
Concept explainers
Suppose the demand and supply equations for a certain commodity are given by
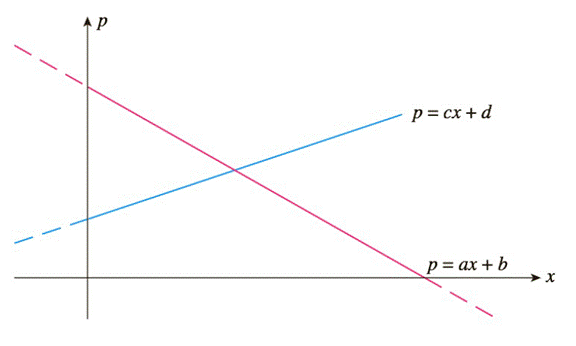
a. Find the equilibrium quantity and equilibrium price in terms of
b. Use part (a) to determine what happens to the market equilibrium if
c. Use part (a) to determine what happens to the market equilibrium if
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 1 Solutions
Finite Mathematics for the Managerial, Life, and Social Sciences, 11th Edition
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Mathematics for the Trades: A Guided Approach (11th Edition) (What's New in Trade Math)
Mathematical Ideas (13th Edition) - Standalone book
Thinking Mathematically (7th Edition)
Basic College Mathematics
Pathways to Math Literacy (Loose Leaf)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
- 23. Consider a simple economy with just two industries: farming and manufacturing. Farming consumes 1/2 of the food and 1/3 of the manufactured goods. Manufacturing consumes 1/2 of the food and 2/3 of the manufactured goods. Assuming the economy is closed and in equilibrium, find the relative outputs of the farming and manufacturing industries.arrow_forwardD. has no effect on either its demand or its supply. QUESTION 5 Suppose the equilibrium price for soft drinks is $1.00. If the current price in the soft drink market is $1.25 each, O A. there willl be a surplus of soft drinks. B. there will be a shortage of soft drinks. O C. the supply curve of soft drinks will shift leftward. D. the demand curve for soft drinks will shift leftward QUESTION 6 If the price of product X falls and this change increases the demand for product Y, then O A.X and Y are complements B. X and Yare substitutes. OC.Xis an inferior good. OD. Y is an inferior good.arrow_forwardProduct A is sold in a perfectly competitive, constant-cost industry. a. Draw a side-by-side graph for product A showing the market in long-run equilibrium with an individual firm earning normal profit. Label each of the following: i. The market's equilibrium price (PE) and quantity (QE) ii. The firm's profit-maximizing quantity (QE) b. How would it affect the quantity demanded if the government imposed a price floor below PE? c. The price of B, a complement for product A, decreases. Illustrate on your graph from part (a) the result of this in the short run. i. Label the new market price (P2) and new market quantity (Q2). ii. Shade completely any profit or loss for the firm. d. The price of B decreased by 10 percent, while the quantity demanded of A changed by 15 percent. What is the cross-price elasticity of A and B? e. What happens to the productive efficiency of the firm in the short run as a result of the change described in part (c)? f. What will happen to the price of A in the…arrow_forward
- SECTIONS 1.4, 5.5 - Use the following equations to answer the questions. Demand Function: p = D(x) = (x - 7)², Supply Function: p = S(x) = x + 2x + 1 %3D a. Find the equilibrium point (xo , Po ).Write as an ordered pair. b. Use calculus to find the consumer surplus at the equilibrium point found in the last question. Write an exact answer. State the formula for consumer surplus. (Note: If you were unable to find the equilibrium point, use (8, 1) for this question.) Formula: Consumer Surplus =, c. Use calculus to find the producer surplus at the equilibrium point found in the second to last question. Write an exact answer. State the formula for consumer surplus. (Note: If you were unable to find the equilibrium point, use (2, 5) for this question.) Formula: Producer Surplus =arrow_forwardIf the market price of a product is above the equilibrium price, the quantity supplied is _____ the quantity demanded. equal to Market price and quantity supply are not related. greater than less thanarrow_forward
 Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
