
(a)
To determine: The magnitude of the relative acceleration as a function of
(a)
Answer to Problem 41AP
Answer: The magnitude of the relative acceleration as a function of
Explanation of Solution
Explanation:
Given information:
A object of mass
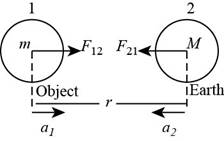
Figure I
Formula to calculate the relative acceleration is,
Formula to calculate the gravitational force exerted by the object on the Earth is,
By Newton’s law the force exerted by the object is,
From equation (II) and equation (III) is,
The forces
Substitute
By Newton’s law the force exerted by the Earth is,
From equation (IV) and equation (V) is,
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnitude of the relative acceleration as a function of
(b)
To determine: The magnitude of the relative acceleration for
(b)
Answer to Problem 41AP
Answer: The magnitude of the relative acceleration for
Explanation of Solution
Explanation:
Given information:
A object of mass
From equation (VI) the relative acceleration is,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnitude of the relative acceleration for
(c)
To determine: The magnitude of the relative acceleration for
(c)
Answer to Problem 41AP
Answer: The magnitude of the relative acceleration for
Explanation of Solution
Explanation:
Given information:
A object of mass
From equation (VI) the relative acceleration is,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnitude of the relative acceleration for
(d)
To determine: The magnitude of the relative acceleration for
(d)
Answer to Problem 41AP
Answer: The magnitude of the relative acceleration for
Explanation of Solution
Explanation:
Given information:
A object of mass
From equation (VI) the relative acceleration is,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnitude of the relative acceleration for
(e)
To determine: The pattern of variation of relative acceleration with
(e)
Answer to Problem 41AP
Answer: The relative acceleration is directly proportional to the mass
Explanation of Solution
Explanation:
Given information:
A object of mass
From equation (VI) the relative acceleration is,
This is the linear equation and shows the relative acceleration is directly proportional to the object having mass
Conclusion:
Therefore, the relative acceleration is directly proportional to the object having mass
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
- Find the center of mass of a cone of uniform density that has a radius R at the base, height h, and mass M. Let the origin be at the center of the base of the cone and have +z going through the cone vertex.arrow_forwardIn an elastic collision of two particles with masses m1 and m2, the initial velocities are u1 and u2 = u1. If the initial kinetic energies of the two particles are equal, find the conditions on u1/u2 and m1/m2 such that m1 is at rest after the collision. Examine both cases for the sign of .arrow_forwardconsider particle A of mass mA being somewhere between particle B of mass mB=2000 kg and particleS of mass mc=1000 kg, at just the right distance so that gravitational attraction to particle B and gravitational attraction to particle C are equal. Is this location nearer Particle B or nearer particle C?arrow_forward
- A space vehicle is traveling at 4450 km/h relative to the Earth when the exhausted rocket motor is disengaged and sent backward with a speed of 82 km/h relative to the command module. The mass of the motor is four times the mass of the module. What is the speed (km/h) of the command module relative to Earth after the separation? (Note: this answer requires slightly higher precision than normal.)arrow_forwardWith what force does a homogeneous ball of mass M attract a material point of mass m, located at distance a from the center of the ball (a>R)?arrow_forwardAnswer without rounding off: (COLLAB Gauss's Law for Mass) Journey through the Center of the Earth. A 1024-kg blue ball is dropped from an initial z-position of 3.8 x 106 m through the center of a planet with a radius of 8.5 x 106 m. If the mass of the planet is 48.8 x 1015 kg, measure the displacement of the ball at time t = 7 s?arrow_forward
- Suppose an object of mass m, initially travelling with a velocity v1, collides with an object of mass m initially at rest. Prove that the angle between the velocity vectors of the two objects of the two particles after the collision is 90 degrees.arrow_forwardTwo manned satellites approaching one another, at a relative speed of 0.250 m/s, intending to dock. The first has a mass of 4.00x103 kg, and the second a mass of 7.50x103 kg. Calculate the final velocity (after docking) by using the frame of reference in which the first satellite was originally at rest. Group of answer choices 0.218 m/s 0.195 m/s 0.172 m/s 0.163 m/sarrow_forwardIt is found that when a particular object with a mass of 0.41 kg is released from rest while immersed within a certain substance, the coefficient of proportionality regarding the resistive force is 0.621 kg/s. What is the magnitude of the resistive force that acts on this mass 1.49 s after being released? Let the resistive force be given by R = -bv (Assume that the gravitational force also acts)arrow_forward
- (Gauss's Law for Mass) Journey through the Center of the Earth. A 1024-kg blue ball is dropped from an initial z-position of 3 x 106 m through the center of a planet with radius 7.6 x 106 m. If the mass of the planet is 47.5 x 1015 kg, measure the displacement of the ball at time t = 7 s?arrow_forwardA space is traveling at 4300 km/hr relative to Earth. When the exhausted rocket motor is. disengaged. and sent backward with a speed of 82 km/hr relative to the command module. The mass of the rocket motor is 4 time the mass of the module. What is the speed of the command module relative to the earth just after the separation. Answer in km/hr.arrow_forward
 Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University


