
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The product obtained from the reaction of cyclohexene with one equivalent of NBS in CCl4 in the presence of light and peroxides is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
NBS stand for N-bromosuccinimide. N-bromosuccinimide is used for the bromination of allylic carbon. When a compound having allylic hydrogen is treated with N-bromosuccinimide in presence of CCl4, allylic bromination takes place.
Answer to Problem 17.6P
The product obtained from the reaction of cyclohexene with one equivalent of NBS in CCl4 in the presence of light and peroxides is 3-bromocyclohexene.
Explanation of Solution
It is known that the N-bromosuccinimide is used for the bromination of allylic carbon. Therefore, the bromination will take place at allylic carbon of cyclohexene. The reaction of cyclohexene with one equivalent of NBS in CCl4 in the presence of light and peroxides is shown below.
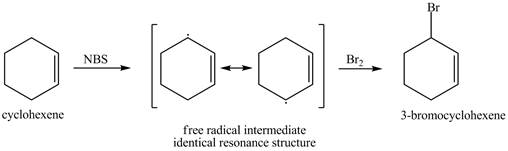
Figure 1
The product obtained from the reaction of cyclohexene with one equivalent of NBS in CCl4 in the presence of light and peroxides is 3-bromocyclohexene.
(b)
Interpretation:
The products obtained from the reaction of 3, 3-dimethylcyclohexene with one equivalent of NBS in CCl4 in the presence of light and peroxides are to be stated.
Concept introduction:
NBS stand for the N-bromosuccinimide. N-bromosuccinimide is used for the bromination of allylic carbon. When a compound having allylic hydrogen is treated with N-bromosuccinimide in presence of CCl4, allylic bromination takes place.
Answer to Problem 17.6P
The product obtained from the reaction of 3, 3-dimethylcyclohexene with one equivalent of NBS in CCl4 in the presence of light and peroxides is 6-bromo-3, 3-dimethylcyclohexene.
Explanation of Solution
It is known that the N-bromosuccinimide is used for the bromination of allylic carbon. Therefore, the bromination will take place at allylic carbon of 3, 3-dimethylcyclohexene. The reaction of 3, 3-dimethylcyclohexene with one equivalent of NBS in CCl4 in the presence of light and peroxides is shown below.
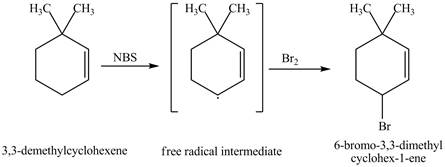
Figure 2
The product obtained from the reaction of 3, 3-dimethylcyclohexene with one equivalent of NBS in CCl4 in the presence of light and peroxides is 6-bromo-3, 3-dimethylcyclohexene.
(c)
Interpretation:
The products obtained from the reaction of trans-2-pentene with one equivalent of NBS in CCl4 in the presence of light and peroxides are to be stated.
Concept introduction:
NBS stand for the N-bromosuccinimide. N-bromosuccinimide is used for the bromination of allylic carbon. When a compound having allylic hydrogen is treated with N-bromosuccinimide in presence of CCl4, allylic bromination takes place.
(c)
Answer to Problem 17.6P
The products obtained from the reaction of trans-2-pentene with one equivalent of NBS in CCl4 in the presence of light and peroxides are 1-bromopent-2-ene and 4-bromopent-2-ene.
Explanation of Solution
It is known that the N-bromosuccinimide is used for the bromination of allylic carbon. Therefore, the bromination will take place at allylic carbon of trans-2-pentene. The reaction of trans-2-pentene with one equivalent of NBS in CCl4 in the presence of light and peroxides is shown below.
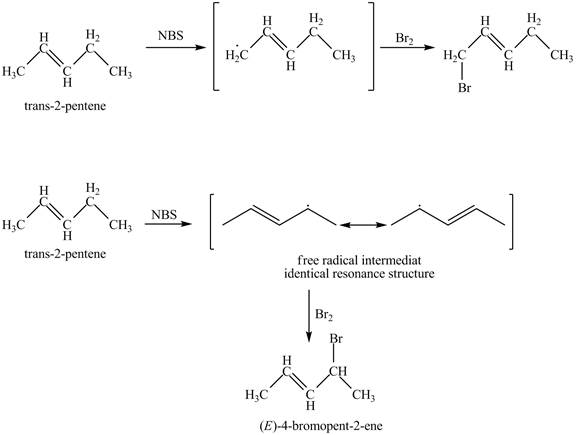
Figure 3
The products obtained from the reaction of trans-2-pentene with one equivalent of NBS in CCl4 in the presence of light and peroxides are 1-bromopent-2-ene and 4-bromopent-2-ene.
(d)
Interpretation:
The product obtained from the reaction of 4-tert-butyltoluene with one equivalent of NBS in CCl4 in the presence of light and peroxides is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
NBS stand for the N-bromosuccinimide. N-bromosuccinimide is used for the bromination of allylic carbon. When a compound having allylic hydrogen is treated with N-bromosuccinimide in presence of CCl4, allylic bromination takes place.
Answer to Problem 17.6P
The product obtained from the reaction of 4-tert-butyltoluene with one equivalent of NBS in CCl4 in the presence of light and peroxides is 1-tert-butyl-4-(bromomethyl)benzene.
Explanation of Solution
It is known that the N-bromosuccinimide is used for the bromination of allylic carbon. Therefore, the bromination will take place at allylic carbon of 4-tert-butyltoluene. The reaction of 4-tert-butyltoluene with one equivalent of NBS in CCl4 in the presence of light and peroxides is shown below.
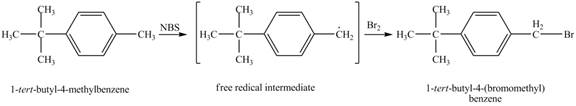
Figure 4
The product obtained from the reaction of 4-tert-butyltoluene with one equivalent of NBS in CCl4 in the presence of light and peroxides is 1-tert-butyl-4-(bromomethyl)benzene.
(e)
Interpretation:
The product obtained from the reaction of l-isopropyl-4-nitrobenzene with one equivalent of NBS in CCl4 in the presence of light and peroxides is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
NBS stand for the N-bromosuccinimide. N-bromosuccinimide is used for the bromination of allylic carbon. When a compound having allylic hydrogen is treated with N-bromosuccinimide in presence of CCl4, allylic bromination takes place.
Answer to Problem 17.6P
The product obtained from the reaction of l-isopropyl-4-nitrobenzene with one equivalent of NBS in CCl4 in the presence of light and peroxides is 1-(2-bromopropan-2-yl)-4-nitrobenzene.
Explanation of Solution
It is known that the N-bromosuccinimide is used for the bromination of allylic carbon. Therefore, the bromination will take place at allylic carbon of l-isopropyl-4-nitrobenzene. The reaction of l-isopropyl-4-nitrobenzene with one equivalent of NBS in CCl4 in the presence of light and peroxides is shown below.
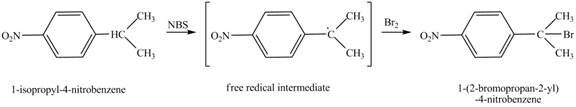
Figure 5
The product obtained from the reaction of l-isopropyl-4-nitrobenzene with one equivalent of NBS in CCl4 in the presence of light and peroxides is 1-(2-bromopropan-2-yl)-4-nitrobenzene.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- 3. You may want to read paragraph 1.5 in your textbook before answering this question. Give electron configuration (short-hand notation is fine) for: (5 points) 3+ a) Manganese atom and Mn³+ b) Se atom c) Cu atom and Cu+arrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't use hand ratingarrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
- Nonearrow_forwardHowever, why are intermolecular forces in metallic and ionic compounds not discussed as extensively? Additionally, what specific types of intermolecular attractions exist in metals and ionic compoundsarrow_forwardWhat is the preparation of 1 Liter of 0.1M NH4Cl buffer at pH 9.0 with solid NH4Cl and 0.1M NaOH. How would I calculate the math to describe this preparation? How would I use Henderson-Hasselbach equation?arrow_forward
- C Predict the major products of this organic reaction. Be sure you use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. : ☐ + x G C RCO₂H Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardFill in the blanks by selecting the appropriate term from below: For a process that is non-spontaneous and that favors products at equilibrium, we know that a) ΔrG∘ΔrG∘ _________, b) ΔunivSΔunivS _________, c) ΔsysSΔsysS _________, and d) ΔrH∘ΔrH∘ _________.arrow_forwardHighest occupied molecular orbital Lowest unoccupied molecular orbital Label all nodes and regions of highest and lowest electron density for both orbitals.arrow_forward
- Relative Intensity Part VI. consider the multi-step reaction below for compounds A, B, and C. These compounds were subjected to mass spectrometric analysis and the following spectra for A, B, and C was obtained. Draw the structure of B and C and match all three compounds to the correct spectra. Relative Intensity Relative Intensity 20 NaоH 0103 Br (B) H2504 → (c) (A) 100- MS-NU-0547 80 40 20 31 10 20 100- MS2016-05353CM 80 60 100 MS-NJ-09-3 80 60 40 20 45 J.L 80 S1 84 M+ absent राग 135 137 S2 62 164 166 11 S3 25 50 75 100 125 150 175 m/zarrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardDon't used hand raitingarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

