
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
1st Edition
ISBN: 9780130970695
Author: Peter S. Shaffer, Lillian C. McDermott
Publisher: Addison Wesley
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 15.3, Problem 6aTH
Carts A and B move along a horizontal track. The strobe diagram shows the locations of the carts at instant 1−5, separated by equal time intervals.
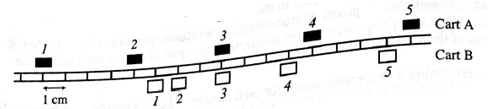
- At instant 3:
- is cart A speeding up, slowing down, or moving with constant speed? Explain.
- is cart B speeding up, slowing down, or moving with constant speed? Explain.
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule01:55
Students have asked these similar questions
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
Chapter 15 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Ch. 15.1 - Describe the motion. During which periods of time,...Ch. 15.1 - Find the object’s instantaneous velocity at each...Ch. 15.1 - For each of the following intervals, find the...Ch. 15.1 - In which of the cased from part c, if any, is the...Ch. 15.1 - In the interval from t=0s to t=6s , does the...Ch. 15.1 - In the small box on the graph above is a portion...Ch. 15.1 - Next, we expand the section of the previous graph...Ch. 15.1 - All three graphs are representations of the same...Ch. 15.1 - Suppose that the object is speeding up. Which of...Ch. 15.1 - Suppose that the object is slowing down. Which of...
Ch. 15.1 - Describe how you could use these devices to...Ch. 15.1 - Describe how you could use these devices to...Ch. 15.2 - In each of the following exercises, a motion will...Ch. 15.2 - In each of the following exercises, a motion will...Ch. 15.2 - In each of the following exercises, a motion will...Ch. 15.2 - In each of the following exercises, a motion will...Ch. 15.2 - In each of the following exercises, a motion will...Ch. 15.2 - In each of the following exercises, a motion will...Ch. 15.2 - In each of the following exercises, a motion will...Ch. 15.2 - In each of the following exercises, a motion will...Ch. 15.2 - There are several answers for most of the...Ch. 15.2 - There are several answers for most of the...Ch. 15.2 - There are several answers for most of the...Ch. 15.3 - A ball rolls up, then down an incline. Sketch an...Ch. 15.3 - Sketch x versus t, v versus t, and a versus t...Ch. 15.3 - Sketch x versus t, v versus t, and a versus t...Ch. 15.3 - Sketch x versus t, v versus t, and a versus t...Ch. 15.3 - Describe the motion of an object: For which the...Ch. 15.3 - Describe the motion of an object: b. For which the...Ch. 15.3 - Describe the motion of an object: c. For which the...Ch. 15.3 - Describe the motion of an object: d. For which the...Ch. 15.3 - Two carts roll toward each other on a level table....Ch. 15.3 - Two carts roll toward each other on a level table....Ch. 15.3 - Two carts roll toward each other on a level table....Ch. 15.3 - In this problem, a Cart moves in various ways on a...Ch. 15.3 - In this problem, a Cart moves in various ways on a...Ch. 15.3 - In this problem, a Cart moves in various ways on a...Ch. 15.3 - Carts A and B move along a horizontal track. The...Ch. 15.3 - Carts A and B move along a horizontal track. The...Ch. 15.3 - Carts A and B move along a horizontal track. The...Ch. 15.3 - Carts A and B move along a horizontal track. The...Ch. 15.3 - Two cars, C and D, travel in the same direction on...Ch. 15.3 - Two cars, P and Q, travel in the same direction on...Ch. 15.3 - Two cars, P and Q, travel in the same direction on...Ch. 15.4 - Prob. 1aTHCh. 15.4 - Prob. 1bTHCh. 15.4 - Describe how you would determine the acceleration...Ch. 15.4 - Copy vG and vH (placed “tailtotail”) in the space...Ch. 15.4 - Generalize your results above and from tutorial to...Ch. 15.4 - For each instant, state whether the object is...Ch. 15.4 - The diagram at right illustrates how the...Ch. 15.4 - For each of the instants 14, compare your...Ch. 15.4 - Choose a point about 1/8th of the way around the...Ch. 15.4 - Prob. 3bTHCh. 15.4 - How would you characterize the direction of v as...Ch. 15.4 - Each of the following statements in incorrect....Ch. 15.4 - On the diagram at right, draw vectors that...Ch. 15.4 - On the diagram at right, draw vectors that...Ch. 15.4 - Draw arrows on the diagram at points AG to...Ch. 15.4 - Next to each of the labeled points, state whether...Ch. 15.4 - Draw arrows on the diagram below to show the...Ch. 15.4 - On the diagram at right, draw velocity vectors for...Ch. 15.4 - On the diagram at right, draw the acceleration...Ch. 15.4 - How does the magnitude of the acceleration at E...Ch. 15.5 - Reference frame of boat B: Complete the upper...Ch. 15.5 - Reference frame of boat A: Complete the diagram at...Ch. 15.5 - Is the speed of the kayak in the frame of boat A...Ch. 15.5 - Rank the following quantities in order of...Ch. 15.5 - A third riverboat, boat C, moves downstream so as...Ch. 15.5 - Prob. 2aTHCh. 15.5 - A car, a truck, and a traffic cone are on a...Ch. 15.5 - The relationship vcar,cone=vcar,truck+vtruck,cone...Ch. 15.5 - Car P moves to the west with constant speed v0...Ch. 15.5 - Car P moves to the west with constant speed v0...Ch. 15.5 - Car P moves to the west with constant speed v0...Ch. 15.5 - Car P moves to the west with constant speed v0...Ch. 15.5 - Car P moves to the west with constant speed v0...Ch. 15.5 - A bicycle coasts up a hill while a car drives up...Ch. 15.5 - A bicycle coasts up a hill while a car drives up...Ch. 15.5 - A bicycle coasts up a hill while a car drives up...Ch. 15.5 - A bicycle coasts up a hill while a car drives up...Ch. 15.5 - A bicycle coasts up a hill while a car drives up...Ch. 15.5 - A bicycle coasts up a hill while a car drives up...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Pigeons may exhibit a checkered or plain color pattern. In a series of controlled matings, the following data w...
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
Q8. Perform the calculation to the correct number of significant figures.
a) 0.121
b) 0.12
c) 0.12131
d) 0.121...
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
How might you isolate a morphologically unique bacterium present in an enrichment culture in relatively low num...
Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition)
28. Consider the reaction
Express the rate of the reaction in terms of the change in concentration of e...
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
10.12 A pair of homologous chromosomes in Drosophila has the following content (single letters represent genes)...
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Examine the graph in Figure 6.3. Note that the growth rate increases slowly until the optimum is reached and th...
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- air is pushed steadily though a forced air pipe at a steady speed of 4.0 m/s. the pipe measures 56 cm by 22 cm. how fast will air move though a narrower portion of the pipe that is also rectangular and measures 32 cm by 22 cmarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward13.87 ... Interplanetary Navigation. The most efficient way to send a spacecraft from the earth to another planet is by using a Hohmann transfer orbit (Fig. P13.87). If the orbits of the departure and destination planets are circular, the Hohmann transfer orbit is an elliptical orbit whose perihelion and aphelion are tangent to the orbits of the two planets. The rockets are fired briefly at the depar- ture planet to put the spacecraft into the transfer orbit; the spacecraft then coasts until it reaches the destination planet. The rockets are then fired again to put the spacecraft into the same orbit about the sun as the destination planet. (a) For a flight from earth to Mars, in what direction must the rockets be fired at the earth and at Mars: in the direction of motion, or opposite the direction of motion? What about for a flight from Mars to the earth? (b) How long does a one- way trip from the the earth to Mars take, between the firings of the rockets? (c) To reach Mars from the…arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwarda cubic foot of argon at 20 degrees celsius is isentropically compressed from 1 atm to 425 KPa. What is the new temperature and density?arrow_forwardCalculate the variance of the calculated accelerations. The free fall height was 1753 mm. The measured release and catch times were: 222.22 800.00 61.11 641.67 0.00 588.89 11.11 588.89 8.33 588.89 11.11 588.89 5.56 586.11 2.78 583.33 Give in the answer window the calculated repeated experiment variance in m/s2.arrow_forward
- How can i solve this if n1 (refractive index of gas) and n2 (refractive index of plastic) is not known. And the brewsters angle isn't knownarrow_forward2. Consider the situation described in problem 1 where light emerges horizontally from ground level. Take k = 0.0020 m' and no = 1.0001 and find at which horizontal distance, x, the ray reaches a height of y = 1.5 m.arrow_forward2-3. Consider the situation of the reflection of a pulse at the interface of two string described in the previous problem. In addition to the net disturbances being equal at the junction, the slope of the net disturbances must also be equal at the junction at all times. Given that p1 = 4.0 g/m, H2 = 9.0 g/m and Aj = 0.50 cm find 2. A, (Answer: -0.10 cm) and 3. Ay. (Answer: 0.40 cm)please I need to show all work step by step problems 2 and 3arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON
Position/Velocity/Acceleration Part 1: Definitions; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4dCrkp8qgLU;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY