
(a)
Interpretation:
The compounds mesitylene, toluene, and
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.44AP
The compounds mesitylene, toluene, and
Explanation of Solution
The structure of mesitylene, toluene, and
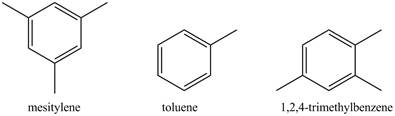
Figure 1
The reaction of any
The methyl group is electron-donating group. It activates the phenyl ring. The toluene has only one methyl group attached to it. Therefore, it will be least reactive towards
The order of reactivity toward nitration reaction is shown below.
The increasing order of reactivity towards toward
(b)
Interpretation:
The compounds chlorobenzene, benzene, and nitrobenzene are to be arranged in increasing order of increasing reactivity toward
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.44AP
The compounds chlorobenzene, benzene, and nitrobenzene are arranged in increasing order of increasing reactivity toward
Explanation of Solution
The structure of chlorobenzene, benzene, and nitrobenzene are shown below.
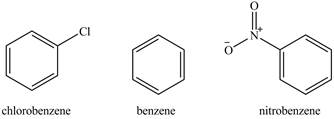
Figure 2
The reaction of any aromatic compound with
The nitro and chloro groups are electron-withdrawing groups. Therefore, the reactivity of the chlorobenzene and nitrobenzene will be less than that of benzene. The nitro group is stronger deactivating group than chloro group. Therefore, the order of reactivity toward nitration reaction is shown below.
The increasing order of reactivity towards toward
(c)
Interpretation:
The compounds
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.44AP
The compounds
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
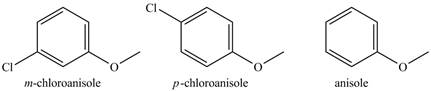
Figure 3
The reaction of any aromatic compound with
The methoxy group and chloro groups are ortho and para directing groups. The methoxy group is electron releasing group and chloro group is electron-withdrawing group.
Therefore, the reactivity of anisole will be highest among the rest of the compound toward
The order of reactivity toward nitration reaction is shown below.
The increasing order of reactivity towards toward
(d)
Interpretation:
The compounds acetophenone,
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.44AP
The compounds acetophenone,
Explanation of Solution
The structure of acetophenone,
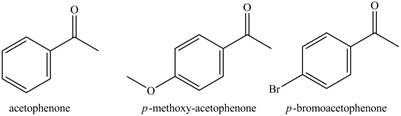
Figure 4
The reaction of any aromatic compound with
The acetyl group and bromo group is electron-withdrawing groups and methoxy group is electron releasing group. Acetophenone has a ring activating group attached on it. Therefore, it is most reactive toward nitration reaction among the rest of the compound. The compound
The increasing order of reactivity towards toward
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Organic Chemistry Study Guide and Solutions
- Explain the following statements. You must use chemical equations to justify your explanation. (ii) (I) Phenol is more acidic than cyclohexanol.arrow_forward(a) One test for the presence of an alkene is to add a smallamount of bromine, which is a red-brown liquid, and lookfor the disappearance of the red-brown color. This test doesnot work for detecting the presence of an aromatic hydrocarbon.Explain. (b) Write a series of reactions leading topara-bromoethylbenzene, beginning with benzene andusing other reagents as needed. What isomeric side productsmight also be formed?arrow_forwardWhich is the stronger acid in each of the following pairs? Explain your reasoning. (a) Phenol or p-hydroxybenzaldehyde (b) m-Cyanophenol or p-cyanophenol (c) o-Fluorophenol or p-fluorophenolarrow_forward
- (a) Which is more reactive towards Electrophilic aromatic substitution (EAS)? (b) Which of the following is a a meta-substituted compound? (c) Which is the least reactive towards Electrophilic aromatic substitution (EAS)? (d) Which is an ortho-substituted compound?arrow_forward11:43 Q1. (a) (c) (d) (b) Two stereoisomers of but-2-ene are formed when 2-bromobutane reacts with ethanolic potassium hydroxide. (i) Explain what is meant by the term stereoisomers. Library Name and outline a mechanism for the reaction of 2-bromo-2-methylpropane with ethanolic potassium hydroxide to form the alkene 2-methylpropene, (CH3)2C=CH₂ Name of mechanism Mechanism (ii) Draw the structures and give the names of the two stereoisomers of but-2-ene. Stereoisomer 1 Name (iii) Name this type of stereoisomerism. Select Name Stereoisomer 2 When 2-bromo-2-methylpropane reacts with aqueous potassium hydroxide, 2-methylpropan-2-ol is formed as shown by the following equation. CH3 H₂C-C-CH3 + KOH Br Page 2 of 14 CH3 H3C-C-CH3 + KBr ОН State the role of the hydroxide ions in this reaction. Write an equation for the reaction that occurs when CH3CH₂CH₂CH₂Br reacts with an excess of ammonia. Name the organic product of this reaction. Equation Name of product 9,284 Photos, 1,166 Videos For You…arrow_forward(a) Give chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds :(i) Pentan-2-ol and Pentan-3-ol (ii) Methanol and Phenol(b) o-nitro phenol is more acidic than o-methoxy phenol. Explain why.arrow_forward
- Synthesize from benzene. (Hint: All of these require diazonium ions.)(a) 3-ethylbenzoic acidarrow_forwardThe hydrocarbon fluorene was treated with potassium t-butoxide in an acid-base reaction, giving the fluorenide anion and t-butyl alcohol. (a) Which way does the equilibrium lie, and by how much? b) What is the proportion of the fluorenide anion to fluorene? (c) Why is fluorene so highly acidic, considering the pKa of an average alkane is above 50?arrow_forward(c) Arrange the following compounds in order of increasing acidity, and explain the reasons for your choice of order: phenol, cyclohexanol, 2-fluorocyclohexanol, 2-fluorophenol.arrow_forward
- Answer ALL parts of this question. (a) Using resonance structures, discuss the following statement; phenols are much stronger acids than aliphatic alcohols. (b) Give the structure of a stronger organic acid than phenol. (c) Rationalise the acidity of the latter organic acid by drawing two resonance structures of the conjugate base. (d) Eugenol is a natural product derived from the dried flower buds of the evergreen tree, Eugenia aromatica. Briefly describe a procedure with reagents required to extract eugenol as a single component from the mixture of compounds present in these flower buds. OH LOCH 3 eugenolarrow_forwardProvide the reagents and solvents (where appropriate) needed to bring about the following transformations. (a) CI (b)arrow_forward(a) (From benzene)arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





