
Shigley's Mechanical Engineering Design (McGraw-Hill Series in Mechanical Engineering)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780073398204
Author: Richard G Budynas, Keith J Nisbett
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 13, Problem 30P
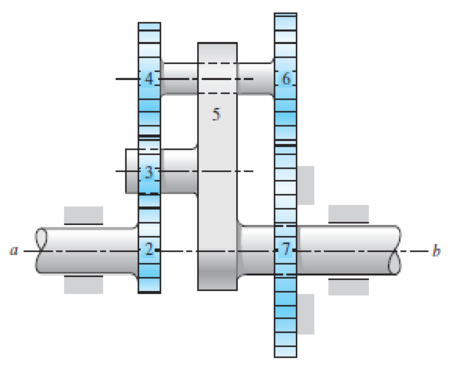
The tooth numbers for the gear train illustrated are N2 = 20, N3 = 16, N4 = 30, N6 = 36, and N7 = 46. Gear 7 is fixed. If shaft a is turned through 10 revolutions, how many turns will shaft b make?
Problem 13-30
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
You are tasked with designing a power drive system to transmit power between a motor and a conveyor belt in a manufacturing facility as illustrated in figure.
The design must ensure efficient power transmission, reliability, and safety. Given the following specifications and constraints, design drive system for this application:
Specifications:
Motor Power: The electric motor provides 10 kW of power at 1,500 RPM.
Output Speed: The output shaft should rotate at 150 rpm.
Design Decisions:
Transmission ratio: Determine the necessary drive ratio for the system.
Shaft Diameter: Design the shafts for both the motor and the conveyor end.
Material Selection: Choose appropriate materials for the gears, shafts.
Bearings: Select suitable rolling element bearings.
Constraints:
Space Limitation:
The available space for the gear drive system is limited to a 1-meter-long section.
Attribute 4 of CEP
Depth of knowledge required
Fundamentals-based, first principles analytical approach…
- |
العنوان
In non-continuous dieless drawing process for copper tube as shown in Fig. (1), take the
following data: Do-20mm, to=3mm, D=12mm, ti/to=0.6 and v.-15mm/s. Calculate: (1)
area reduction RA, (2) drawing velocity v. Knowing that: ti: final thickness
V.
Fig. (1)
ofthre
A direct extrusion operation produces the cross section shown in Fig. (2) from an aluminum
billet whose diameter 160 mm and length - 700 mm. Determine the length of the extruded
section at the end of the operation if the die angle -14°
60
X
Fig. (2) Note: all dimensions in mm.
Chapter 13 Solutions
Shigley's Mechanical Engineering Design (McGraw-Hill Series in Mechanical Engineering)
Ch. 13 - A 17-tooth spur pinion has a diametral pitch of 8...Ch. 13 - A 15-tooth spur pinion has a module of 3 mm and...Ch. 13 - A spur gearset has a module of 6 mm and a velocity...Ch. 13 - A 21-tooth spur pinion mates with a 28-tooth gear....Ch. 13 - A 20 straight-tooth bevel pinion having 14 teeth...Ch. 13 - A parallel helical gearset uses a 20-tooth pinion...Ch. 13 - A parallel helical gearset consists of a 19-tooth...Ch. 13 - To avoid the problem of interference in a pair of...Ch. 13 - Prob. 9PCh. 13 - Prob. 10P
Ch. 13 - Prob. 11PCh. 13 - Prob. 12PCh. 13 - Prob. 13PCh. 13 - Prob. 14PCh. 13 - A parallel-shaft gearset consists of an 18-tooth...Ch. 13 - The double-reduction helical gearset shown in the...Ch. 13 - Shaft a in the figure rotates at 600 rev/min in...Ch. 13 - The mechanism train shown consists of an...Ch. 13 - The figure shows a gear train consisting of a pair...Ch. 13 - A compound reverted gear trains are to be designed...Ch. 13 - Prob. 21PCh. 13 - Prob. 22PCh. 13 - Prob. 23PCh. 13 - A gearbox is to be designed with a compound...Ch. 13 - The tooth numbers for the automotive differential...Ch. 13 - Prob. 26PCh. 13 - In the reverted planetary train illustrated, find...Ch. 13 - Prob. 28PCh. 13 - Tooth numbers for the gear train shown in the...Ch. 13 - The tooth numbers for the gear train illustrated...Ch. 13 - Shaft a in the figure has a power input of 75 kW...Ch. 13 - The 24T 6-pitch 20 pinion 2 shown in the figure...Ch. 13 - The gears shown in the figure have a module of 12...Ch. 13 - The figure shows a pair of shaft-mounted spur...Ch. 13 - Prob. 35PCh. 13 - Prob. 36PCh. 13 - A speed-reducer gearbox containing a compound...Ch. 13 - For the countershaft in Prob. 3-72, p. 152, assume...Ch. 13 - Prob. 39PCh. 13 - Prob. 40PCh. 13 - Prob. 41PCh. 13 - Prob. 42PCh. 13 - The figure shows a 16T 20 straight bevel pinion...Ch. 13 - The figure shows a 10 diametral pitch 18-tooth 20...Ch. 13 - Prob. 45PCh. 13 - The gears shown in the figure have a normal...Ch. 13 - Prob. 47PCh. 13 - Prob. 48PCh. 13 - Prob. 49PCh. 13 - The figure shows a double-reduction helical...Ch. 13 - A right-hand single-tooth hardened-steel (hardness...Ch. 13 - The hub diameter and projection for the gear of...Ch. 13 - A 2-tooth left-hand worm transmits 34 hp at 600...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For hot rolling processes, show that the average strain rate can be given as: = (1+5)√RdIn(+1)arrow_forward: +0 usão العنوان on to A vertical true centrifugal casting process is used to produce bushings that are 250 mm long and 200 mm in outside diameter. If the rotational speed during solidification is 500 rev/min, determine the inside radii at the top and bottom of the bushing if R-2R. Take: -9.81 mis ۲/۱ ostrararrow_forward: +0 العنوان use only In conventional drawing of a stainless steel wire, the original diameter D.-3mm, the area reduction at each die stand r-40%, and the proposed final diameter D.-0.5mm, how many die stands are required to complete this process. онarrow_forward
- In non-continuous dieless drawing process for copper tube as shown in Fig. (1), take the following data: Do-20mm, to=3mm, D=12mm, ti/to=0.6 and vo-15mm/s. Calculate: (1) area reduction RA, (2) drawing velocity v. Knowing that: t₁: final thickness D₁ V. Fig. (1) Darrow_forwardA vertical true centrifugal casting process is used to produce bushings that are 250 mm long and 200 mm in outside diameter. If the rotational speed during solidification is 500 rev/min, determine the inside radii at the top and bottom of the bushing if R-2Rb. Take: 8-9.81 m/sarrow_forwardIn conventional drawing of a stainless steel wire, the original diameter D.-3mm, the area reduction at each die stand r-40%, and the proposed final diameter D₁-0.5mm, how many die stands are required to complete this process.arrow_forward
- A vertical true centrifugal casting process is used to produce bushings that are 250 mm long and 200 mm in outside diameter. If the rotational speed during solidification is 500 rev/min, determine the inside radii at the top and bottom of the bushing if R-2Rb. Take: 8-9.81 m/sarrow_forwardIn non-continuous dieless drawing process for copper tube as shown in Fig. (1), take the following data: Do-20mm, to=3mm, D=12mm, ti/to=0.6 and vo-15mm/s. Calculate: (1) area reduction RA, (2) drawing velocity v. Knowing that: t₁: final thickness D₁ V. Fig. (1) Darrow_forward-6- 8 من 8 Mechanical vibration HW-prob-1 lecture 8 By: Lecturer Mohammed O. attea The 8-lb body is released from rest a distance xo to the right of the equilibrium position. Determine the displacement x as a function of time t, where t = 0 is the time of release. c=2.5 lb-sec/ft wwwww k-3 lb/in. 8 lb Prob. -2 Find the value of (c) if the system is critically damping. Prob-3 Find Meq and Ceq at point B, Drive eq. of motion for the system below. Ш H -7~ + 目 T T & T тт +arrow_forward
- Q For the following plan of building foundation, Determine immediate settlement at points (A) and (B) knowing that: E,-25MPa, u=0.3, Depth of foundation (D) =1m, Depth of layer below base level of foundation (H)=10m. 3m 2m 100kPa A 2m 150kPa 5m 200kPa Barrow_forwardW PE 2 43 R² 80 + 10 + kr³ Ø8=0 +0 R²+J+ kr200 R² + J-) + k r² = 0 kr20 kr20 8+ W₁ = = 0 R²+1) R²+J+) 4 lec 8.pdf Mechanical vibration lecture 6 By: Lecturer Mohammed C. Attea HW1 (Energy method) Find equation of motion and natural frequency for the system shown in fig. by energy method. m. Jo 000 HW2// For the system Fig below find 1-F.B.D 2Eq.of motion 8 wn 4-0 (1) -5- marrow_forwardThe hose supplying the cylinder operating the bucket of a large excavator has fluid at 1000 psi flowing at 5 gpm. What is theavailable power in the line?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Power Transmission; Author: Terry Brown Mechanical Engineering;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YVm4LNVp1vA;License: Standard Youtube License