
a)
To determine: The total cost of producing in Country M.
Introduction:
Supplier selection is the process of evaluating the performance of each supplier and comparing it with in-house production to choose a capable supplier to support the output of the organization.
a)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
It is given that Company D is considering outsourcing its door production to Country M. The price quoted by the company of Country M is $83 for 5,000 units of standard door per year. The transportation cost is $825, which holds 250 doors. In order to send engineers to prequalify plant costs, $5,000 is required and to negotiate the contract, $1,000. The inventory cost is a 20 percent carrying charge for an average of 6 months.
Company D is currently situated in Country U, where the production cost is $119. In addition to this, the following information is given:
| Criteria | Weight | Supplier from Country M | In-house | ||
| Rating | Score | Rating | Score | ||
| Quality and delivery | 16% | 3 | 4 | ||
| Price | 60% | 5 | 4 | ||
| Social responsibility | 7% | 2 | 5 | ||
| Currency risk | 17% | 3 | 5 | ||
| Total | 100% | ||||
Determine the total cost producing in Country M:
| Price of the door | ₹ 83.00 |
| Transportation cost | ₹ 3.30 |
| Pre-qualify supplier | ₹ 1.00 |
| Manage contract | ₹ 0.20 |
| Inventory carrying | ₹ 8.30 |
| Total | ₹ 95.80 |
Working note:
Price of the door, pre-quality supplier, and manager contract are given.
Compute transportation cost:
The transportation cost is $825 for one run, which holds 250 doors.
Compute inventory carrying cost:
The inventory cost is 20 percent carrying charge for an average of 6 months
Hence, the total cost of producing in Country M is $95.80 (refer to the table) per door, which is less than producing in Country U ($119).
b)
To determine: The total weighed scores for in-house production and Country M’s supplier.
Introduction:
Supplier selection is the process of evaluating the performance of each supplier and comparing it with in-house production to choose the capable supplier to support the output of the organization.
b)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
It is given that Company D is considering outsourcing its door production to Country M. The price quoted by the company of Country M is $83 for 5,000 units of standard door per year. The transportation cost is $825, which holds 250 doors. In order to send engineers to prequalify plant costs, $5,000 is required and to negotiate the contract, $1,000. The inventory cost is a 20 percent carrying charge for an average of 6 months.
Company D is currently situated in Country U, where the production cost is $119. In addition to this, the following information is given:
| Criteria | Weight | Supplier from Country M | In-house | ||
| Rating | Score | Rating | Score | ||
| Quality and delivery | 16% | 3 | 4 | ||
| Price | 60% | 5 | 4 | ||
| Social responsibility | 7% | 2 | 5 | ||
| Currency risk | 17% | 3 | 5 | ||
| Total | 100% | ||||
Determine the total weighted score:
| Criteria | Weight | Supplier from Country M | In-house | ||
| Rating | Score | Rating | Score | ||
| Quality and delivery | 16% | 3 | 0.48 | 4 | 0.64 |
| Price | 60% | 5 | 3 | 4 | 2.4 |
| Social responsibility | 7% | 2 | 0.14 | 5 | 0.35 |
| Currency risk | 17% | 3 | 0.51 | 5 | 0.85 |
| Total | 100% | 4.13 | 4.24 | ||
Computation of total weighted score:
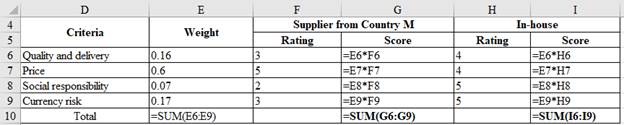
Hence, the weighed score is 4.13 for the supplier from Country M and 4.24 for in-house production.
c)
To determine: Whether the firm should outsource or not.
Introduction:
Supplier selection is the process of evaluating the performance of each supplier and comparing it with in-house production to choose a capable supplier to support the output of the organization.
c)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
It is given that Company D is considering outsourcing its door production to Country M. The rice quoted by the company of Country M is $83 for 5,000 units of standard door per year. The transportation cost is $825, which holds 250 doors. In order to send engineers to prequalify plant costs, $5,000 is required and to negotiate the contract, $1,000. The inventory cost is a 20 percent carrying charge for an average of 6 months.
Company D is currently situated in Country U, where the production cost is $119. In addition to this, the following information is given:
| Criteria | Weight | Supplier from Country M | In-house | ||
| Rating | Score | Rating | Score | ||
| Quality and delivery | 16% | 3 | 4 | ||
| Price | 60% | 5 | 4 | ||
| Social responsibility | 7% | 2 | 5 | ||
| Currency risk | 17% | 3 | 5 | ||
| Total | 100% | ||||
Determine whether the firm should outsource or not:
It is better to produce the door in-house rather than outsourcing. Even though the price is less for outsourcing, the other ratings favor in-house production. The weighted score is maximum for in-house production. Hence, there is no need to outsource the production.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT IN THE SUPPLY CHAIN: DECISIONS & CASES (Mcgraw-hill Series Operations and Decision Sciences)
- Asia Furnishing is a retailer of modular toilet products. Currently, the lead time for one of the products, the toilet door, is relatively high, at 5 weeks. The average demand for toilet doors is 200 per week. The standard deviation of demand during the lead time is 85 doors. The store plans to provide a service level of 99 per cent. (a) The store is looking for another supplier who can supply the doors in one week at the same price. Analyse how much safety stock can be reduced by moving to the new supplier without reducing the 99 per cent cycle-service level. (b) The store hired a new manager who insists on using a probability distribution for the lead time of supply, instead of a fixed lead time. Based on the historical data from the present supplier, she estimated that the standard deviation of lead time is 1 week. How will the amount of safety stock change after including this information? What should be the reorder level for the store? Do state all…arrow_forwardOp2. Define the parties involved directly and indirectly in the supply chain and their role in the smooth running of the business?arrow_forwardBradley Solutions and Alexander Limited are two well-established suppliers of inexpensive tools. Meanwhile, Weekend Projects is a national chain of retail outlets and wants to find a supplier for a particular tool set that promises to be a big seller. Expected annual sales are 100,000 units (D). Weekend's warehouses operate 50 weeks a year. Management collected data on the two suppliers, which are contained in the table below: Annual Freight Costs Shipping Quantity (Q) Annual Lead Annual Supplier 20,000 40,000 Price/unit(p) Administrative Holding Cost/Unit(H) (L)(wks) $1.5 $1.8 Time Cost Bradley $30,000 $20,000 Alexander $25,000 $22,000 $6 $5 $20,000 $30,000 4 What is the total annual cost for Weekend Projects if the company chooses Alexander as the supplier and determines the shipping quantity at 40,000 units per shipment? $608,600 O $609,600 $606,600 O $607,600arrow_forward
- please answer correctly in a detailed manner.arrow_forwardHorizon Cellular manufactures cell phones for exclusive use in its communication network. Management must select a circuit board supplier for a new phone soon to be introduced to the market. The annual requirements (D) are 40,000 units and Horizon's plant operates 250 days per year. The data for three suppliers are in the attached table. Annual Freight Costs Shipping Quantity (Q) Supplier 10,000 20,000 Price/Unit (p) Annual Holding Cost/Unit (H) Lead Time (L) (days) Annual Administrative Cost Material Costs Abbott $11,000 $8,500 $29 $5.80 4 $11,000 $232,000.00 Baker $12,000 $9,500 $31 $6.20 3 $12,000 $1,240,000 Carpenter $9,000 $7,000 $28 $5.60 8 $9,000 $1,120,000 Which supplier and shipping quantity will provide the lowest total cost for Horizon Cellular? Using the supplier [X] and a shipping quantity of [X] units is the lowest cost alternative, with annual total costs to Horizon Cellular of [X]. (Quantity and Annual Total Costs are integer…arrow_forwardBriefly describe the primary risk mitigation strategies based on the idea of flexibility that supply chain managers can use.arrow_forward
- One of your Taiwanese suppliers has bid on a new line of molded plastic parts that is currently being assembled at your plant. The supplier has bid $0.10 per part, given a forecast you provided of 200,000 parts in year 1; 300,000 in year 2; and 500,000 in year 3. Shipping and handling of parts from the supplier’s factory is estimated at $0.01 per unit. Additional inventory handling charges should amount to $0.005 per unit. Finally, administrative costs are estimated at $20 per month. Although your plant is able to continue producing the part, the plant would need to invest in another molding machine, which would cost $10,000. Direct materials can be purchased for $0.05 per unit. Direct labor is estimated at $0.03 per unit plus a 50 percent surcharge for benefits; indirect labor is estimated at $0.011 per unit plus 50 percent benefits. Up-front engineering and design costs will amount to $30,000. Finally, management has insisted that overhead be allocated if the parts are made in-house…arrow_forwardOne of your Taiwanese suppliers has bid on a new line of molded plastic parts that is currently being assembled at your plant. The supplier has bid $0.10 per part, given a forecast you provided of 300,000 parts in year 1; 500,000 in year 2; and 700,000 in year 3. Shipping and handling of parts from the supplier's factory is estimated at $0.03 per unit. Additional inventory handling charges should amount to $0.004 per unit. Finally, administrative costs are estimated at $20 per month. Although your plant is able to continue producing the part, the plant would need to invest in another molding machine, which would cost $10,000. Direct materials can be purchased for $0.04 per unit. Direct labor is estimated at $0.05 per unit for wages plus a 50 percent surcharge for benefits and, indirect labor is estimated at $0.013 per unit plus 50 percent benefits. Up-front engineering and design costs will amount to $40,000. Finally, management has insisted that overhead be allocated if the parts are…arrow_forwardAnswer the given question with a proper explanation and step-by-step solution. Monczka-Trent Shipping is the logistics vendor for Handfield Manufacturing Co. in Ohio. Handfield has daily shipments of a power-steering pump from its Ohio plant to an auto assembly line in Alabama. The value of the standard shipment is $255.930. Monczka-Trent has two options: (1) its standard 2-dav shipment or (2) a subcontractor who will team drive overnight with an effective deliverv of ' dav. The extra driver costs $190. Handfied's holding cost is 35% annuallv for this kind of inventorv. Part A: Alternative 2 is more economical, with a daily cost of $_____ . (Enter your response as a whole number.)arrow_forward
- Identify the SKU’s that management should spend time on and give reasons for your choice(s) in the diagram below. Explain your answer.arrow_forwardA company's distribution and warehouse expenses do NOT include which one of the following? a) The costs of processing, boxing, packaging, handling, and shipping orders to footwear retailers and -online buyers b)A standard import tariff of $4.00 per pair on any pairs imported from the company's foreign production facilities--tariffs are due and payable at the port of entry rather than when the pairs are sold c)Annual leasing and maintenance fees of $1 million for each of the company's four distribution centers; however, such expenses fall to 5 times the number of pairs sold when warehouse volume in any region is less than 200,000 pairs annually (should company managers decide to abandon selling footwear in a geographic region, leasing and maintenance costs will fall to $0 (resuming if/when sales begin again) d)The inventory costs of carrying unsold pairs over from the prior year ($0.50 per pair on required inventrory and $1 per pair on additional unsold pairs) e)Per pair freight…arrow_forwardThe Bennet Company purchases one of its essential raw materials from three suppliers. Bennet's current policy is to distribute purchases equally among the three suppliers. The owner's son, Benjamin Bennet, just graduated from a business college. He proposes that these suppliers be rated (high numbers mean a good performance) on six performance criteria weighted as shown in the table. A total score hurdle of 0.60 is proposed to screen suppliers. Purchasing policy would be revised to order raw materials from suppliers with performance scores greater than the total score hurdle, in proportion to their performance rating scores. Rating Supplier A Performance Criterion 1. Price 2. Quality 3. Delivery 4. Production facilities 5. Environmental protection 6. Financial position Weight Supplier B Supplier C 0.2 0.5 0.6 0.8 0.3 0.5 0.6 0.8 0.2 0.3 0.8 0.7 0.1 0.6 0.3 0.4 0.1 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.1 0.8 0.7 09 Use a preference matrix to calculate the total weighted score for each supplier. The weighted…arrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Operations ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781259667473Author:William J StevensonPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Operations ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781259667473Author:William J StevensonPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781259666100Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B ChasePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781259666100Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B ChasePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781478623069Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon OlsenPublisher:Waveland Press, Inc.
Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781478623069Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon OlsenPublisher:Waveland Press, Inc.





