the rate equations for DMA, NH2C1, DMCA, UDMH and NDMA.arrow_forward
- You wish to add enough NaOCl (sodium hypochlorite) to a 150 m³ swimming pool to provide a dose of 5.0 mg/L TOTOCI as Cl2. (a) How much NaOCI (kg) should you add? (Note: the equivalent weight of NaOCl is based on the reaction: NaOCl + 2H + 2 e→CI + Na +H₂O.) (10 pts) (atomic weight: Na 23, O 16, C1 35.5) (b) The pH in the pool after the NaOCl addition is 8.67. To improve disinfection, you want at least 90% of the TOTOCI to be in the form of HOCI (pKa 7.53). Assuming that HOCI/OCI is the only weak acid/base group in solution, what volume (L) of 10 N HCl must be added to achieve the goal? (15 pts) Note that part a) is a bonus question for undergraduate students. If you decide not to work on this part of the question, you many assume TOTOCI = 7×10-5 M for part b).arrow_forwardPart A 2K(s)+Cl2(g)+2KCI(s) Express your answer in grams to three significant figures. Part B 2K(s)+Br2(1)→2KBr(s) Express your answer in grams to three significant figures. Part C 4Cr(s)+302(g)+2Cr2O3(s) Express your answer in grams to three significant figures. Part D 2Sr(s)+O2(g) 2SrO(s) Express your answer in grams to three significant figures. Thank you!arrow_forwardA solution contains 10-28 M TOTCO3 and is at pH 8.1. How much HCI (moles per liter of solution) is required to titrate the solution to pH 7.0? (H2CO3: pKa1=6.35, pKa2=10.33)arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co


