
A chemical plant makes three major products on a weekly basis. Each of these products requires a certain quantity of raw chemical and different production times, and yields different profits. Thepertinentin formation is in Table P16.5. Note that there is sufficient warehouse space at the plant to store a total of 450 kg/week.
TABLE P16.5
| Product 1 | Product 2 | Product 3 | Resource Availability | |
| Raw chemical |
|
|
13kg/kg |
|
| Production time |
|
|
0.2hr/kg |
|
| Product |
|
|
|
(a) Set up a linear programming problem to maximize profit.
(b) Solve the linear programming problem with the simplex method.
(c) Solve the problem with a software package.
(d) Evaluate which of the following options will raise profits the most: increasing raw chemical, production time, or storage.
(a)
A linear programming problem for a chemical plant that makes three products on a weekly basis. The data is given below:
Answer to Problem 5P
Solution:
The Linear Programming formulation is given as:
Subject to Constraints:
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
Following data is given for a chemical plant that makes three products on a weekly basis:
Also, the warehouse can store a total of
Let
The Linear Programming Model can be set up as follows:
As Profit is to be maximized, the objective function is
The constraints are:
The raw chemical constraint is
As the total production time must be equal to or less than
The storage available is
Also, the weights can never be negative. Thus, positivity constraint is
Hence, the Linear Programming formulation is given as:
Subject to Constraints:
(b)
To calculate: The solution of the linear programming problem given below:
Subject to Constraints:
Answer to Problem 5P
Solution:
The values of variables are
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
A linear programming problem,
Subject to Constraints:
Calculation:
Consider the provided linear programming problem,
Subject to Constraints:
First convert the above problem to standard form by adding slack variables.
As the constraints are subjected to less than condition, non- negative slack variables are added to reach equality.
Let the slack variables be
Thus, the linear programming model would be:
The above linear programming models consist of three non-basic variables
Now the apply the Simplex method and solve the above problem as:
The negative minimum, P is
The minimum ratio is 230.7692 and it corresponds to basis variable S1. So, the leaving variable is S1.
Therefore, the pivot element is 13.
The negative minimum, P is
The minimum ratio is 356.25 and it corresponds to basis variable S3. So, the leaving variable is S3.
Therefore, the pivot element is 0.61539.
Since
Hence, the values of variables are
(c)
To calculate: The solution of the linear programming problem given below using software package:
Subject to Constraints:
Answer to Problem 5P
Solution:
The values of variables are
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
A linear programming problem,
Subject to Constraints:
Calculation:
Consider the provided linear programming problem,
Subject to Constraints:
The solution can be obtained using Excel.
Set up the values and use the formula as shown below:
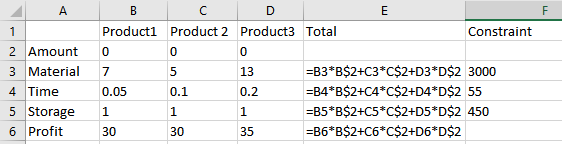
The values obtained are:
Now press Solver under Data tab and enter the constraints and objective as shown below:
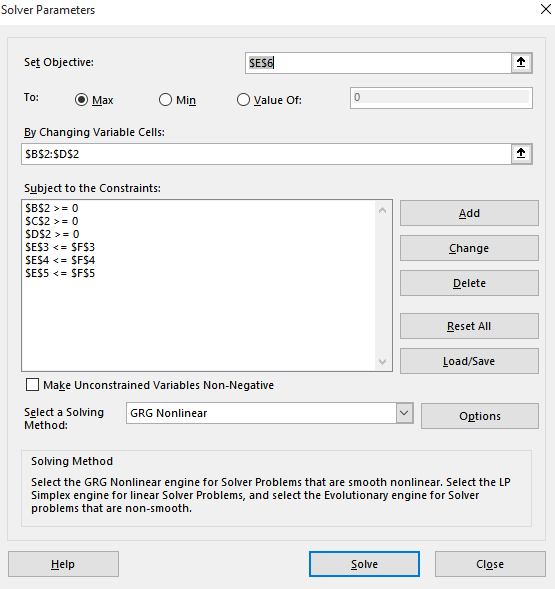
The resulting solution is:
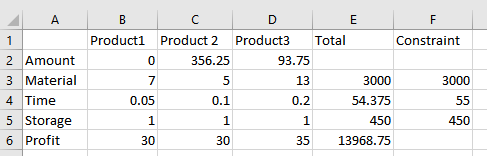
Hence, the values of variables are
(d)
The factor among increasing raw material, production time or storage that will rise profits the most for the linear programming problem given below:
Subject to Constraints:
Answer to Problem 5P
Solution:
Increasing storage will result in the most profits.
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
A linear programming problem,
Subject to Constraints:
Calculation:
Open the Excel sheet of part (c), then Press Solver under Data and select Simplex LP as a solving method as shown below:
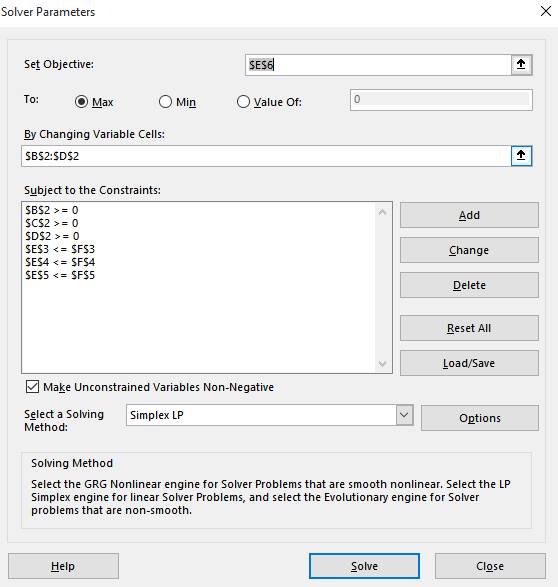
Press solve then select Sensitivity in reports as shown below:
The sensitivity report obtained is:
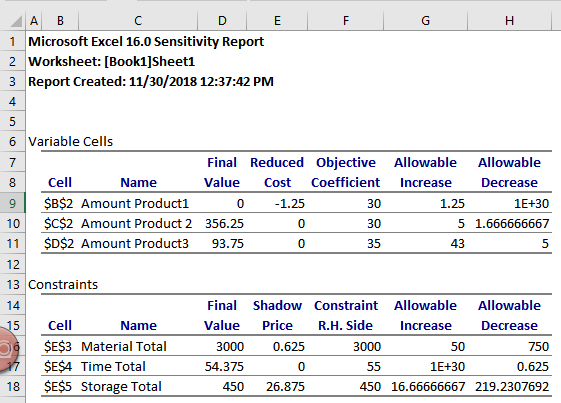
The high shadow price for storage implies that increasing storage will result in the most profits.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
EBK NUMERICAL METHODS FOR ENGINEERS
- Q5. An established company has decided to add a new product to its line. It will buy the product from a manufacturing concern, package it, and sell it to a number of distributors that have been selected on a geographical basis. Market research has already indicated the volume expected and the size of sales force required. The steps shown in the following table are to be planned. Activity Description Predecessor Activity Duration (days) A B C D E F LL C A B C A E E E H,L K 14 4 2 1 2 3 2 4 3 12 4 2 2 G H 1 J K L M H,L (a) Draw an arrow diagram for the project. (b) Indicate the criticla path. (c) For each non-critical activity, find the total and free float. D,F,G Jarrow_forwardProblem 2.3 The following problem can be solved using the generalized conservation and accounting principle to determine if a recycling plant is profitable annually. Operating information: ● ● The plant operates 9 hours each day, 5 days each week, and 48 weeks each year. The plant purchases 30 tons of aluminum (at a rate of $0.02/lb) during each operating week. The plant has 5 full-time employees who are paid $18 per hour. All employees work during all of the plant's operating hours. The plant produces 7 bales of recycled aluminum per day, which it sells for $950 per bale. [Note: 1 ton = 2000 lb] Answer the following questions: (a) Identify the system (in words). (b) Identify the "stuff" you are accounting for in this analysis. (c) In order to determine the plant's annual profitability, would one be interested in studying the instantaneous rate of change in "stuff" (i.e. rate form) or the total change in "stuff" over an interval (i.e. finite-time form)? (d) On a system diagram (hint:…arrow_forwardExample 3: A plant produces 1200 liters of biogas daily. Calculate the size of gasholder and gasholder capacity for a biogas plant that feeds a constant load during the following periods daily (Assume uniform consumption of gas) From 06:00 to 08:00 hours (2hrs) From 12:00 14:00 hours (2hrs) - From 19:00-21:00 hours (2hrs) -arrow_forward
- Problem 2.3 The following problem can be solved using the generalized conservation and accounting principle to determine if a recycling plant is profitable annually. Operating information: ● ● The plant operates 9 hours each day, 5 days each week, and 48 weeks each year. The plant purchases 30 tons of aluminum (at a rate of $0.02/lb) during each operating week. The plant has 5 full-time employees who are paid $18 per hour. All employees work during all of the plant's operating hours. The plant produces 7 bales of recycled aluminum per day, which it sells for $950 per bale. [Note: 1 ton = 2000 lb] Answer the following questions: (c) In order to determine the plant's annual profitability, would one be interested in studying the instantaneous rate of change in "stuff" (i.e. rate form) or the total change in "stuff" over an interval (i.e. finite-time form)? (d) On a system diagram (hint: think dashed lines!), use labeled arrows to identify each individual input and output of "stuff". (e)…arrow_forward3. The U.S. auto industry produces approximately 6 million vehicles a year, each containing roughly 1.5 metric tons of fabricated metal. Consider a future wind-turbine industry having half of the auto industry's mass throughout of wind turbine units. Each unit has a specific weight of 75 kg/kW rated (nacelle components plus tubular tower only). a. At a wind-turbine capacity factor of 0.3, how long would it take to replicate the 2008 U.S.-installed average electric power rating of 1035 GW? b. Discuss (5-10 sentences) the relevant factors that would determine whether a wind machine industry of this size could be successfully operated sustainably over periods on the order of several centuries.arrow_forwardA family wishes to buy a 2020 Toyota Camry. The two options the consider are (a) a standard automobile with and SI engine that gets 34 mpg and costs $18,000; and (b) a hybrid automobile that gets 52 mpg and costs $32,000. On average, the family drives 16,000 miles each year ad gasoline costs $1.65 per gallon. Calculate: (Show your clear solution) The amount of gasoline each vehicle would use each year. Gasoline cost savings of hybrid over standard. Time in months it would take to make up the difference in vehicle cost with fuel savings.arrow_forward
- A plant produces 300 units of an equipment a month of P3,600 each. A unit sells for P4,800.00. The company has 10,000 shares of stock at P200 par value whose annual dividend is 20%. The fixed cost of production is P120,000 a month. (a) What is the break-even point? (b) What is the"unhealthy point"? (c) What is the profit or loss if production is 60% Of capacity? Ans.(a) 100 units/month, (b) 128 units/month, (c) P62,667 per montharrow_forward15. 10 kg of water is heated in an insulated tank by a churning process from 300 K to 350 K. Determine the loss in availability for the process if the surrounding temperature is 300 K. [Ans. 1968 kJ)arrow_forwardA family wishes to buy a 2020 Toyota Camry. The two options the consider are (a) a standard automobile with and SI engine that gets 34 mpg and costs $18,000; and (b) a hybrid automobile that gets 52 mpg and costs $32,000. On average, the family drives 16,000 miles each year ad gasoline costs $1.65 per gallon. Calculate: (Show your complete solution) The amount of gasoline each vehicle would use each year. Gasoline cost savings of hybrid over standard. Time in months it would take to make up the difference in vehicle cost with fuel savings.arrow_forward
- C O O n t e n t Explore some of the projects described by William McDonough (Liuzhou City, Ford River Rouge Truck Plant green roof, Gap San Bruno office, etc). • What became of them? Consider the gap between ambition and reality when it comes to sustainability and sustainable energy generation. Discuss how this gap relates to the perspectives given in the other TED talks as ● well. Do you agree with the presenters' perspectives on the future? • What sustainability factors are they considering (or not) in their assessment of the future?arrow_forwardSalvage value is the life. value of asset when sold after the end of useful (a) Estimated (b) Fixed (c) Variable (d) Depreciationarrow_forwardi) Describe what is threshold problems? ii) Figure 1 illustrates a composite curve for a set of process stream data. With the aid of a diagram, explain what will happen to the utility consumptions if AT min is further reduced until AT min < AT threshold: 200 180 Qn 160 140 120 100 AT threshold 80 60 40 20 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 H (KW) Figure 1 TEMPERATURE (°C)arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





