
To find:
• The
• The graph of the projectile at suitable x values.
• The graph of the height versus time.
• The range of the given projectile equations.
Answer to Problem 46E
Solution:
• The required range is
• The required graph is stated as follows.
• The required graph is stated as follows.
• The required apex is
Explanation of Solution
• The range of the given projectile equations.
The given equations are,
The formula to calculate the range is,
Here,
Let
Substitute
MATLAB Code:
t = 0:0.001:2;
v0 = 2;
g = 9.81;
theta = 30;
x = v0.*cosd(theta).*t;
y = v0.*sind(theta).*t -0.5.*g.*t.*t;
range = v0.^2.*sind(2*theta)/g
Save the MATLAB function with name chapter14_54793_14_46_1E.m in the current folder. Execute the function by typing the function name at the command window to generate output.
Result:
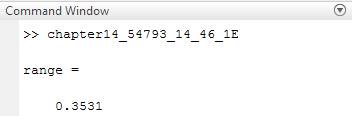
Therefore, the result is stated above.
• The graph of the projectile at suitable x values.
MATLAB Code:
t = 0:0.001:2;
v0 = 2;
g = 9.81;
theta = 30;
x = v0.*cosd(theta).*t;
y = v0.*sind(theta).*t -0.5.*g.*t.*t;
plot(t, x)
title('Position(x) vs Time(t)')
Save the MATLAB function with name chapter14_54793_14_46_2E.m in the current folder. Execute the function by typing the function name at the command window to generate output.
Result:
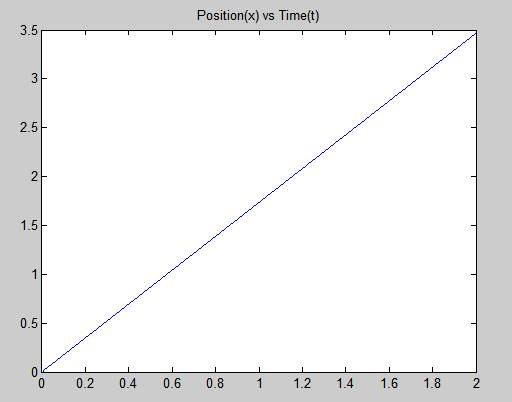
Therefore, the result is stated above.
• The graph of the height versus time.
MATLAB Code:
t = 0:0.001:2;
v0 = 2;
g = 9.81;
theta = 30;
x = v0.*cosd(theta).*t;
y = v0.*sind(theta).*t -0.5.*g.*t.*t;
plot(t, y)
title('Height(y) vs Time(t)')
Save the MATLAB function with name chapter14_54793_14_46_3E.m in the current folder. Execute the function by typing the function name at the command window to generate output.
Result:
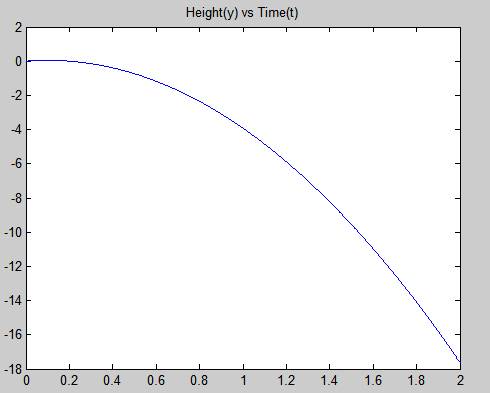
Therefore, the result is stated above.
• The range of the given projectile equations.
The given equations are,
The formula to calculate the maximum time,
Here,
Let
Substitute
MATLAB Code:
t = 0:0.001:2;
v0 = 2;
g = 9.81;
theta = 30;
x = v0.*cosd(theta).*t;
y = v0.*sind(theta).*t -0.5.*g.*t.*t;
apex_time = v0*sind(theta)/g;
fprintf('The apex is %.1f\n', apex_time)
Save the MATLAB function with name chapter14_54793_14_46_4E.m in the current folder. Execute the function by typing the function name at the command window to generate output.
Result:
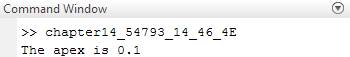
Therefore, the required apex is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
MATLAB: A Practical Introduction to Programming and Problem Solving
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





