
Design the optimal cylindrical container (Fig. P16.1) that is open at one end and has walls of negligible thickness. The container is to hold
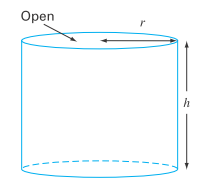
FIGURE P16.1
The design of the optimal cylindrical container to hold
Answer to Problem 1P
Solution: The optimal design of the optimal cylinder has radius and height same and its values is
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The volume of the cylinder is
Formula used:
Write the expression of surface area of a cylindrical container.
Here,
Write the expression of volume of a cylindrical container.
Calculation:
Recall the expression of volume of a cylindrical container.
The container holds
Rearrange the expression of volume for height
Recall the expression of surface area of a cylindrical container.
Substitute
To find the conditions to minimize the area solve
Solve further,
Volume of the container remains constant therefore, substitute the value of
Therefore, the value of height and radius are same to obtain to minimize the surface areas.
Substitute
Therefore, the value of the radius and the height to obtain the maximum surface area is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
EBK NUMERICAL METHODS FOR ENGINEERS
- PROBLEM # 3 1. A solid block is 70 cm wide, 80 cm long and 20 cm tall, and has a mass of 6700 gm. Estimate the solid block volume (in m). 2. Estimate the density of the block in kg/ m. 3. If the block were floating in fresh water (with the 70 cm by 80 cm face down), the block would be submerged under water by what length? 4. How much extra mass can the block support without sinking?arrow_forwardQV: a hydraulic press is used to compact powdered samples. The device is made of two interconnected cylindrical chambers filled with oil if density psubscripto anc closed by two pistons. The small chamber on the right has diameter d and the large chamber on the left has diameter 5d. A lever is attached to the piston pushing down on the fluid in the small cylinder. The horizontal lever is hinged on the left, at distance L from the small piston, and a force of magnitude Fsubscript0 is applied vertically down at distance 2L from the hinge (Fig.5). You may assume that the lever and pistons have negligible mass. a. Determine the magnitude of the force Fin that the small piston exerts on the fluid in the small cylinder. Hint: you may consider that the lever is at rest in the horizontal position. b. Determine the pressure change applied to the fluid by the small piston. c. Determine the magnitude Fout of the force that the fluid applies to the large piston.arrow_forwardA lead sphere has volume 6.0 cm3 when it is resting on a lab table, where the pressure applied to the sphere is atmospheric pressure. The sphere is then placed in the fluid of a hydraulic press. What increase in the pressure above atmospheric pressure produces a 0.50% decrease in the volume of the sphere?arrow_forward
- As shown in the figures below, and the Video, a rectangular barge floats in a stable configuration provided the distance between the center of gravity, CG, of the object (boat and load) and the center of buoyancy, C, is less than a certain amount, H. If this distance is greater than H, the boat will tip over. Assume H is a function of the boat's width, b, length, I, and draft, h. The results of a set of experiments with a model barge with a width of 1.8 m are shown in the table. Plot these data in dimensionless form. Determine (a) D and (b) E in a power-law equation relating the dimensionless parameters: H/b = D(h/b). 1, m 2.0 4.0 2.0 4.0 2.0 4.0 (a) D= h, m 0.10 0.10 0.20 H, m 1.82 0.20 0.912 1.82 i 0.912 0.35 0.521 0.35 0.521 0.5668 (b) E= i 0.9968327209213169 CG d h Unstable 1. H CG Overturning couple CGarrow_forwardSolve the following problems. Show your solution and create a simple illustration of the problem. 3. A dam (h= 25 m) is used as a reservoir in order for us to have a constant supply of water. Shown here is a cross section of a dam, what pressure should the bottom part of the dam resist to prevent it from overturning? The height of the water reservoir is at 14 m. Water is at standard conditions.arrow_forward5.4 A cylindrical float has a 10-in diameter and is 12 in long. What should be the specific weight of the float material if it is to have 9/10 of its volume below the surface of a fluid with a specific gravity of 1.10? m in diameter and 1.2 m 1:J lisarrow_forward
- 1. SOLVE BELOW PROBLEMS CORRECTLY BY SHOWING YOUR STEP BY STEP COMPUTATION. THEN PUT YOUR FINAL ANSWER INA BOX. ON YOUR COMPUTATION SET YOUR CALCULATORS TO ROUND OFF YOUR RESULTS TO 3 DECIMAL PLACES. IF YOU ARE COMPUTING FOR NUMBERS THAT ARE LESS THAN ONE, ROUND IT OFF TO FOUR DECIMAL PLACES 1. A 2.5 m tall steel cylinder has a cross sectional area of 1.5 m2. At the bottom with a height of 0.5 m is liauid water on top of which is a 1 m high layer of gasoline. The gasoline surface is exposed to atmospheric air at kPa. What is the highest pressure in the water in kilopascals? Note: Substitute your corresponding assigned number to the blank 22 AIR GASOLINE WATER 0.5 marrow_forward4. Assuming standard condition, what is the altitude in ft where the density is 0.001845 slug/ft3?arrow_forwardProblem: A 1-m diameter and 1.6-m height cylindrical drum is filled with a fluid whose density is 850 kgm/m3. Determine the following: Volume of the fluid in ft3. Mass of the fluid in lbm. Specific volume in ft3/lbm. Specific weight in lbf/ft3. Problem: 6.5 psig to MPaa 330 mm Hggauge to mm Hgabs and kPag Problem: Compute the height in feet of a high building if the pressure at the ground floor is 30 in Hg and at the top of the building is 28.5 in Hg. Assume that the density of air is 0.075 lbm/ft3.arrow_forward
- 1. What is the pressure acting on the water at a depth of 1m at 4°C? What is the pressure acting on the water at a depth of 3ft at 32°F? 2. 3. An Aquarium has a Volume of 75000 in 3 , width of 60 inch, length of 50 inch and with a density of 1030 Kg/m3 . Find the hydrostatic Pressure. A water tank for a large industrial space is planned to be placed underground. In designing a level indicator, pressure will be measured at two depths and two locations shown in schematic below. Determine the pressure below at these points. The Pressure measurement devices is 2 meter long. 4. |1.5m 2.5m 6marrow_forwardErample 2.17: A ship displacing 1000 tons has the horizontal cross section at water line shown in Fig. 2.41. Its center of buoyancy is 6.0 ft below water surface, and its center of gravity is 1.0 ft below water surfacc. metacentric height for rolling (about y-y-axis) and for pitching (about r--axis). Determine its 30 ft 20 ft +80 ft- 20 ftarrow_forwardSolve completely and support your solution with diagrams or figures. The storage tank of a water tower is nearly spherical in shape with a radius of 30 ft. If the density of the water is 62.4 lb/ft3, what is the mass of water stored in the tower, in lb, when the tank is full? What is the weight, in lbf, of the water if the local acceleration of gravity is 32.1 ft/s2?arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





