
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781305970939
Author: Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 17, Problem 17.8P
Refer to Problem 17.7 and Figure 17.16. Suppose a footing (1.5 m × 1.5 m) is constructed at a depth of 1 m.
a. Estimate the design values for N60 and
b. What is the net allowable load that the footing can carry? The maximum allowable 17.7 settlement is 25 mm. Use Eqs. (16.56) and (16.61).
Refer to the boring log shown in Figure 17.16. Estimate the average drained friction angle,
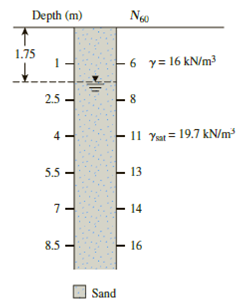
Figure 17.16
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A cut slope was excavated in sand. The slope is shown in following attachment .
To find the properties of the sand, representative samples were taken for the soil and tested in atriaxial apparatus. A consolidated drained triaxial test was conducted. The result is given below:Chamber pressure = 103 kN/m2Deviator stress at failure = 234.6 kN/m2We know the unit weight of the sand is 16 kN/m3.Use the ordinary method of slices (use 7 slices) and estimate the factor of safety against sliding forshown slip surface and comment on the calculated factor of safety.Please note that:1. The figure is not in scale. You may resketch it in scale and calculate the factor of safety2. The slip surface is circular and passes through the toe of the embankment
A 15 cm diameter borehole has been drilled through a fine sand deposit to a depth of 7 m. At this depth, the SPT,using a US safety hammer and a standard SPT sampler, gave Nfield = 23. Boring then continued to greater depths,encountering water table at a depth of 11 m. Compute N'60, Ø', and Dr at the test location, and use the data toestimate the denseness of the sand.
Ex1: A footing is uniformly loaded with q = 100 kN/m² as shown in the figure.
Compute the vertical stress increments under Points A, B, and C at z = 10 m.
By
13.5
Footing
12m
Use Vertical stress Increment
under corner of rectangular
footing
7
(Plane view)
6
Chapter 17 Solutions
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap Course List)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Plate load test performed on a uniform deposit of sand and the following observations were recorded. The size of the plate was 45cm x 45cm. Plot the Pressure-Settlement Curve and determine the safe load on a footing 2m x 2m if the settlement is not to exceed 40mm. Pressure (kPa) 2 4 8 12 |16 24 Settlement 3 6 | 20 | 40 |60 100 (mm)arrow_forwardQia: Compute the depth of drilling required for site investigation purposes. The type of foundation is circular foundation with diameter equal to 12 m, the depth of foundation is 2 m and the stress intensity is q. = 130 kN/m². Assume that average unit weight of soil equal to 18 kN/m². -You may need the following equation AP=q. (1-(1/(1+(B/2z)2)15)) in the solution. the cample disturbance; write thearrow_forwardA rectangular footing is constructed on saturated sand. This footing is placed under 1000 KN column load and 500 KN.m moment as shown in the image. Find the eccentricity in both directions and calculate the equivalent footing size. 3.0 M=500 KN.m 0.50 2.5 P1=1000 KN 0.50arrow_forward
- 1. Using the boring log shown below determine the ultimate bearing capacity of a rectangular footing having a width of 4 feet and a length of 8 feet. Standard Penetration Tests were conducted at 5 foot intervals. The depth of footing will be 3 feet below the ground surface. Project Name: Johnson Hall Location: Birmingham, Alabama Boring No.: В-2 Date: January 4, 2019 Surface Elev.: 357 ft Depth (ft) Moisture N No. qu (tsf) Description 4 inches of top soil (%) Comments y = 120 pcf Reddish Brown silty Clay 14 1.2 LL = 43 PI = 20 $ = 7° 10 Dark Reddish Brown silty Clay 15 22 1.3 15 15 21 1.6 GNE Boring Terminated at 15 feet Boring Checked after 24 hours N - Standard Penetration Test Number LL – Liquid Limit qu – Unconfined Compression Strength $ - Angle of Internal Friction PI – Plastic Index GNE – Groundwater Not Encountered 20arrow_forwardThe figure below shows a proposed site where an excavation will be made. The 12 ft layer of sand will be removed, so that the top of the 30 ft normally consolidated clay layer will be exposed (Assume that changes in GWT do not affect γt of clay). a. Assume that the water-table location remains the same during excavation. Compute the σ, σ′v, and u values at the middle of the clay layer before and after the excavation b. Assuming 1-D conditions, compute how much the clay layer will deform due to this excavation, in inches. Specify whether this is settlement or heavearrow_forwardA rectangular footing shown below, 10m x 15m, is uniformly loaded with q=100 kPa. Determine the change in vertical stress change 10m below point A, which lies outside the loadad area. You may use the finely-graduated chart used in the class discussions. A 5m 2- Loaded 10m Area 15m 5m 42 kPa O 100 kPa O 4.2 kPa O 21 kPaarrow_forward
- o T ☺ ť (Q4): For the soil profile shown in figure (2) find the difference in stress in (kPa) at point located at a depth (10m) under the center of the circular foundation when using the below formulas and when using the approximation method 1 Ao, = q [(R/2)* + 1] Dia4m q0.21 N/mm N.G.S Sand e0.8 G.-2.6 3m W.L e0.7 G-2.7 5m Clayey - Sand e045 G.-2.68 مر ر ل لأعلى لاستعراض الفلاتر إضافة شرح. .. mum < IIarrow_forwardFrom the given soil element, determine the major principal stress, in kPa, using the Pole Method. 150 kPa A 60 kPa 45⁰ 90 kPa 60 kPa Barrow_forwardExample: 1 • A square footing 2.5m x 2.5m is shown in the figure below. Determine the magnitude of the safe gross load (using MEYERHOF'S method and factor of safety of 3) that the footing can carry. 1m Bearing Capacity 1m y = 15kN/m³ c=0 = 35⁰ Yat=19kN/m²arrow_forward
- An excavation is rapidly made on site as depicted in the Figure below. The soil wedge above the critical slip surface is divided into thirteen slices. Based on the ordinary method of slices, calculate the ratio (R/S) between the Resisting Force (R) and the Driving Force (S) for slice #3, shortly after the excavation is completed. (Acceptable tolerance = 4%). The geometry of slice #3 and the soil properties are provided in the tables below. The height of water at the middle of the slice is hw = 3.0 m. Note that the total weight of the slice is equal to the weight of the saturated soil below the water table plus the weight of the moist soil above the water table. Hint: the weight of slice #3 is 495 kNarrow_forward8.10 The results of standard penetration tests in a granular soil deposit are as follows: Depth Standard penetration (m) number, N60 1.5 11 3.0 10 4.5 12 6.0 9 7.5 14 What will be the net allowable bearing capacity of a founda- tion planned to be 1.83 m x 1.83 m? Let D,: = 0.91 m and the allowable settlement = 25 mm, and use the relationship presented in Table 8.9.arrow_forwardThe column in the proposed rectangular footing depicted below has a size of 0.5x0.5 m. If the stress distribution is uniform, calculate the length of the footing under the design loads. M1-400 KN.m P1=1200 KN 6.50 M2 200 KN.m P1-600 KN 4arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305970939
Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Types of Foundation in building construction in detail - Civil Engineering Videos; Author: Civil Engineers;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7sl4KuM4UIE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Types of Foundation || Foundation Engineering; Author: Civil Engineering;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AFLuAKGhanw;License: Standard Youtube License