
Econ Macro (book Only)
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337408745
Author: William A. McEachern
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 15, Problem 6P
To determine
To Calculate:The velocity of money under different circumsances.
Concept Introduction: The American economist, Irving Fisher, explained the quantity theory of money by examining the variables of money, price level and 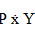 where P is the price level and Y is real GDP is called velocity of money (V). This velocity is the average number of times the dollar is spent in buying the total amount of goods and services produced in the economy. The quantity theory of money explains the link in the variables.
where P is the price level and Y is real GDP is called velocity of money (V). This velocity is the average number of times the dollar is spent in buying the total amount of goods and services produced in the economy. The quantity theory of money explains the link in the variables.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
In the quantity theory of money, velocity is assumed
A) to increase with increases in the money supply.
B) to equal 1.4.
C) constant.
D) to be a declining number.
Velocity is
A) not constant
if the demand for money depends on the interest rate.
B) infinite
C) zero
If the demand for money depends on the
quantity theory of money
A) interest rate; does not hold
C) level of GDP; still holds
If the equation for the
for money depends on nominal income but not the interest rate.
D) constant
and the velocity is not constant, then the
B) interest rate; still holds
D) level of GDP; does not hold
is looked on as a demand-for-money equation, then the demanc
A) unanticipated inflation rate
C) Keynesian income-expenditure model
Monetarists and Keynesians
impact of fiscal policy on the economy.
A) agree; agree
C) disagree; disagree
B) real business cycle theory
D) quantity theory of money
For price stability, monetarists argue that the money supply should grow at a rate
average growth of real output.…
How does the concept of velocity of money relate to the quantity theory of money, and what factors can influence the velocity of money in an economy? A) The velocity of money has no connection to the quantity theory of money. B) The velocity of money represents the rate at which money changes hands in the economy and is a key factor in the quantity theory of money; factors like consumer confidence and banking practices can influence it. C) The velocity of money measures the total money supply in an economy and is unrelated to the quantity theory of money. D) The velocity of money is determined solely by government policies.
Provide the equation for the velocity of money in terms of Price level (P), output (Y), and the amount of money in the economy (M)
a) Explain what will happen to velocity if P increases and why.
b) Explain what will happen to velocity if Y increases and why.
c) Explain what will happen to velocity if M increases and why.
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Suppose the money supply is €200, real output is 1,000 units, and the price per unit of output is €1. a. What is the value of velocity? b. If velocity is fixed at the value you solved for in part (a), what does the quantity theory of money suggest will happen if the money supply is increased to €400?arrow_forwardQ1. In 2019, an economy produces wheat only and has enough labor, capital, and land to produce 500 bushels of wheat (Y or real GDP). Price of wheat and money supply are $2 per bushel and $1,000 respectively. In 2020, the central bank increases money supply by $ 1040. Suppose both the velocity of money (V) and the amount of wheat produced remain unchanged. a. Compute the velocity of money and nominal GDP in 2019. b. Calculate inflation rate in year 2020. c. Use a well-labelled money supply-demand diagram to illustrate and explain what happen to the price level and the value of money after such money injection?arrow_forwardIf the money supply is $60 and nominal GDP is $360, then Group of answer choices A) the velocity of money must be 300. B) the velocity of money must be 4.2. C) the velocity of money must be 3. D) the velocity of money must be 60. E) the velocity of money must be 6.arrow_forward
- Question 41 6. Table 6-1 contains historical data for nominal GDP, M1, and M2. 6.1 Use this data to compute V1, velocity based on M1; and V2, velocity based on M2. Be sure to round your answers for velocity to two decimal places. Note that Nominal GDP indicates PY in the quantity theory of money. Table 6-1. GDP, Money, and Velocity Year Nominal GDP ($B) M1 ($B) 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 7,000 7,500 8,300 8,700 9,200 900 1,100 1,000 1,200 1,300 M2 ($B) 3,200 3,700 3,600 4,100 4,300 V1 V2arrow_forwardSuppose you are put in charge of the central bank in an economy where potential GDP is growing at 3% and inflation has been 5% a year for the past few years. a) You find out that your predecessor had increased the money supply by 7% a year during this time. What does that say about the rate of velocity growth in this economy? b) You decide that 5% inflation is too high a rate, and that you need to take steps to reduce inflation to 2% a year. Assuming that the growth rate of velocity is a constant, what is the new rate of money growth you should implement in this economy? c) Continuing with your answer from b), what is the new rate of money growth you should implement in this economy to keep inflation at 2% a year if all else equal i) The growth rate of potential output rises to 4% ii) The growth rate of velocity falls to 0% d) How would your answer to b) would change if velocity growth was not constant, but instead was a random variable vt? You can answer this with algebra or words,…arrow_forwardIf GDP now falls back to 1,500 and the money supply falls to 350, what is velocity?arrow_forward
- If GDP now rises to 1,600, but the money supply does not change, how has velocity changed? If GDP now falls back to 1,500 and the money supply falls to 350, what is velocity?arrow_forwardQuestion 2: Suppose the money supply is $50 in an economy where the nominal GDP is $1000, and the real GDP is $500. a) Can you calculate the price level? b) Can you calculate the money velocity? c) Now suppose output increases by 10 percent and the velocity is constant. Suppose Fed wants to keep prices constant through monetary policy. What will happen to the nominal GDP and price level? d) Suppose Fed targets 5 percent inflation. What money supply should the Fed set to achieve that?arrow_forwardConsider the following scenario: a. In Argentina, the central bank needs to determine by how much to increase the money supply next year. Suppose they estimate an increase in the overall economic activity (real GDP) of 2.5% percent and have a target inflation rate of 4%. The velocity of money has been observed to be constant over the past many years. By what level should the central bank change the money supply to achieve its inflation target? b. Next year, the central bank of Argentina wishes to reduce inflation to 2 percent, and estimates an increase in real GDP by 1.5 percent. What should be the change in the money supply? c. What is an "inflation tax", and how might it explain the creation of inflation by a central bank?arrow_forward
- Suppose the supply of money, measured by M1, is $3.0 trillion, output, measured by real GDP, is $18.7 trillion, and the velocity of money is 7.1. Suppose the supply of money increases to $3.7 trillion but GDP and the velocity of money do not change. What is the percent by which prices change? Provide your answer as a percentage rounded to two decimal places. Do not include any symbols, such as "$," "," "%," or "," in your answer. Your Answer: Answerarrow_forwardSuppose that velocity of money is constant, the expected inflation rate is always equal to the actual inflation rate, and the expected real interest rate is 3%. Answer the following questions. Justify your answers. a)Let the growth rate of the money supply rise to 10% without affecting the growth rate of real GDP or velocity. What happens to the inflation rate? If this new inflation rate becomes the expected inflation rate what happens to the nominal interest rate? b)Has the increase in the growth rate of money supply been generated by an open market operation conducted by the central bank? If so, how did the central bank generate this increase in the money supply? Only a qualitative answer is required.arrow_forwardIn the country Constantania, suppose the velocity of money is always the same. Last year, the money supply was $2 billion and real GDP was $5 billion. This year, the money supply increased by 6 percent, real GDP by 4 percent, and nominal GDP is $6.5 billion. a) Calculate the velocity of money and the price levels in the two years, and then calculate the inflation rate. b) Calculate the inflation rate using the formula AM/M + AV/V = AP/P + AY/Y, where the Greek letter A represents a change and the ratio AM/Mx 100 is the percentage change (or the rate of change) in M. Compare this result with the result you obtained in part a. Why could there be some difference? c) What is the difference between commodity money and fiat money? Why do people accept fiat currency in trade for goods and services?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you




 Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax
Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax





Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:9781947172364
Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:OpenStax