
A prototype rotating bicycle rack is designed to save space at a train station. The combined weight of platform BD and the bicycle is 40 lb and is centered at 1 ft above the midpoint of the platform. The motor at A causes the support beam AB to have an angular velocity of 10 rpm and zero angular acceleration at θ = 60°. At this instant, determine the vertical components of the forces exerted on platform BD by the pins at B and D.
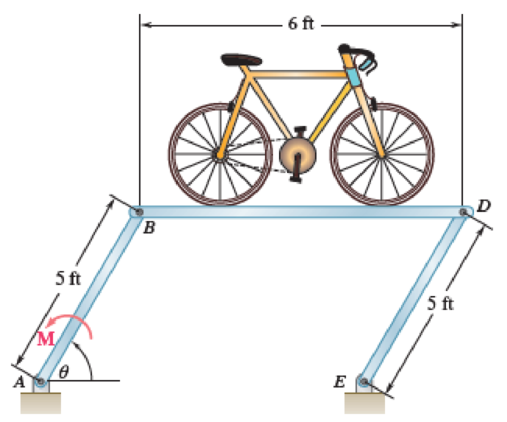
Fig. P16.18
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 16 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
BASIC BIOMECHANICS
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Modern Database Management
- please find Ix and Iy in mm4arrow_forwardHomework#7arrow_forwardComputing Angles of Rotation and Angles of Tilt In each of the following problems, the axis of a hole is shown in a rectangular solid. In order to position the hole axis for drilling, the angle of rotation and the angle of tilt must be determined. Compute angles to the nearer minute in triangles with customary unit sides. Compute angles to the nearer hundredth degree in triangles with metric unit sides. a. Compute the angle of rotation, R. b. Compute the angle of tilt, T. 7. Given: H= 2.600 in. L = 2.400 in. a. W= 1.900 in. 8. Given: H= 55.00 mm b. Use this figure for #7 and #8. AXIS OF HOLE L 48.00 mm W= 30.00 mm H a. b. 9. Given: H = 4.750 in. L = 4.000 in. W= 3.750 in. a. 10. Given: H=42.00 mm b. L37.00 mm W = 32.00 mm a. b. 11. Given: H = 0.970 in. L = 0.860 in. W= 0.750 in. a. 12. Given: H= 22.00 mm L 18.00 mm = W = 15.00 mm a. b. Use this figure for #9 and #10. ZR AXIS OF HOLE Use this figure for #11 and #12. H b. L AXIS OF HOLE Tarrow_forward
- This is a tilt and rotation question. Here are notes attached for reference. I prefer handwritten solutions. ONLY UPLOAD A SOLUTION IF YOU ARE SURE ABOUT THE ANSWER PLEASE. I prefer handwritten solutions.arrow_forwardConsider a constant area semi-infinite fin of a circular cross section of radius r. and thermal conductivity k. The base is maintained at T. and the surface of the fin exchanges heat by convection to an ambient fluid at T with a heat transfer coefficient h. It is desired to increase the heat transfer from the fin. The following suggestions are made: (i) doubling k, (ii) doubling ro, (iii) doubling h. Which suggestion will bring about the largest increase in heat transfer? To x h, T C A h, Tarrow_forwardA 20 cm long 304 stainless steel bar is initially at 18°C. One end of the bar is suddenly maintained at 100°C. Assuming that your finger can tolerate a 60°C temperature, what is the longest time you are willing to wait before you touch the other end? Be on the safe side and select a conservative model. h,T oil bath glass ballarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





