
Concept explainers
Write structural formulas for the following compounds.
- a. ethyl isopropyl ether
- b. di-n-butyl ether
- c. 2-ethoxyoctane
- d. divinyl ether
- e. allyl methyl ether
- f. cyclohexene oxide
- g. cis-2,3-epoxyhexane
- h. (2R, 3S)-2-methoxypentan-3-ol
- i. trans-2,3-dimethyloxirane
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure formula for the given compound is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
An organic compound where an oxygen atom is attached to two alkyl or aryl groups is known as ether. The general formula of ethers is
Answer to Problem 14.29SP
The structure of ethyl isopropyl ether is shown in Figure 1.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is ethyl isopropyl ether. The root name isopropyl signifies three carbon atoms in a chain. Ethyl and isopropyl are the groups attached to an oxygen atom. The structure of ethyl isopropyl ether is shown below.
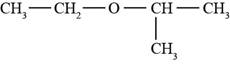
Figure 1
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure formula for the given compound is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
An organic compound where an oxygen atom is attached to two alkyl or aryl groups is known as ether. The general formula of ethers is
Answer to Problem 14.29SP
The structure of di-n-butyl ether is shown in Figure 2.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is di-n-butyl ether. The root name butyl signifies four carbon atoms in a chain and di-n-butyl indicates that two butyl groups are attached to an oxygen atom. The structure of di-n-butyl ether is shown below.
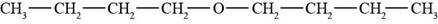
Figure 2
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure formula for the given compound is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
An organic compound where an oxygen atom is attached to two alkyl or aryl groups is known as ether. The general formula of ethers is
Answer to Problem 14.29SP
The structure of 2-ethoxyoctane is shown in Figure 3.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is 2-ethoxyoctane. The root octane signifies eight carbon atoms in a chain and 2-ethoxy shows that ethoxy group is present at second carbon atom of a chain. The structure of 2-ethoxyoctane is shown below.
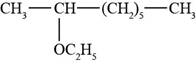
Figure 3
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure formula for the given compound is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
An organic compound where an oxygen atom is attached to two alkyl or aryl groups is known as ether. The general formula of ethers is
Answer to Problem 14.29SP
The structure of divinyl ether is shown in Figure 4.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is divinyl ether. The Vinyl group is the functional group having a formula
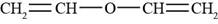
Figure 4
(e)
Interpretation:
The structure formula for the given compound is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
An organic compound where an oxygen atom is attached to two alkyl or aryl groups is known as ether. The general formula of ethers is
Answer to Problem 14.29SP
The structure of allyl methyl ether is shown in Figure 5.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is allyl methyl ether. An allyl group is used as a substituent and has a formula of
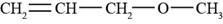
Figure 5
(f)
Interpretation:
The structure formula for the given compound is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
An organic compound where an oxygen atom is attached to two alkyl or aryl groups is known as ether. The general formula of ethers is
Answer to Problem 14.29SP
The structure of cyclohexene oxide is shown in Figure 6.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is cyclohexene oxide. The root name cyclohexene signifies six carbon atoms in a ring and oxide indicated the presence of epoxide ring. The structure of cyclohexene oxide is shown below.
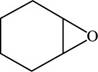
Figure 6
(g)
Interpretation:
The structure formula for the given compound is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
An organic compound where an oxygen atom is attached to two alkyl or aryl groups is known as ether. The general formula of ethers is
Answer to Problem 14.29SP
The structure of
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
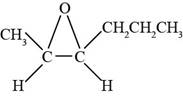
Figure 7
(h)
Interpretation:
The structure formula for the given compound is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
An organic compound where an oxygen atom is attached to two alkyl or aryl groups is known as ether. The general formula of ethers is
Answer to Problem 14.29SP
The structure of
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
According to Fisher projection,
For
The structure of
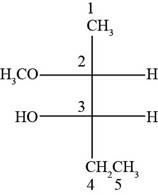
Figure 8
(i)
Interpretation:
The structure formula for the given compound is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
An organic compound where an oxygen atom is attached to two alkyl or aryl groups is known as ether. The general formula of ethers is
Answer to Problem 14.29SP
The structure of
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
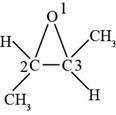
Figure 9
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Books a la Carte Edition (9th Edition)
- Reagents a. CeHsCHO b. NaOH, ethanol c. Pyrrolidine, cat. H* d. H2C=CHCN e. H30* f. LDA g. ELOC(=0)CO,Et h. BRCH2CH=CH2 Na* OEt, ethanol j. Br2, H* k. K* t-BuO 1. CH2(CO2Et)2 m. heat Select reagents from the table to synthesize this compound from cyclopentanone. Enter the letters of the chosen reagents, in the order that you wish to use them, without spaces or punctuation (i.e. geda). Submit Answer Try Another Version 1 Item attempt remainingarrow_forward4- Choose the correct reactants required to synthesize the following molecule. H3CO OCH 3 A. Acetone and methanal B. Acetone and methanol C. Formaldehyde and propanal D. Formaldehyde and propanol 5- What is the IUPAC name of the following compound? CI A. 6-Chloro-4-ethoxy-1-octanal B. 6-Chloro-4-ethoxyoctanal C. 6-Chloro-4-ethoxycyclooctanal D. 4-Ethoxy-6-chlorooctanal - What is the IUPAC name of the following compound? 0 Br. Br Cl A. 2,6-Dibromo-3-chloro-5,5-dimethylhexanone B. 2,6-Dibromo-3-chloro-5,5-dimethylcyclohexanone C. 2,6-Dibromo-5-chloro-3,3-dimethylhexanone D. 2,6-Dibromo-5-chloro-3,3-dimethylcyclohexanonearrow_forward1. Fill in the boxes with the missing reagents or major organic products for the alkene reactions. a. HCl b. H2O, H2SO4 с. d. 1. ВН, 2. H2O2, NaOH е. f. CI .CI g. Cl2, H2O h. 1. Н-О, Hg(OАс)2 2. NaBH4, NaOH i. 1. O3 2. Н:0, H-02 j. OH HO.arrow_forward
- Draw the structure of the following compounds. a. 1-ethyl-3-methylcycloheptane b. Cyclopropylcyclopentane c. 1,1-diethyl-4-(3,3-dimethylbutyl)cyclohexanearrow_forwardStructure please ?arrow_forwardCH2 H3C H3C COOH Reagents e. PB13 f. NaCN then H3O* g. NBS, CCI4 h. CrO3, H2SO4 а. HBr b. Mg, ether c. CO2, ether then H3O* d. BH3, THF then H2O2, OH"arrow_forward
- 3.arrow_forwardShow how to convert propene to each of these compounds, using any inorganic reagents as necessary. a. Propane b.1,2-Propanediol c. 1-Propanol d. 2-Propanol e. Propanal f. Propanone g. Propanoic acid h. l-Bromo-2-propanol i. 3-Chloropropene j. 1,2,3-Trichloropropane k. 1-Chloropropane l. 2-Chloropropane m. 2-Propen-1-ol n. Propenalarrow_forwardCompound III (in the provided image) is I. CH3-CH2-C = C-CH3 III. CH3-CH-C=C-CH-CH3 O a. 2-ethyl-5-methyl-3-heptyne O b. 2,5-dimethyl-3-heptyne O c. 2,5-dimethyl-3-hexyne O d. 2-ethyl-5-methyl-3-hexyne CH3 CH2-CH3 II. CH2=CH-CH2-CH-CH3 CH3arrow_forward
- 10. How many true statement(s) in the followings. a. 1,2-Dimethylcyclohexene occurs as E and Z isomers. b. 2,3-Dimethyl-3-hexene occurs as E and Z isomers. c. There are 4 possible E,Z isomers of 1,3-pentadiene.arrow_forwardDraw the structures of the compoundsarrow_forwardPp.30. Subject :- Chemistryarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





