
CHEMISTRY 1111 LAB MANUAL >C<
1st Edition
ISBN: 9781307092097
Author: Chang
Publisher: MCG/CREATE
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 13, Problem 13.77QP
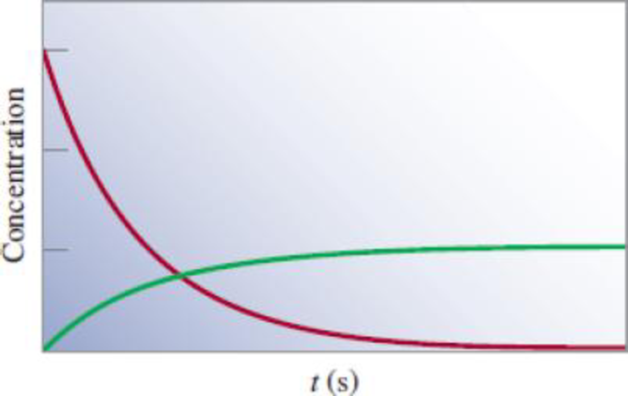
Which of the following equations best describes the diagram shown: (a) A → B, (b) A → 3B, (c) 3A → B?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Reaction 1
FeO(s) + CO(g) → Fe(1) + CO2(g)
AG" > 0
Reaction 2:
C(s) + CO2(g) → 2 CO(g)
AGzn <0
Overall reaction:
FeO(s) + C(s) → Fe(l) + CO(g)
AG n < 0
Subm
The chemical equations above represent the main reactions that occur during the production of Fe(l) under certain conditions. The overall reaction couples reactions 1 and 2, resulting in a
< 0?
thermodynamically favorable process. Which of the following best explains whether or not a particle diagram could represent how the coupling of reaction 1 and reaction 2 results in AG
A particle diagram that represents the increase in the volume of gaseous product particles would be a good representation of how the coupling of reactions 1 and 2 results in a
thermodynamically favorable process.
A particle diagram that represents the decrease in the average kinetic energy of the particles would be a good representation of how the coupling of reactions 1 and 2 results in a
thermodynamically favorable process.
A particle diagram cannot represent…
Consider the following scenario:
Carbon and oxygen combine to form carbon dioxide.
A chemical equation you might write for this reaction is C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g)-
If you were watching this reaction occur, how would you know when it was finished?
Hint: There is evidence in the equation!
Chlorine atoms in the atmosphere can react with ozone. Mathematically combine
the following two reactions to create an overall balanced equation with the lowest
whole-number coefficients. All chemical species in the reaction are gas-phase.
Which of the following best represents the overall reaction?
C1+03 → Clo+0₂
c10+ 0 → Cl + 0₂
To combine the reactions to create the overall balanced equation, you need to eliminate spectator
species and only include the remaining species.
O There are two lone chlorine atoms in the overall balanced reaction.
O Two chlorine atoms can cause the production of two oxygen molecules.
O CIO appears on the reactant and product side of the overall balanced reaction.
Lone oxygen atoms are consumed by the overall reaction.
O There is a net conversion of O2 to 03.
Chapter 13 Solutions
CHEMISTRY 1111 LAB MANUAL >C<
Ch. 13.1 - Write the rate expressions for the following...Ch. 13.1 - Consider the reaction 4PH3(g)P4(g)+6H2(g) Suppose...Ch. 13.1 - Write a balanced equation for a gas-phase reaction...Ch. 13.2 - The reaction of peroxydisulfate ion (S2O82) with...Ch. 13.2 - The relative rates of the reaction 2A + B ...Ch. 13.3 - The reaction 2A B is first order in A with a rate...Ch. 13.3 - Ethyl iodide (C2H5I) decomposes at a certain...Ch. 13.3 - Calculate the half-life of the decomposition of...Ch. 13.3 - Consider the first-order reaction A B in which A...Ch. 13.3 - The reaction 2A B is second order with a rate...
Ch. 13.3 - Consider the reaction A products. The half-life...Ch. 13.4 - The second-order rate constant for the...Ch. 13.4 - The first-order rate constant for the reaction of...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 1RCCh. 13.5 - The reaction between NO2 and CO to produce NO and...Ch. 13.5 - The rate law for the reaction H2 + 2IBr I2 + 2HBr...Ch. 13.6 - Which of the following is false regarding...Ch. 13 - What is meant by the rate of a chemical reaction?...Ch. 13 - Distinguish between average rate and instantaneous...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.3QPCh. 13 - Can you suggest two reactions that are very slow...Ch. 13 - Write the reaction rate expressions for the...Ch. 13 - Write the reaction rate expressions for the...Ch. 13 - Consider the reaction 2NO(g)+O2(g)2NO2(g) Suppose...Ch. 13 - Consider the reaction N2(g)+3H2(g)2NH3(g) Suppose...Ch. 13 - Explain what is meant by the rate law of a...Ch. 13 - What are the units for the rate constants of...Ch. 13 - Consider the zero-order reaction: A product. (a)...Ch. 13 - On which of the following properties does the rate...Ch. 13 - The rate law for the reaction...Ch. 13 - Use the data in Table 13.2 to calculate the rate...Ch. 13 - Consider the reaction A+Bproducts From the...Ch. 13 - Consider the reaction X+YZ From the following...Ch. 13 - Determine the overall orders of the reactions to...Ch. 13 - Consider the reaction AB The rate of the reaction...Ch. 13 - Cyclobutane decomposes to ethylene according to...Ch. 13 - The following gas-phase reaction was studied at...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.21QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.22QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.23QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.24QPCh. 13 - What is the half-life of a compound if 75 percent...Ch. 13 - The thermal decomposition of phosphine (PH3) into...Ch. 13 - The rate constant for the second-order reaction...Ch. 13 - The rate constant for the second-order reaction...Ch. 13 - Consider the first-order reaction A B shown here....Ch. 13 - The reaction X Y shown here follows first-order...Ch. 13 - Define activation energy. What role does...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.32QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.33QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.34QPCh. 13 - Sketch a potential energy versus reaction progress...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.36QPCh. 13 - The diagram in (a) shows the plots of ln k versus...Ch. 13 - Given the same reactant concentrations, the...Ch. 13 - Some reactions are described as parallel in that...Ch. 13 - Variation of the rate constant with temperature...Ch. 13 - For the reaction NO(g)+O3(g)NO2(g)+O2(g) the...Ch. 13 - The rate constant of a first-order reaction is...Ch. 13 - The rate constants of some reactions double with...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.44QPCh. 13 - Consider the second-order reaction...Ch. 13 - The rate at which tree crickets chirp is 2.0 102...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.47QPCh. 13 - What do we mean by the mechanism of a reaction?...Ch. 13 - Classify each of the following elementary steps as...Ch. 13 - Reactions can be classified as unimolecular,...Ch. 13 - Determine the molecularity and write the rate law...Ch. 13 - What is the rate-determining step of a reaction?...Ch. 13 - The equation for the combustion of ethane (C2H6)...Ch. 13 - Specify which of the following species cannot be...Ch. 13 - The rate law for the reaction...Ch. 13 - For the reaction X2 + Y + Z XY + XZ it is found...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.57QPCh. 13 - The rate law for the reaction...Ch. 13 - How does a catalyst increase the rate of a...Ch. 13 - What are the characteristics of a catalyst?Ch. 13 - A certain reaction is known to proceed slowly at...Ch. 13 - Distinguish between homogeneous catalysis and...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.63QPCh. 13 - The concentrations of enzymes in cells are usually...Ch. 13 - The diagram shown here represents a two-step...Ch. 13 - Consider the following mechanism for the...Ch. 13 - The following diagrams represent the progress of...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.68QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.69QPCh. 13 - List four factors that influence the rate of a...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.71QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.72QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.73QPCh. 13 - The following data were collected for the reaction...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.75QPCh. 13 - The rate of the reaction...Ch. 13 - Which of the following equations best describes...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.78QPCh. 13 - The bromination of acetone is acid-catalyzed:...Ch. 13 - The decomposition of N2O to N2 and O2 is a...Ch. 13 - The reaction S2O82+2I2SO42+I2 proceeds slowly in...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.82QPCh. 13 - The integrated rate law for the zero-order...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.84QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.85QPCh. 13 - The diagrams here represent the reaction A + B C...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.87QPCh. 13 - The rate law for the reaction 2NO2 (g) N2O4(g) is...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.89QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.90QPCh. 13 - Briefly comment on the effect of a catalyst on...Ch. 13 - When 6 g of granulated Zn is added to a solution...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.93QPCh. 13 - A certain first-order reaction is 35.5 percent...Ch. 13 - The decomposition of dinitrogen pentoxide has been...Ch. 13 - The thermal decomposition of N2O5 obeys...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.97QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.99QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.100QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.101QPCh. 13 - Chlorine oxide (ClO), which plays an important...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.103QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.104QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.105QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.106QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.107QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.108QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.109QPCh. 13 - Thallium(I) is oxidized by cerium(IV) as follows:...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.111QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.112QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.113QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.114QPCh. 13 - Strontium-90, a radioactive isotope, is a major...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.117QPCh. 13 - Consider the following potential energy profile...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.119QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.120QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.121QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.122QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.123QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.124QPCh. 13 - Polyethylene is used in many items, including...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.126QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.127QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.128QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.129QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.130QPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.131QPCh. 13 - A gas mixture containing CH3 fragments, C2H6...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.133QPCh. 13 - The activation energy (Ea) for the reaction...Ch. 13 - The rate constants for the first-order...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.136QPCh. 13 - An instructor performed a lecture demonstration of...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.138IMECh. 13 - Is the rate constant (k) of a reaction more...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.140IMECh. 13 - Prob. 13.141IMECh. 13 - Prob. 13.142IME
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 4.65 Using the web, find out how lead “poisons” the catalyst in a catalytic converter.arrow_forward4.80 The reaction shown below is used to destroy Freon-12 (CF2Cl2), preventing its release into the atmosphere. What mass of NaF will be formed if 250.0 kg of CF2Cl2 and 400.0 kg of Na2C2O4 are heated and allowed to react to completion? CF2Cl2+2Na2C2O42NaF+2NaCl+C+4CO2arrow_forwardConsider the two space shuttle fuel reactions in Exercises 81 and 82. Which reaction produces more energy per kilogram of reactant mixture (stoichiometric amounts)? 81. The reusable booster rockets of the space shuttle use a mixture of aluminum and ammonium perchlorate as fuel. A possible reaction is 3Al(s)+3NH4ClO4(s)Al2O3(s)+AlCl3(s)+3NO(g)+6H2O(g) Calculate H for this reaction 82. The space shuttle Orbiter utilizes the oxidation of methylhydrazine by dinitrogen tetroxide for propulsion: 4N2H3CH3(l)+5N2O4(l)12H2O(g)+9N2(g)+4CO2(g) Calculate H for this reactionarrow_forward
- Indicate to which of the following types of reactions each of the statements listed applies: combination, decomposition, displacement, exchange, and combustion. More than one answer is possible for a given statement. a. An element may be a reactant. b. An element may be a product. c. A compound may be a reactant. d. A compound may be a product.arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward1.14 g H2 is allowed to react with 10.2 g N2, producing 1.08 g NH3.arrow_forward
- The cycle of copper reactions illustrates important principles of chemical reactions. The cycle begins with elemental copper, which in a first reaction is oxidized to copper(II) cation. Copper(II) is then carried through different solid forms. In the last step, copper(II) cation is reduced, the copper metal is regenerated, and the cycle is closed. The five key steps are 1. 3Cu(s) + 2NO, + 8H* → 2. Cu?* (аq) + 2ОН (аq) — Си(ОН),(s) 3. Cu(OH),(s) → CuO(s) + H2O 4. CuO(s) + 2H* → * (aq) + Zn(s) → Zn²+ (aq) + Cu(s) 3Cu2+ (aq) + 4H2O + 2NO Cu?* (аq) + Ha0 5. Сu2+ Assume that you want to carry out a sequence of cycle reactions. In order to use the right amount of reagents, present answers to the following questions. Question 1 How much HNO3 is required to completely react with 1.84 g of copper in the first step of the cycle? mmol What volume of 16M HNO3 solution provides the required amount of the acid? mL How much NaOH is required to precipitate all formed copper(II) cations as Cu(OH), in…arrow_forwardBlast furnaces extra pure iron from the iron(III) oxide in iron ore in a two step sequence. In the first step, carbon and oxygen react to form carbon monoxide: 2C(s) + O₂(g) → 2CO (g) In the second step, iron(III) oxide and carbon monoxide react to form iron and carbon dioxide: Fe₂O3(s) + 3CO(g) → 2Fe(s) + 3 CO₂ (g) crosoft C tab Suppose the yield of the first step is 60.% and the yield of the second step is 72.%. Calculate the mass of carbon required to make 5.0 kg of iron. Be sure your answer has a unit symbol, if needed, and is rounded to the correct number of significant digits. 0 W Microsoft Microsoft 6.52.210... s lock esc Explanation 1 Q A N 10 2 Check 9,041 W S X H 1 control option command # #3 E D x10 6 14 X $ 4 DEC 3 C R ロ・ロ F S Q Search or enter website name ci dº % 5 V T tv G > MacBook Pro 6 B Y H & 7 Ⓒ2022 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center Accessibility U N 00 * 8 J 1 M 7 ( 9 K A O H O L P I W [ command option ? C HAI barrow_forwardSuppose a pair of chemical compounds A and B can react in two different ways: A+B → C Reaction 1 gives product C. A+B → D Reaction 2 gives product D. The following facts are known about the two reactions: ● Reaction 1 is endothermic and Reaction 2 is exothermic. • If a reaction vessel is charged ("filled") with A and B, then at first C is produced faster than D. Use these facts to sketch a qualitative reaction energy diagram for both reactions. Note: because these sketches are only qualitative, the energies don't have to be exact. They only have to have the right relationship to each other. For exam if one energy is less than another, that fact should be clear in your sketch. Reaction 1 Reaction 2 energy energy reaction coordinate A + B A + B reaction coordinate Darrow_forward
- Detonation of nitroglycerin proceeds as follows:4 C3H5N3O9(l)------>12 CO2(g) + 6 N2(g) + O2(g) + 10 H2O(g)(a) If a sample containing 2.00 mL of nitroglycerin (density =1.592 g/mL) is detonated, how many moles of gas are produced?(b) If each mole of gas occupies 55 L under the conditionsof the explosion, how many liters of gas are produced?(c) How many grams of N2 are produced in the detonation?arrow_forwardSuppose a pair of chemical compounds A and B can react in two different ways: A+B C Reaction 1 gives product C. A+B D →> Reaction 2 gives product D. The following facts are known about the two reactions: • Reaction 1 is endothermic and Reaction 2 is exothermic. • If a reaction vessel is charged ("filled") with A and B, then at first C is produced faster than D. Use these facts to sketch a qualitative reaction energy diagram for both reactions. Note: because these sketches are only qualitative, the energies don't have to be exact. They only have to have the right relationship to each other. For if one energy is less than another, that fact should be clear in your sketch. energy A + B Reaction 1 reaction coordinate energy A + B Reaction 2 reaction coordinate ☑arrow_forwardHydrogen peroxide decomposes as shown below: 2 H2O2 → 2 H2O + O2 molar mass H2O2 = (34.0 g/mol) A sample of hydrogen peroxide solution was analyzed using the procedure from the “Enzymatic Decomposition and Analysis of Hydrogen Peroxide” experiment. A 7.54 g sample of the solution generated 0.0277 mol of oxygen gas. Calculate the mass percent of H2O2 in the solution.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399425
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Cengage Learning

General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285853918
Author:H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079243
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Kinetics: Chemistry's Demolition Derby - Crash Course Chemistry #32; Author: Crash Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7qOFtL3VEBc;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY