
Organic Chemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781305080485
Author: John E. McMurry
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 13.8, Problem 15P
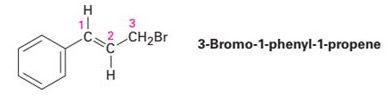
3-Bromo-1-phenyl-1-propene shows a complex NMR spectrum in which the vinylic proton at C2 is coupled with both the C1 vinylic proton (J = 16 Hz) and the C3 methylene protons (J = 8 Hz). Draw a tree diagram for the C2 proton signal, and account for the fact that a five-line multiplet is observed.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Q3: Write in the starting alkyl bromide used to form the following products. Include any
reactants, reagents, and solvents over the reaction arrow. If more than one step is
required, denote separate steps by using 1), 2), 3), etc.
H
OH
racemic
OH
OH
5
racemic
Draw the Lewis structure of the SO3-O(CH3)2 complex shown in the bottom right of slide 2in lecture 3-3 (“Me” means a CH3 group) – include all valence electron pairs and formal charges.From this structure, should the complex be a stable molecule? Explain.
Predict all organic product(s), including stereoisomers when applicable.
Chapter 13 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 1PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 2PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 3PCh. 13.3 - The following 1H NMR peaks were recorded on a...Ch. 13.3 - When the 1Η NMR spectrum of acetone, CH3COCH3, is...Ch. 13.4 - Each of the following compounds has a single 1H...Ch. 13.4 - Identify the different types of protons in the...Ch. 13.5 - How many peaks would you expect in the 1H NMR...Ch. 13.6 - Predict the splitting patterns you would expect...Ch. 13.6 - Draw structures for compounds that meet the...
Ch. 13.6 - The integrated 1H NMR spectrum of a compound of...Ch. 13.7 - Identify the indicated sets of protons as...Ch. 13.7 - How many kinds of electronically nonequivalent...Ch. 13.7 - How many absorptions would you expect (S)-malate,...Ch. 13.8 - 3-Bromo-1-phenyl-1-propene shows a complex NMR...Ch. 13.9 - How could you use 1H NMR to determine the...Ch. 13.11 - Prob. 17PCh. 13.11 - Propose structures for compounds that fit the...Ch. 13.11 - Prob. 19PCh. 13.12 - Prob. 20PCh. 13.12 - Prob. 21PCh. 13.12 - Prob. 22PCh. 13.13 - Prob. 23PCh. 13.SE - Into how many peaks would you expect the 1H NMR...Ch. 13.SE - How many absorptions would you expect the...Ch. 13.SE - Sketch what you might expect the 1H and 13C NMR...Ch. 13.SE - How many electronically nonequivalent kinds of...Ch. 13.SE - Identify the indicated protons in the following...Ch. 13.SE - Prob. 29APCh. 13.SE - Prob. 30APCh. 13.SE - When measured on a spectrometer operating at 200...Ch. 13.SE - Prob. 32APCh. 13.SE - Prob. 33APCh. 13.SE - How many types of nonequivalent protons are...Ch. 13.SE - The following compounds all show a single line in...Ch. 13.SE - Prob. 36APCh. 13.SE - Propose structures for compounds with the...Ch. 13.SE - Predict the splitting pattern for each kind of...Ch. 13.SE - Predict the splitting pattern for each kind of...Ch. 13.SE - Identify the indicated sets of protons as...Ch. 13.SE - Identify the indicated sets of protons as...Ch. 13.SE - The acid-catalyzed dehydration of...Ch. 13.SE - How could you use 1H NMR to distinguish between...Ch. 13.SE - Propose structures for compounds that fit the...Ch. 13.SE - Propose structures for the two compounds whose 1H...Ch. 13.SE - Prob. 46APCh. 13.SE - How many absorptions would you expect to observe...Ch. 13.SE - Prob. 48APCh. 13.SE - How could you use 1H and 13C NMR to help...Ch. 13.SE - How could you use 1H NMR, 13C NMR, and IR...Ch. 13.SE - Assign as many resonances as you can to specific...Ch. 13.SE - Assume that you have a compound with the formula...Ch. 13.SE - The compound whose 1H NMR spectrum is shown has...Ch. 13.SE - The compound whose 1H NMR spectrum is shown has...Ch. 13.SE - Propose structures for compounds that fit the...Ch. 13.SE - Long-range coupling between protons more than two...Ch. 13.SE - The 1H and 13C NMR spectra of compound A, C8H9Br,...Ch. 13.SE - Propose structures for the three compounds whose...Ch. 13.SE - The mass spectrum and 13C NMR spectrum of a...Ch. 13.SE - Compound A, a hydrocarbon with M+=96 in its mass...Ch. 13.SE - Propose a structure for compound C, which has...Ch. 13.SE - Prob. 62GPCh. 13.SE - Propose a structure for compound E, C7H12O2, which...Ch. 13.SE - Compound F, a hydrocarbon with M+=96 in its mass...Ch. 13.SE - 3-Methyl-2-butanol has five signals in its 13C NMR...Ch. 13.SE - A 13C NMR spectrum of commercially available...Ch. 13.SE - Carboxylic acids (RCO2H) react with alcohols (ROH)...Ch. 13.SE - Prob. 68GPCh. 13.SE - The proton NMR spectrum is shown for a compound...Ch. 13.SE - The proton NMR spectrum of a compound with the...Ch. 13.SE - The proton NMR spectrum is shown for a compound...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What I Have Learned Directions: Given the following reaction and the stress applied in each reaction, answer the question below. A. H2(g) + Cl2(g) 2 HCl(g) Stress applied: Decreasing the pressure 1. What is the Keq expression? 2. What will be the effect in the number of moles of HCl(g)? 3. What will be the Equilibrium Shift or the reaction? B. Fe3O4(s) + 4 H2(g) + heat 53 Fe(s) + 4 H₂O(g) Stress applied: Increasing the temperature 1. What is the Keq expression?. 2. What will be the effect in the volume of water vapor collected? 3. What will be the Equilibrium Shift or the reaction? C. 4 NH3(g) + 5 O2(g) 4 NO(g) + 6 H2O(g) + heat Stress applied: Increasing the volume of the container 1. What is the Keq expression?. 2. What will be the effect in the amount of H₂O? 3. What will be the Equilibrium Shift or the reaction?arrow_forwardConsider the solubility products (Ksp values) for the following compounds:SrSO4 (Ksp = 7.6 x 10−7), BaSO4 (Ksp = 1.5 x 10−9), SrCO3 (Ksp = 7.0 x 10−10), BaCO3 (Ksp = 1.6 x 10−9)Which anion is the harder base, CO32− or SO42−? Justify your answer.arrow_forwardQ1: a) Arrange the compounds in order of decreasing pKa, highest first. ОН ΟΗ ῸΗ дон ОН ОН CI Brarrow_forward
- (4 pts - 2 pts each part) A route that can be taken to prepare a hydrophobic (water-repellent) aerogel is to start with trichloromethylsilane, CH3SiCl3 as the silicon source. a. What is the chemical reaction that this undergoes to form a product with Si-OH groups? Write as complete of a chemical equation as you can. CI CI-SI-CH3 CI b. The formation of a byproduct is what drives this reaction - what is the byproduct (if you didn't already answer it in part (a)) and how/why does it form?arrow_forwardb) Circle the substrate that would not efficiently generate a Grignard reagent upon reaction with Mg in ether. CI Br ד c) Circle the Grignard reagents that contain incompatible functional groups. MgBr HO MgBr MgBr MgBr MgBr HO MgBrarrow_forwardQ2: Predict all organic product(s), including stereoisomers when applicable. PCC OH a) CH2Cl2 Page 2 of 5 Chem 0310 Organic Chemistry 1 HW Problem Sets b) .OH Na2Cr2O7, H+ OH PCC CH2Cl2 c) OHarrow_forward
- d) Circle the substrates that will give an achiral product after a Grignard reaction with CH3MgBr. Harrow_forwardQ4: Predict the organic products for the following reactions. Then draw curved arrow electron- pushing mechanism for the reactions. a) NaBH4 EtOH Page 4 of 5 Chem 0310 Organic Chemistry 1 HW Problem Sets b) 요 1. Et₂O H MgBr 2. H+, H₂Oarrow_forward5Helparrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning


Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning
NMR Spectroscopy; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SBir5wUS3Bo;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY