
Organic Chemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781305080485
Author: John E. McMurry
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Relative Intensity
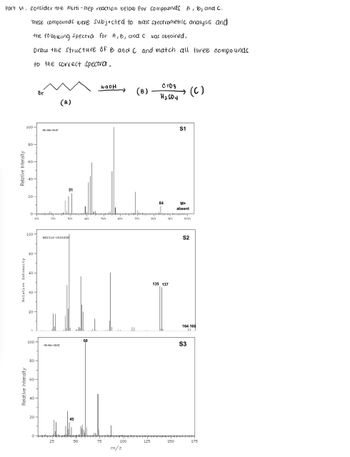
Part VI. consider the multi-step reaction below for compounds A, B, and C.
These compounds were subjected to mass spectrometric analysis and
the following spectra for A, B, and C was obtained.
Draw the structure of B and C and match all three compounds
to the correct spectra.
Relative Intensity
Relative Intensity
20
NaоH
0103
Br
(B)
H2504
→ (c)
(A)
100-
MS-NU-0547
80
40
20
31
10
20
100-
MS2016-05353CM
80
60
100
MS-NJ-09-3
80
60
40
20
45
J.L
80
S1
84
M+
absent
राग
135 137
S2
62
164 166
11
S3
25
50
75
100
125
150
175
m/z
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 8. Propose a mechanism for the light-initlated free-radical monofluorination of ethane: CH;CH, + F2 → CH;CH,F + HF (a) Show both initiation and propagation steps. (b) Calculate AH° for each step in the reaction and characterize each as exothermic or endothermic. (c) Calculate the overall value of AH° for this reaction (omit the initiation step).arrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwritten solution ...arrow_forwardDon't use hand raiting pleasearrow_forward
- The following initial rate data are for the reaction of tertiary butyl bromide with hydroxide ion at 55 oC:(CH3)3CBr + OH- (CH3)3COH + Br- Experiment [(CH3)3CBr]o, M [OH-]o, M Initial Rate, Ms-1 1 0.378 0.324 4.23×10-3 2 0.378 0.648 4.23×10-3 3 0.756 0.324 8.47×10-3 4 0.756 0.648 8.47×10-3 Complete the rate law for this reaction in the box below.Use the form k[A]m[B]n , where '1' is understood for m or n and concentrations taken to the zero power do not appear. Don't enter 1 for m or n Rate = From these data, the rate constant is _______s-1.arrow_forwardUse the Text Submission box to answer the following question. Consider the reaction shown below. For a particular concentration of sodium methoxide, the absorbance at 244 nm is measured using UV-vis spectroscopy. Over an initial period, the absorbance at 244 nm increases from 0.50 to 0.60. When the concentration of sodium methoxide is doubled, the absorbance at 244 nm measured after the same initial period is 0.70. What can you conclude about the mechanism of the reaction? NaOCH 3 Amax = 244 nmarrow_forwardGive detailed Solution with explanation neededarrow_forward
- Given the reaction coordinate diagram and the mechanism below: Rxn 1 Bxn 2 21 reaction coordinate > Rxn 1: AC + B У АВ + С Rxn 2: AB + D → AD+B Overall: -> Select all of the species that would be present at Point 2 under Rxn 1 BAD AC potential energy>arrow_forwardN-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) is a suspected carcinogen that can form via reactions between dimethylamine (DMA) and monochloramine (NH2Cl). The relevant elementary reactions and the corresponding rate constants are as shown below. Reaction Rate constant (M¹s¹) DMA + NH2Cl = DMCA + NH3 k =1.4×10-1, kr = 5.83×10-3 1.28×10-3 DMA + NH2Cl → UDMH UDMH + NH2Cl → NDMA -> 1.11×10-1 If the initial concentrations of DMA and NH2Cl are given, you should be able to predict the concentrations of all species at any given reaction time. Please write down the rate equations for DMA, NH2C1, DMCA, UDMH and NDMA.arrow_forwardCompound D, shown below, reacts with hydrogen bromide by electrophilic addition. A mixture of two organic compounds, E and F, is formed. CH3 CH₂CH₂ CH3 H compound D HBr Mixture of organic compounds E and F (i) Name the the two organic compounds E and F and show their condensed formula. (ii) Briefly explain the mechanism of the reaction between compound D and hydrogen bromide to form either compound E or compound F. (You can list/state the main steps) (iii) Which compound, E or F is the major product?arrow_forward
- 01:50 4G File Details 4CH003/UM1: Fundamentals of... Introduction NaBH4 OH C=0 H benzophenone diphenylmethanol Ketones are readily reduced to secondary alcohols by reaction with sodium borohydride. The aim of this experiment is to determine the time required to effect the complete conversion of the ketone, benzophenone to diphenylmethanol at room temperature. This investigation may be achieved by isolating and analyzing the reaction product after different reduction times. Infrared spectroscopy affords a convenient method of analysis; by comparing the IR spectrum of the crude reaction product at different time intervals one would expect to see the intensity of the hydroxyl absorption peak increase relative to that of the original carbonyl peak. From this you can deduce the optimum time for the reduction process at room temperature. Procedure Note the "reduction time" that the demonstrator assigns to your group. Different groups will be assigned different times, eithert = 2.5 minutes,…arrow_forwardwrite mechanism step by step for the reaction ?arrow_forward5. Use curved arrows to depict the mechanism of the following reaction: :Ö O: 4. 2 NH₂ H-O NH₂ :0 NH, ĐH NH₂ 0: H - C XX - H HI + ✪ NH₂ H H + H NH₂ -ÖH ÖH -H₂O --H₂O c H H NH₂ — NH₂ 2:— H-N: — H H-OⒸ H H O-H -ÖH H H-OⒸ H 04 H H Harrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning


Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning