
Loose Leaf for Engineering Circuit Analysis Format: Loose-leaf
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781259989452
Author: Hayt
Publisher: Mcgraw Hill Publishers
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 14.9, Problem 19P
Using the method of source transformation, reduce the circuit of Fig. 14.24 to a single s-domain current source in parallel with a single impedance.
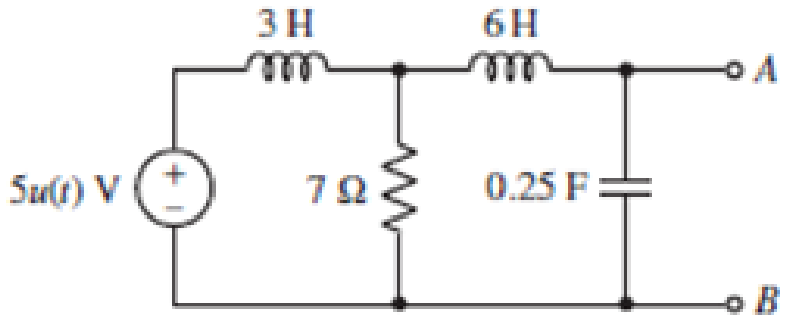
FIGURE 14.24
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Don't use ai to answer I will report you answer
Not use ai please
49.
For the circuit below, what is the best connection of the capacitor to filte
voltage?
ბი
DO
A O
BO
wwwww
wwwww
M
m
H
E
LOAD
Chapter 14 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Engineering Circuit Analysis Format: Loose-leaf
Ch. 14.1 - Identify all the complex frequencies present in...Ch. 14.1 - Use real constants A, B, C, , and so forth, to...Ch. 14.2 - Let f (t) = 6e2t [u(t + 3) u(t 2)]. Find the (a)...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 4PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 5PCh. 14.4 - Prob. 6PCh. 14.4 - Prob. 7PCh. 14.4 - Prob. 8PCh. 14.4 - Prob. 9PCh. 14.5 - Prob. 10P
Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 11PCh. 14.5 - Prob. 12PCh. 14.6 - Prob. 13PCh. 14.7 - Prob. 14PCh. 14.7 - Prob. 15PCh. 14.8 - Find the mesh currents i1 and i2 in the circuit of...Ch. 14.8 - Prob. 17PCh. 14.8 - Prob. 18PCh. 14.9 - Using the method of source transformation, reduce...Ch. 14.9 - Prob. 20PCh. 14.10 - The parallel combination of 0.25 mH and 5 is in...Ch. 14.11 - Prob. 22PCh. 14.11 - Prob. 23PCh. 14.11 - Prob. 24PCh. 14.11 - Prob. 25PCh. 14.12 - Prob. 26PCh. 14 - Determine the conjugate of each of the following:...Ch. 14 - Compute the complex conjugate of each of the...Ch. 14 - Several real voltages are written down on a piece...Ch. 14 - State the complex frequency or frequencies...Ch. 14 - For each of the following functions, determine the...Ch. 14 - Use real constants A, B, , , etc. to construct the...Ch. 14 - The following voltage sources AeBt cos(Ct + ) are...Ch. 14 - Prob. 8ECh. 14 - Compute the real part of each of the following...Ch. 14 - Your new assistant has measured the signal coming...Ch. 14 - Prob. 11ECh. 14 - Prob. 12ECh. 14 - Prob. 13ECh. 14 - Prob. 14ECh. 14 - Prob. 15ECh. 14 - Prob. 16ECh. 14 - Determine F(s) if f (t) is equal to (a) 3u(t 2);...Ch. 14 - Prob. 18ECh. 14 - Prob. 19ECh. 14 - Prob. 20ECh. 14 - Prob. 21ECh. 14 - Evaluate the following: (a)[(2t)]2 at t = 1;...Ch. 14 - Evaluate the following expressions at t = 0: (a)...Ch. 14 - Prob. 24ECh. 14 - Prob. 25ECh. 14 - Prob. 26ECh. 14 - Prob. 27ECh. 14 - Prob. 28ECh. 14 - Prob. 29ECh. 14 - Prob. 30ECh. 14 - Prob. 31ECh. 14 - Prob. 32ECh. 14 - Prob. 33ECh. 14 - Obtain the time-domain expression which...Ch. 14 - Prob. 35ECh. 14 - Prob. 36ECh. 14 - Prob. 37ECh. 14 - Prob. 38ECh. 14 - Prob. 39ECh. 14 - Prob. 40ECh. 14 - Prob. 41ECh. 14 - Obtain, through purely legitimate means, an...Ch. 14 - Prob. 43ECh. 14 - Employ the initial-value theorem to determine the...Ch. 14 - Prob. 45ECh. 14 - Prob. 46ECh. 14 - Prob. 47ECh. 14 - Prob. 48ECh. 14 - Prob. 49ECh. 14 - Prob. 52ECh. 14 - Determine v(t) for t 0 for the circuit shown in...Ch. 14 - Prob. 54ECh. 14 - Prob. 55ECh. 14 - For the circuit of Fig. 14.54, (a) draw both...Ch. 14 - Prob. 58ECh. 14 - Prob. 59ECh. 14 - Prob. 60ECh. 14 - For the circuit shown in Fig. 14.58, let is1 =...Ch. 14 - Prob. 63ECh. 14 - Prob. 64ECh. 14 - For the circuit shown in Fig. 14.62, determine the...Ch. 14 - Prob. 67ECh. 14 - Prob. 68ECh. 14 - Determine the poles and zeros of the following...Ch. 14 - Use appropriate means to ascertain the poles and...Ch. 14 - Prob. 71ECh. 14 - For the network represented schematically in Fig....Ch. 14 - Prob. 73ECh. 14 - Prob. 74ECh. 14 - Prob. 75ECh. 14 - Prob. 76ECh. 14 - Prob. 77ECh. 14 - Prob. 78ECh. 14 - Prob. 79ECh. 14 - Prob. 80ECh. 14 - Prob. 81ECh. 14 - Prob. 82ECh. 14 - Design a circuit which produces the transfer...Ch. 14 - Prob. 84ECh. 14 - Prob. 85ECh. 14 - An easy way to get somebodys attention is to use a...Ch. 14 - Prob. 87E
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Assume a telephone signal travels through a cable at two-thirds the speed of light. How long does it take the s...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
1.2 Explain the difference between geodetic and plane
surveys,
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
What is an uninitialized variable?
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
How are relationships between tables expressed in a relational database?
Modern Database Management
Comprehension Check 7-14
The power absorbed by a resistor can be given by P = I2R, where P is power in units of...
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
What types of coolant are used in vehicles?
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 5.25. Determine the corner frequency resulting from Cin in Fig. 5.47(d). For simplicity, assume C₁ is a short circuit. TVDD C₁ M2 RF Vin H w - Vout Cin M₁arrow_forwardIn the below circuit, find out the value of equivalent Thevenin's voltage and Thevenin's resistance at the terminal. 2000 0.25 A 400 2 800 2 0.1 Aarrow_forwardQ1: For the circuit shown in Figure-1, (a) Calculate the equivalent resistance of the circuit, RAB at the terminals A and B. [10] (b) When 50V dc source is switched at terminals A-B, solve for the voltage V₁ at the location shown. [10] 50V www 12Ω 10Ω 5Ω www www A + B 200 Figure-1 www 10Ω ww 25Ω 100arrow_forward
- a. Write a PLC ladder diagram that allows the teacher to teach AND, OR, and XOR logic gates through using three PLC's digital input points and only one digital output point.arrow_forwardrately by PRACTICE 4.2 For the circuit of Fig. 4.5, compute the voltage across each curren source. 202 ww 3A 30 ww 4Ω S 50 www Reference node FIGURE 4.5 Ans: V3A =5.235 V; 7A = 11.47 V. 7 Aarrow_forwardQ2) a) design and show me your steps to convert the following signal from continuous form to digital form: s(t)=3sin(3πt) -1 373 Colesarrow_forward
- A sequence is defined by the relationship r[n] = [h[m]h[n+m]=hn*h-n where h[n] is a minimum-phase sequence and r[n]= 4 4 (u[n]+ 12" [n-1] 3 (a) Find R(z) and sketch the pole-zero diagram. (b) Determine the minimum-phase sequence h[n] to within a scale factor of ±1. Also, determine the z-transform H(z) of h[n].arrow_forwardusıng j-k and D flipflop design a counter that counts 0,2,1 again as shown below ın the tablearrow_forwardfind the minterms of the followıng boolean expressıon desıgn F's cırcuit using one of the approciate decoders given below and a NOR gateF(A,B,C,D)=(A+'BC)(B 'C+'A 'D + CD)arrow_forward
- 64) answer just two from three the following terms: A) Design ADC using the successive method if the Vmax=(3) volt, Vmin=(-2) volt, demonstrate the designing system for vin-1.2 volt. Successive Approximation ADC Input Voltage-1.1 V -4-3.5-3 -2.5 -2 -1.5 +1 -0.5 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 1 T -8 -7 -6 -5 -3 +2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 X=1??? 1st guess: -0.25 V (too high) X=11?? 2nd guess: -2.25 V (too low) 3rd guess: -1.25 V (too low) X=1110 X=111? 4th guess: -0.75 V (too high) Make successive guesses and use a comparator to tell whether your guess is too high or too low. Each guess determines one bit of the answer and cuts the number of remaining possibilities in half.arrow_forwardDatacommunıcatıonin a commuinaction ASYNCHRONOUS TRANSMİTİON is used in this transmistion 7-bit chatacter will be transfered even parity will be used ,stop element is as 1,5 bits a)=select a chracter yourself and dısplay the signal transfered in this transmission , and calculate the overhead in this transmisionarrow_forward(i) Find the inverse z-transform of the system H(z) = for the following regions of convergence. Write in the final answer for each case in the allocated rectangular box below (a) |z| 3 (c) 1arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Norton's Theorem and Thevenin's Theorem - Electrical Circuit Analysis; Author: The Organic Chemistry Tutor;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-kkvqr1wSwA;License: Standard Youtube License