
Biology 2e
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9781947172517
Author: Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher: OpenStax
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 16, Problem 2VCQ
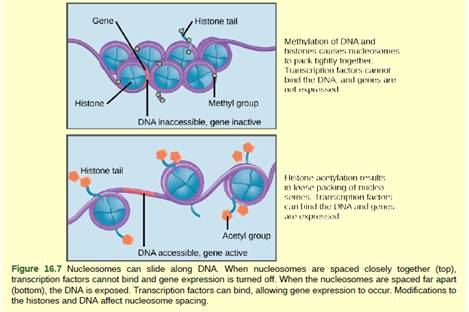
Figure 16.7 In females, one of the two X chromosomes is inactivated during embryonic development because of epigenetic changes to the chromatin. What impact do you think these changes would have on nucleosome packing?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Find the dental formula and enter it in the following format:
I3/3 C1/1 P4/4 M2/3 = 42 (this is not the correct number, just the correct format)
Please be aware: the upper jaw is intact (all teeth are present). The bottom jaw/mandible is not intact. The front teeth should include 6 total rectangular teeth (3 on each side) and 2 total large triangular teeth (1 on each side).
Answer i
Answer
Chapter 16 Solutions
Biology 2e
Ch. 16 - Figure 16.5 In E. coli, the tip operon is on by...Ch. 16 - Figure 16.7 In females, one of the two X...Ch. 16 - Figure 16.13 An increase in phosphorylation levels...Ch. 16 - Control of gene expression in eukaryotic cells...Ch. 16 - Post-translational control refers to: regulation...Ch. 16 - How does the regulation of gene expression support...Ch. 16 - If glucose is absent, but so is lactose, the lac...Ch. 16 - Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus. Therefore, the...Ch. 16 - The a/a operon is an inducible operon that...Ch. 16 - What are epigenetic modifications? the addition of...
Ch. 16 - Which of the following are true of epigenetic...Ch. 16 - The binding of _____ is required for transcription...Ch. 16 - What will result from the binding of a...Ch. 16 - A scientist compares the promoter regions of two...Ch. 16 - Which of the following are involved in post...Ch. 16 - Binding of an RNA binding protein will the...Ch. 16 - An unprocessed pre-mRNA has the following...Ch. 16 - IS. Alternative splicing has been estimated to...Ch. 16 - Post-translational modifications of proteins can...Ch. 16 - A scientist mutates elF-2 to eliminate its GTP...Ch. 16 - Cancer causing genes are called transformation...Ch. 16 - Targeted therapies are used in patients with a set...Ch. 16 - Name two differences between prokaryotic and...Ch. 16 - Describe how controlling gene expression will...Ch. 16 - Describe how transcription in prokaryotic cells...Ch. 16 - What is the difference between a repressible and...Ch. 16 - In cancer cells, alteration to epigenetic...Ch. 16 - A scientific study demonstrated that rat mothering...Ch. 16 - Some autoimmune diseases show a positive...Ch. 16 - A mutation within the promoter region can alter...Ch. 16 - What could happen if a cell had too much of an...Ch. 16 - A scientist identifies a potential transcription...Ch. 16 - Describe how RBPs can prevent miRNAs from...Ch. 16 - How can external stimuli alter...Ch. 16 - Protein modification can alter gene expression in...Ch. 16 - Alternative forms of a protein can be beneficial...Ch. 16 - Changes in epigenetic modifications alter the...Ch. 16 - A scientist discovers a virus encoding a Protein X...Ch. 16 - New drugs are being developed that decrease DNA...Ch. 16 - How can understanding the gene expression pattern...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
1. ___ Mitosis 2. ___ Meiosis 3. __ Homologous chromosomes 4. __ Crossing over 5. __ Cytokinesis A. Cytoplasmic...
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Why is an endospore called a resting structure? Of what advantage is an endospore to a bacterial cell?
Microbiology: An Introduction
How do you think a cell performing cellular respiration rids itself of the resulting CO2?
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
For the generic equilibrium HA(aq) ⇌ H + (aq) + A- (aq), which of these statements is true?
The equilibrium con...
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Identify each of the following characteristics as belonging to cervical, thoracic, or lumbar vertebrae; the sac...
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
1. If an object is not moving, does that mean that there are no forces acting on it? Explain.
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- calculate the questions showing the solution including variables,unit and equations all the questiosn below using the data a) B1, b) B2, c) hybrid rate constant (1) d) hybrid rate constant (2) e) t1/2,dist f) t1/2,elim g) k10 h) k12 i) k21 j) initial concentration (C0) k) central compartment volume (V1) l) steady-state volume (Vss) m) clearance (CL) AUC (0→10 min) using trapezoidal rule n) AUC (20→30 min) using trapezoidal rule o) AUCtail (AUC360→∞) p) total AUC (using short cut method) q) volume from AUC (VAUC)arrow_forwardQUESTION 8 For the following pedigree, assume that the mode of inheritance is X-linked recessive, and that the trait has full penetrance and expressivity and occurs at a very low frequency in the hum population. Using XA for the dominant allele and Xa for the recessive allele, assign genotypes for the following individuals (if it is not possible to figure out the second allele of a genotype, that with an underscore): 2 m 1 2 1 2 4 5 6 7 8 9 IV 1 2 3 5 6 7 8 CO 9 10 12 13 V 1, 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 a. Il-1: b. 11-2: c. III-3: d. III-4: e. If individuals IV-11 and IV-12 have another child, what is the probability that they will have a boy with the disorder?arrow_forwardAnswerrarrow_forward
- please,show workings ahd solutions calculate the questions showing the solution including variables,unit and equations all the questiosn below using the data a) B1, b) B2, c) hybrid rate constant (1) d) hybrid rate constant (2) e) t1/2,dist f) t1/2,elim g) k10 h) k12 i) k21 j) initial concentration (C0) k) central compartment volume (V1) l) steady-state volume (Vss) m) clearance (CL) AUC (0→10 min) using trapezoidal rule n) AUC (20→30 min) using trapezoidal rule o) AUCtail (AUC360→∞) p) total AUC (using short cut method) q) volume from AUC (VAUC)arrow_forwardQuestion about consensus and the relationship to transcriptional activityarrow_forwardQuestion about archaea and eukaryotic general transcription homologsarrow_forward
- Question about general transcription factors and their relationship to polymerasesarrow_forwardIdentify the indicated structure?arrow_forwardrewrite: Problem 1 (Mental Health): The survivor victim is dealing with acute stress and symptoms of a post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) due to their traumatic experience during the January 2025 wildfire. Goal 1: To alleviate the client's overall level, frequency, and intensity of anxiety and PTSD symptoms so that daily functioning remains unimpaired. Objective 1: The client will learn and regularly use at least two anxieties management techniques to reduce anxiety symptoms to less than three episodes per week. Intervention 1: The therapist will provide psychoeducation about anxiety and PTSD, including their symptoms and triggers. The therapist will also teach and assist the client in adopting relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises and progressive muscle relaxation, to better manage anxiety and lessen PTSD symptoms.arrow_forward
- O Macmillan Learning You have 0.100 M solutions of acetic acid (pKa = 4.76) and sodium acetate. If you wanted to prepare 1.00 L of 0.100 M acetate buffer of pH 4.00, how many milliliters of acetic acid and sodium acetate would you add? acetic acid: mL sodium acetate: mLarrow_forwardHow does the cost of food affect the nutritional choices people make?arrow_forwardBiopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics:Two-Compartment Model Zero-Order Absorption Questions SHOW ALL WORK, including equation used, variables used and each step to your solution, report your regression lines and axes names (with units if appropriate) :Calculate a-q a) B1, b) B2, c) hybrid rate constant (1) d) hybrid rate constant (2) e) t1/2,dist f) t1/2,elim g) k10 h) k12 i) k21 j) initial concentration (C0) k) central compartment volume (V1) l) steady-state volume (Vss) m) clearance (CL) AUC (0→10 min) using trapezoidal rule n) AUC (20→30 min) using trapezoidal rule o) AUCtail (AUC360→∞) p) total AUC (using short cut method) q) volume from AUC (VAUC)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305112100
Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...
Biology
ISBN:9781305117396
Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning
QCE Biology: Introduction to Gene Expression; Author: Atomi;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a7hydUtCIJk;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY