
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The resulting alkane should be identified after reacting the following compound with
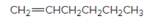
Concept Introduction:
Reaction of alkene with
Answer to Problem 53P
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated (
(b)
Interpretation:
The resulting alkane should be identified after reacting the following compound with
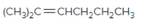
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of alkene with
Answer to Problem 53P
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated (
(c)
Interpretation:
The resulting alkane should be identified after reacting the following compound with
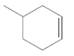
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of alkene with
Answer to Problem 53P
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated (
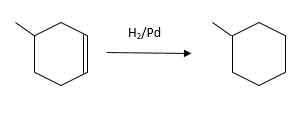
(d)
Interpretation:
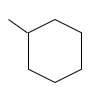
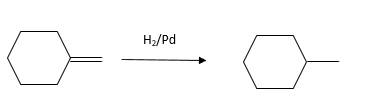
The resulting alkane should be identified after reacting the following compound with
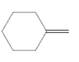
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of alkene with
Answer to Problem 53P
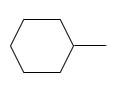
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated (
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Connect One Semester Access Card for General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry
- I. Write the IUPAC name of each organic compound. Structure NH2-C-CH-C СН 2-О-СН2-СH3 ČI ČI 1. H3C-CH=CH-C-CH, 2. OH CH CHCH CC=CH CH CH 3.arrow_forwardGive the structure of an alkane that fi ts each description. a. an alkane that contains only 1 ° and 4 ° carbons b. a cycloalkane that contains only 2 ° carbons c. an alkane of molecular formula C 6H 14 that contains a 4 ° carbon d. a cycloalkane that contains 2 ° and 3 ° carbonsarrow_forwardIn which of the following alkanes are two secondary carbon atoms present? CH CH3 CH, CH, b. CH-CH, a. CH, - сн c. CHy-CH-CH, CH3 d. CH y-CH CH -CHs Obl Barrow_forward
- Complete and balance each hydrocarbon combustion reaction. a. CH;CH;CH,CH3 + O2 b. CH2=CHCH, + 02 c. CH=CCH,CH3 + O2arrow_forward3. Name the following alkenes and alkynes. HC-CH-C=C-CH-CH--CH3 CH-CH H H H H. H C= C C C-H H. H.arrow_forwardIdentify the alkene from the following four molecules. HyC. CH HgC. CHa CH CH CH3 1. 2.arrow_forward
- Name each alkyne. CH,-C=C-CH, CH3 b. CH;-C=C-C-CH,-CH, CH3 c. CH=C-CH-CH2-CH2-CH, CH-CH, ČH,arrow_forwardP. CH3-CH2-CH3 Q. CH3-CH2-CH=CH-CH3 R. CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3 S. CH3-CH=CH-CH2-CH3 Which compounds belong to the same homologous series? P and Q Q and R R and S P and R Which structures show unsaturated hydrocarbons? P and Q P and R Q and S R and Sarrow_forwardname and draw the product/s formed from the reaction of 3-methylpent-2-ene: 1. with HBr 2. with Cl2 3. H2O in the presence of H2SO4 4. ethanol in the presence of H2SO4 5. Br2, H2O 6. [1] 9-BBN; [2] H2O2, OH-arrow_forward
- 1,4-Pentadiene (CH2=CH-CH2-CH=CH2) is a liquid at room temperature and has a density of 0.66 g/mL and molar mass of 68.12 g/mol. In a laboratory experiment, 3.80 mL of this compound was treated with 4.80 mL of conc. H2SO4 (100% w/w; molar mass 98.08 g/mol). Note that the density of conc. H2SO4 is 1.84 g/mL. The resulting sulfate ester was then treated with 1.20 mL of water (molar mass 18.02 g/mol) affording, after work- up, 2,4-pentanediol (molar mass 104.15 g/mol) as the crude product. The crude product was then purified by simple distillation, which yielded 2.00 g of pure product. a. Provide a balanced chemical equation to show the reaction between 1,4-pentadiene and sulfuric acid. Do not use molecular formulas in the chemical equation except for sulfuric acid. b. What reactant is the limiting reagent in this chemical equation? Show calculations to support your answer.arrow_forward1,4-Pentadiene (CH2=CH-CH2-CH=CH2) is a liquid at room temperature and has a density of 0.66 g/mL and molar mass of 68.12 g/mol. In a laboratory experiment, 3.80 mL of this compound was treated with 4.80 mL of conc. H2SO4 (100% w/w; molar mass 98.08 g/mol). Note that the density of conc. H2SO4 is 1.84 g/mL. The resulting sulfate ester was then treated with 1.20 mL of water (molar mass 18.02 g/mol) affording, after work- up, 2,4-pentanediol (molar mass 104.15 g/mol) as the crude product. The crude product was then purified by simple distillation, which yielded 2.00 g of pure product. What is the theoretical yield of 2,4-pentanediol expressed in grams? Show calculations. What is the percentage yield of pure 2,4-pentanediol?arrow_forward3. Name the following unbranched alkanes and indicate the type of formula being used. CH3 CH3 b. CH:(CH),CH, CH2 а. H-Ç-ç-C-c-ç-H d. ннннн C. f. H2C CH2 C,H12 е. H2C H2C `CH3arrow_forward
 Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning


