
Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780133915389
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 17.3, Problem 43P
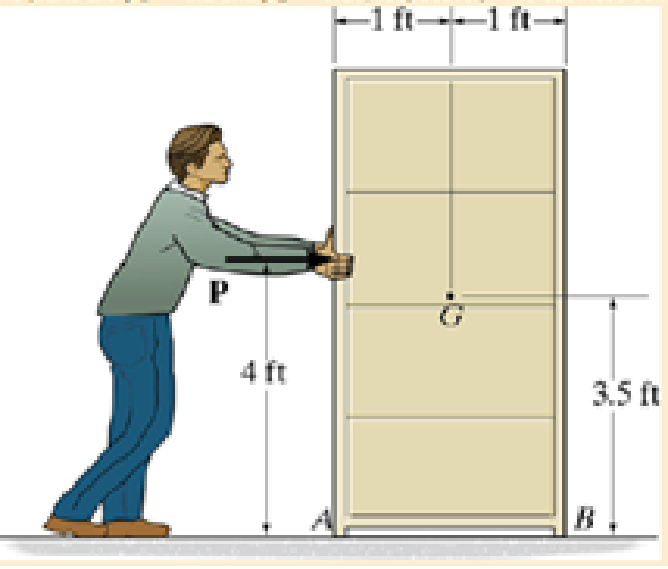
The coefficients of static and kinetic friction between the cabinet and the plane are μs = 0.2 and μk = 0.15, respectively. The cabinet’s center of gravity is located at G.
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule10:00
Students have asked these similar questions
How do i solve this problem?
Q4/ A compressor is driven motor by mean of a flat belt of thickness 10 mm and a width of
250 mm. The motor pulley is 300 mm diameter and run at 900 rpm and the compressor
pulley is 1500 mm diameter. The shaft center distance is 1.5 m. The angle of contact of
the smaller pulley is 220° and on the larger pulley is 270°. The coefficient of friction
between the belt and the small pulley is 0.3, and between the belt and the large pulley is
0.25. The maximum allowable belt stress is 2 MPa and the belt density is 970 kg/m³.
(a) What is the power capacity of the drive and (b) If the small pulley replaced by
V-grooved pulley of diameter 300 mm, grooved angle of 34° and the coefficient of
friction between belt and grooved pulley is 0.35. What will be the power capacity in this
case, assuming that the diameter of the large pulley remain the same of 1500 mm.
You are tasked with designing a power drive system to transmit power between a motor and a conveyor belt in a manufacturing facility as illustrated in figure.
The design must ensure efficient power transmission, reliability, and safety. Given the following specifications and constraints, design drive system for this application:
Specifications:
Motor Power: The electric motor provides 10 kW of power at 1,500 RPM.
Output Speed: The output shaft should rotate at 150 rpm.
Design Decisions:
Transmission ratio: Determine the necessary drive ratio for the system.
Shaft Diameter: Design the shafts for both the motor and the conveyor end.
Material Selection: Choose appropriate materials for the gears, shafts.
Bearings: Select suitable rolling element bearings.
Constraints:
Space Limitation:
The available space for the gear drive system is limited to a 1-meter-long section.
Attribute 4 of CEP
Depth of knowledge required
Fundamentals-based, first principles analytical approach…
Chapter 17 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics (14th Edition)
Ch. 17.1 - The rod's density end cross-sectional area. A are...Ch. 17.1 - Determine the mass of the cylinder end its moment...Ch. 17.1 - The nag has a mass m.Ch. 17.1 - Determine the radius of gyration kx. The density...Ch. 17.1 - The specific weight of the material is = 380...Ch. 17.1 - Determine the moment of inertia Iz and express the...Ch. 17.1 - Determine the moment of inertia Ix and express the...Ch. 17.1 - Defending the moment of inertia Iy and express the...Ch. 17.1 - Express the result in terms of the mass m of the...Ch. 17.1 - Determine me radius of gyration of the pendulum...
Ch. 17.1 - Determine the mass moment of inertia of the...Ch. 17.1 - Determine the moment of inertia of the solid steel...Ch. 17.1 - Determine the wheels moment of inertia about an...Ch. 17.1 - If the large ring, small ring and each of the...Ch. 17.1 - The thin plate has a hole in its center its...Ch. 17.1 - The material has a mass per unit area of 20 kg/m2.Ch. 17.1 - The block has a mass of 3 kg and the semicylinder...Ch. 17.1 - The block has a mass of 3 kg and the semicylinder...Ch. 17.1 - The material has a specific weight = 90 lb/ft3.Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 20PCh. 17.1 - Determine the location y of the center of mass G...Ch. 17.1 - The material is steel having a density of = 7.85...Ch. 17.1 - The material is steel having a density of = 7.85...Ch. 17.3 - Draw the free-body and kinetic diagrams of the...Ch. 17.3 - Draw the free-body and kinetic diagrams of the...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the acceleration of the can and the...Ch. 17.3 - If the 80-kg cabinet is allowed to roll down the...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the maximum acceleration of the frame...Ch. 17.3 - Also what is the corresponding normal reaction on...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the tension developed in the rods and...Ch. 17.3 - If it is subjected to a couple moment M = 450 N ...Ch. 17.3 - Determine how far the door moves in 25, starting...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the constant force F that must be...Ch. 17.3 - Initially at take-off the engines provide a thrust...Ch. 17.3 - If it starts from rest it causes the rear wheels...Ch. 17.3 - If the winch at B draws in the cable with an...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the greatest acceleration of the...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the internal axial, shear, and...Ch. 17.3 - If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the reactions at both the wheels at A...Ch. 17.3 - Also, what is the acceleration of the cart? The...Ch. 17.3 - If it is subjected to a horizontal force of P =...Ch. 17.3 - Determine its initial acceleration if a man pushes...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the initial acceleration of a desk when...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the maximum force P that can be applied...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the maximum force P that can be applied...Ch. 17.3 - If it is released from rest, determine the...Ch. 17.3 - It is carried on a truck as shown. Determine the...Ch. 17.3 - It is carried on a truck as shown. If the truck...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the smallest acceleration that will...Ch. 17.3 - The coefficients of static and kinetic friction...Ch. 17.3 - If the collar is given a constant acceleration of...Ch. 17.3 - If it is supported by the cable AB and hinge at C,...Ch. 17.3 - If it is supported by the cable AB and hinge at C,...Ch. 17.3 - If the acceleration is a = 20 ft/s2, determine the...Ch. 17.3 - If h = 3 ft, determine the snowmobiles maximum...Ch. 17.3 - If the carts mass is 30 kg and it is subjected to...Ch. 17.3 - The uniform rod BC has a mass of 15 kg.Ch. 17.3 - If the acceleration of the truck is at = 0.5 m/s2,...Ch. 17.3 - If the angle = 30, determine the acceleration of...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the largest initial angular acceleration...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the initial friction and normal force of...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the largest initial angular acceleration...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the normal force NE, shear force VE, and...Ch. 17.4 - If the wheel starts from rest determine its...Ch. 17.4 - Determine the angular velocity of the disk when t...Ch. 17.4 - Determine the tangential and normal components of...Ch. 17.4 - Determine the tangential and normal components or...Ch. 17.4 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 17.4 - If the rod has a counterclockwise angular velocity...Ch. 17.4 - If the wheel is subjected to a moment M = (5t) N ...Ch. 17.4 - Determine its initial angular acceleration and the...Ch. 17.4 - If it is released from rest when = 0. determine...Ch. 17.4 - If it is released from rest in the position shown,...Ch. 17.4 - The reel rests on rollers at A and B and has a...Ch. 17.4 - The spring has a stiffness k = 5 lb ft/rad, so...Ch. 17.4 - The spring has a stiffness k = 5 lb ft/rad, so...Ch. 17.4 - If a force of F=(142)N, where is in radians, is...Ch. 17.4 - If no slipping occurs between them determine the...Ch. 17.4 - Show that IG may be eliminated by moving the...Ch. 17.4 - Treat the beam as a uniform slender rod.Ch. 17.4 - It consists of a 100-kg steel plate AC and a...Ch. 17.4 - It is pin supported at both ends by two brackets...Ch. 17.4 - It is pin supported at both ends by two brackets...Ch. 17.4 - Determine its angular velocity when t = 2 s...Ch. 17.4 - If it is placed on the ground for which the...Ch. 17.4 - Compute the time needed to unravel 5 m of cable...Ch. 17.4 - If the rotor always maintains a constant clockwise...Ch. 17.4 - It is originally spinning at = 40 rad/s. If it is...Ch. 17.4 - It is pin supported at both ends by two brackets...Ch. 17.4 - Disk E has a weight of 60 lb and is initially at...Ch. 17.4 - If the cylinders are released from rest, determine...Ch. 17.4 - If the pulley can be treated as a disk of mass 3...Ch. 17.4 - If the pulley can be treated as a disk of mass M,...Ch. 17.4 - Assume that the board is uniform and rigid, and...Ch. 17.4 - At the instant the rolor is horizontal it has an...Ch. 17.4 - Determine the initial tending moment at the fixed...Ch. 17.4 - Movement is controlled by the electromagnet E,...Ch. 17.4 - If it is rotating in the vertical plane at a...Ch. 17.4 - Determine the angular acceleration of the rod and...Ch. 17.4 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 17.4 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 17.5 - If the powder burns at a constant rate of 20 g/s...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the acceleration of the bars mass center...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the acceleration of its mass center and...Ch. 17.5 - When the wheel is subjected to the couple moment,...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the angular acceleration of the sphere...Ch. 17.5 - If the couple moment is applied to the spool and...Ch. 17.5 - If the rod is released from rest at = 0,...Ch. 17.5 - rolls without slipping, show that when moments are...Ch. 17.5 - If it is initially at rest and is subjected to a...Ch. 17.5 - The uniform 150-lb beam is initially at rest when...Ch. 17.5 - If the coefficients of static and kinetic friction...Ch. 17.5 - If the coefficients of static and kinetic friction...Ch. 17.5 - If the coefficients of static and kinetic friction...Ch. 17.5 - Solve Prob.17-96 if the cord and force P = 50 N...Ch. 17.5 - If the coefficients of static and kinetic friction...Ch. 17.5 - If a horizontal force of F = 80 N is applied to...Ch. 17.5 - If slipping does not occur, determine the rings...Ch. 17.5 - Neglect the thickness of the ring.Ch. 17.5 - Using a collar of negligible mass, its end A is...Ch. 17.5 - If the pin is connected to a track which is giver...Ch. 17.5 - Assume the roller to be a uniform cylinder and...Ch. 17.5 - Also, find the angular acceleration of the roller....Ch. 17.5 - Determine the bars initial angular acceleration...Ch. 17.5 - Solve Prob.17-106 if the roller is removed and the...Ch. 17.5 - If the coefficient of static friction at A is s, =...Ch. 17.5 - If the truck has an acceleration of 3 m/s2...Ch. 17.5 - A cord is wrapped around the periphery of the disk...Ch. 17.5 - If the coefficient of static friction at A is s =...Ch. 17.5 - At this instant the center of gravity of the...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the initial angular acceleration of the...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the time before it starts to roll...Ch. 17.5 - If they are released from rest determine the...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the normal force which the path exerts...Ch. 17.5 - If it is originally at rest while being supported...Ch. 17.5 - If the pin support at A suddenly fails, determine...Ch. 17.5 - Determine its angular acceleration.Ch. 17.5 - If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the normal reactions at each of the...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the internal axial force Ex, shear force...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the maximum acceleration it can have if...Ch. 17.5 - The roil rest against a wall for which the...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the magnitude of force F and the initial...Ch. 17.5 - Compute the reaction at the pin O just after the...Ch. 17.5 - if the coefficient of kinetic friction at the...Ch. 17.5 - The coefficient of kinetic friction is A = 0.3.
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Explain what can be done with primary keys to eliminate key ripple effects as a database evolves.
Modern Database Management
Write some code that will create a stream named textStream that is an object of the class PrintWriter and that ...
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
For the circuit shown, use the node-voltage method to find v1, v2, and i1.
How much power is delivered to the c...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
What are the two primary functions of the electrodes in resistance welding?
Degarmo's Materials And Processes In Manufacturing
In each case, determine the internal bending moment as a function of x, and state the necessary boundary and/or...
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
17–1C A high-speed aircraft is cruising in still air. How does the temperature of air at the nose of the aircra...
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- - | العنوان In non-continuous dieless drawing process for copper tube as shown in Fig. (1), take the following data: Do-20mm, to=3mm, D=12mm, ti/to=0.6 and v.-15mm/s. Calculate: (1) area reduction RA, (2) drawing velocity v. Knowing that: ti: final thickness V. Fig. (1) ofthrearrow_forwardA direct extrusion operation produces the cross section shown in Fig. (2) from an aluminum billet whose diameter 160 mm and length - 700 mm. Determine the length of the extruded section at the end of the operation if the die angle -14° 60 X Fig. (2) Note: all dimensions in mm.arrow_forwardFor hot rolling processes, show that the average strain rate can be given as: = (1+5)√RdIn(+1)arrow_forward
- : +0 usão العنوان on to A vertical true centrifugal casting process is used to produce bushings that are 250 mm long and 200 mm in outside diameter. If the rotational speed during solidification is 500 rev/min, determine the inside radii at the top and bottom of the bushing if R-2R. Take: -9.81 mis ۲/۱ ostrararrow_forward: +0 العنوان use only In conventional drawing of a stainless steel wire, the original diameter D.-3mm, the area reduction at each die stand r-40%, and the proposed final diameter D.-0.5mm, how many die stands are required to complete this process. онarrow_forwardIn non-continuous dieless drawing process for copper tube as shown in Fig. (1), take the following data: Do-20mm, to=3mm, D=12mm, ti/to=0.6 and vo-15mm/s. Calculate: (1) area reduction RA, (2) drawing velocity v. Knowing that: t₁: final thickness D₁ V. Fig. (1) Darrow_forward
- A vertical true centrifugal casting process is used to produce bushings that are 250 mm long and 200 mm in outside diameter. If the rotational speed during solidification is 500 rev/min, determine the inside radii at the top and bottom of the bushing if R-2Rb. Take: 8-9.81 m/sarrow_forwardIn conventional drawing of a stainless steel wire, the original diameter D.-3mm, the area reduction at each die stand r-40%, and the proposed final diameter D₁-0.5mm, how many die stands are required to complete this process.arrow_forwardA vertical true centrifugal casting process is used to produce bushings that are 250 mm long and 200 mm in outside diameter. If the rotational speed during solidification is 500 rev/min, determine the inside radii at the top and bottom of the bushing if R-2Rb. Take: 8-9.81 m/sarrow_forward
- In non-continuous dieless drawing process for copper tube as shown in Fig. (1), take the following data: Do-20mm, to=3mm, D=12mm, ti/to=0.6 and vo-15mm/s. Calculate: (1) area reduction RA, (2) drawing velocity v. Knowing that: t₁: final thickness D₁ V. Fig. (1) Darrow_forward-6- 8 من 8 Mechanical vibration HW-prob-1 lecture 8 By: Lecturer Mohammed O. attea The 8-lb body is released from rest a distance xo to the right of the equilibrium position. Determine the displacement x as a function of time t, where t = 0 is the time of release. c=2.5 lb-sec/ft wwwww k-3 lb/in. 8 lb Prob. -2 Find the value of (c) if the system is critically damping. Prob-3 Find Meq and Ceq at point B, Drive eq. of motion for the system below. Ш H -7~ + 目 T T & T тт +arrow_forwardQ For the following plan of building foundation, Determine immediate settlement at points (A) and (B) knowing that: E,-25MPa, u=0.3, Depth of foundation (D) =1m, Depth of layer below base level of foundation (H)=10m. 3m 2m 100kPa A 2m 150kPa 5m 200kPa Barrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
Mechanical Engineering: Centroids & Center of Gravity (1 of 35) What is Center of Gravity?; Author: Michel van Biezen;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Tkyk-G1rDQg;License: Standard Youtube License