
Concept explainers
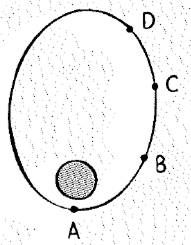
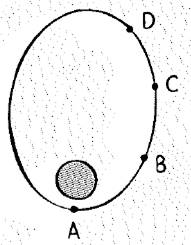
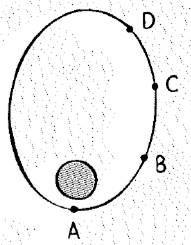
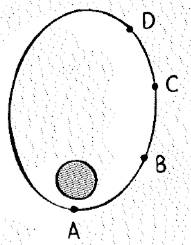
The positions of a satellite in elliptical orbit are indicated.
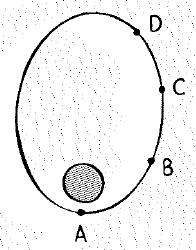
Rank these quantities from greatest to least.
a. gravitational force
b. speed
c. momentum
d. KE
e. PE
f. total energy
g. acceleration
(a)
To rank: Gravitational force at different points from greatest to least.
Answer to Problem 22A
Gravitational force, from greatest to least is, A>B>C>D
Explanation of Solution
Given:
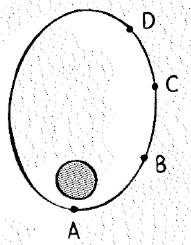
The position of satellite in elliptical orbit are shown below.
Formula used:
Gravitational force of attraction between two massive bodies of mass is
Where,
G = Gravitational constant =
r = distance between to body.
Calculation:
From above equation, gravitational force is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between two body.
From figure, distance of the satellite from the earth is given at different position is,
(Position A) < (Position B) < (Position C) < (Position D)
Since less be the distance, large will be the force of gravity
Conclusion:
Therefore, gravitational force, from greatest to least is, A > B > C > D.
(b)
To rank: Speed of satellite, from greatest to least.
Answer to Problem 22A
Speed of satellite, from greatest to least is, A > B > C > D
Explanation of Solution
Given:
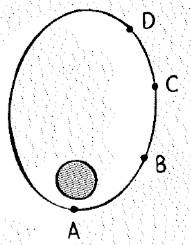
The position of satellite in elliptical orbit are shown below.
Formula:
The speed of the satellite in elliptical orbit is,
Where,
G = Gravitational constant = 6.67×10-11 N.m2/kg2
M = Mass of the satellite
r = The distance of the satellite from the earth
a = Semi-major axis
Calculation:
From given formula,
From the given formula, distance of the satellite increases as the satellite near to the earth. So, the speed is increases from position A to position D
Conclusion:
Therefore, speed of satellite, from greatest to least is, A>B>C>D
(c)
To rank: Momentum of satellite, from greatest to least.
Answer to Problem 22A
Momentum of satellite, from greatest to least is, A>B>C>D
Explanation of Solution
Given:
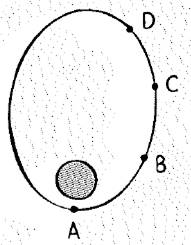
The position of satellite in elliptical orbit are shown below.
Formula:
The momentum of the satellite in elliptical orbit is,
Where,
M = Mass of the satellite
v = Speed of the satellite.
P = momentum of the satellite.
Calculation:
Since from the given formula, momentum of the satellite is directly proportional to the velocity of the satellite.
As from the given formula, speed of the satellite increases as the satellite near to the earth. So, the momentum is increases from D position A
Conclusion:
Therefore, momentum of satellite, from greatest to least is, A>B>C>D
(d)
To rank: Kinetic energy of satellite, from greatest to least.
Answer to Problem 22A
Kinetic energy of satellite, from greatest to least is, A>B>C>D
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The position of satellite in elliptical orbit are shown below.
Formula:
The kinetic energy of the satellite in elliptical orbit is,
Where,
KE = kinetic energy of satellite
M = Mass of the satellite
v = Speed of the satellite.
Calculation:
Since from the given formula, kinetic energy of the satellite is directly proportional to the velocity of the satellite.
From the given formula, speed of the satellite increases as the satellite near to the earth. So, the kinetic energy is increases from position D to position A
Conclusion:
Therefore, momentum of satellite, from greatest to least is, A>B>C>D
(e)
To rank: Potential energy of satellite, from greatest to least.
Answer to Problem 22A
Potential energy of satellite, from greatest to least is, D>C>B>A
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The position of satellite in elliptical orbit are shown below.
Formula:
The potential energy of the satellite in elliptical orbit is,
Where,
G = Gravitational constant= 6.67×10-11 N.m2/kg2
M = Mass of the satellite
m = Mass of the earth
r = The distance of the satellite from the earth
R = Radius of earth
Calculation:
From given formula,
From the given formula, distance of the satellite increases as the satellite near to the earth. Since the potential is negative. So, the potential energy is decreases from position A to position D
Conclusion:
Therefore, potential energy of satellite, from greatest to least is, D > C > B > A
(f)
To rank: Total energy ( E ) of satellite, from greatest to least.
Answer to Problem 22A
Total energy ( E ) of satellite, from greatest to least is, A = B = C = D
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The position of satellite in elliptical orbit are shown below.
Formula:
The total energy ( E ) of the satellite in elliptical orbit is,
Where,
PE = Potential energy of the satellite
KE = Kinetic energy of the satellite
Calculation:
According to conservation of energy, the total energy is constant in any process. When satellite move around the earth in elliptical orbit, depending on its position, velocity of the satellite get changed. When particle is move near to the earth due to gravitational pull, speed of the satellite increases. That increase in the speed of the satellite responsible for the higher kinetic energy. Similarly, as particle move away from the earth, its potential energy increases. Since the total energy of the satellite during its journey is remain constant.
Conclusion:
Therefore, total energy ( E ) of satellite, from greatest to least is, A = B = C = D
(g)
To rank: Acceleration of satellite, from greatest to least.
Answer to Problem 22A
Acceleration of satellite, from greatest to least is, A > B > C > D
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The position of satellite in elliptical orbit are shown below.
Formula:
The acceleration of the satellite in elliptical orbit is,
F= ma
Where,
F = Force acting on the satellite
m = mass of the satellite
a =Acceleration of the satellite
Calculation:
It is known from the part (a), as the distance between the satellite and Earth decreases gravitational force acting on the satellite increases. Since the acceleration of the satellite is directly proportional to the gravitational force on the satellite. Therefore, as distance between earth and satellite decreases, acceleration of the satellite increases.
Conclusion:
Therefore, acceleration of satellite, from greatest to least is, A > B > C > D
Chapter 14 Solutions
Conceptual Physics: The High School Physics Program
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Modern Physics
Introduction to Electrodynamics
Essential University Physics: Volume 1 (3rd Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Edition)
The Cosmic Perspective (8th Edition)
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





