
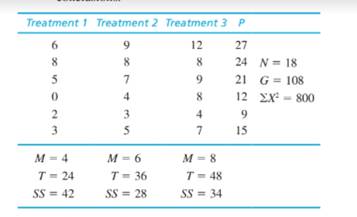
One of the primary advantages of a repealed-measures design, compared to an independent-measures design, is that it reduces the overall variability by removing variance caused by individual differences. The following data are from a research study comparing three treatment conditions.
- a. Assume that the data are from an independent- measures study using three separate samples, each with n = 6 participants. Ignore the column of P totals and use an independent-measures ANOVA with σ = .05 to test the significance of the
mean differences. - b. Now assume that the data are from a repealed- measures study using the same sample of n = 6 participants in all three treatment conditions. Use a repealed-measures ANOVA with α = .05 to test the significance of the mean differences.
- c. Explain why the two analyses lead to different conclusions.
a.
To test: The significance of the mean difference using independent measure ANOVA with
Answer to Problem 9P
The test of significance of the mean difference using independent measure ANOVA with
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
The data is provided in the question.
| Treatment 1 | Treatment 2 | Treatment 3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Calculation:
Step 1:
The null and alternative hypotheses are:
Null hypothesis:
Where
Alternate hypothesis:
Step 2:
Compute the degrees of freedom (df) for the between treatment effects, within treatment effects and total and corresponding sum of squares (SS).
Now, it is known that, for a given sample size, the degrees of freedom (df) is:
Thus,
The number of treatments,
As within treatments degrees of freedom,
With
Step 3:
Compute F-ratio.
The total sum of squares is:
The within treatment sum of squares is:
The within treatment sum of squares is:
Thus, here,
Now,
Similarly,
Finally F-ratio formula is:
Step 4:
Decision rule:
If
If
Since
Based on the result we fail to reject null and conclude, there is no significance difference among the three treatment.
b.
Answer to Problem 9P
Using repeated-measures ANOVA with
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Step 1:
The null and alternative hypotheses are:
Null hypothesis:
Where
Alternate hypothesis:
Step 2:
First stage:
Compute the degrees of freedom (df) for the between treatment effects, within treatment effects and total and corresponding sum of squares (SS).
Second stage:
Compute the values of between subject sum of squares and sum of squares due to error.
The between subject sum of squares is:
The sum of squares due to error is:
Thus,
Here,
Thus,
Step 3:
Step 4:
Decision rule:
If
If
Since
Based on result reject null and conclude significance mean difference exists.
c.
To find: Why the results of analysis differ in part a and part b.
Explanation of Solution
In part a, in independent-measures ANOVA, the individual differences is not present while in part b the individual differences exists. As a result, the individual differences have been eliminated in part b as these effects impact the results.
Thus, the results of analysis differ in part a and part b.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Aplia, 1 term Printed Access Card for Gravetter/Wallnau's Essentials of Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences, 8th
 Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning


