
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
1st Edition
ISBN: 9780130970695
Author: Peter S. Shaffer, Lillian C. McDermott
Publisher: Addison Wesley
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 12.2, Problem 4cT
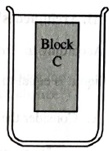
A third block, C, of the same size and shape as A and B but with slightly greater mass thanblock B is released from rest at the center of the beaker. Two students predict the finalposition of the block and draw the sketch at right.
| Student 1: | Since this block is heavier than block B, it will not go up as high after it is released, as shown at right. |
| Student 2: | Yes, I agree, the buoyant force is slightly less than the weight of this block, so it should come to rest a bit below the surface. |
Explain what is wrong with each statement and with the diagram.
Student drawing
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
a cubic foot of argon at 20 degrees celsius is isentropically compressed from 1 atm to 425 KPa. What is the new temperature and density?
Calculate the variance of the calculated accelerations. The free fall height was 1753 mm. The measured release and catch times were:
222.22 800.00
61.11 641.67
0.00 588.89
11.11 588.89
8.33 588.89
11.11 588.89
5.56 586.11
2.78 583.33
Give in the answer window the calculated repeated experiment variance in m/s2.
No chatgpt pls will upvote
Chapter 12 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Ch. 12.1 - For each layer, draw a free-body diagram in the...Ch. 12.1 - Imagine that a small hole is opened in the...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 2aTCh. 12.1 - Suppose you wanted to determine the pressure at...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 2cTCh. 12.1 - Prob. 2dTCh. 12.1 - Draw a freebody diagram for the small voulme of...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 3bTCh. 12.1 - Use your answer to part B to compare the pressures...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 3dT
Ch. 12.1 - Consider the following student dialogue: Student...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 4aTCh. 12.1 - The right end of the tube is now scaled with a...Ch. 12.1 - A syringe is used to remove some water from the...Ch. 12.2 - A cubical block is observed to float in a beaker...Ch. 12.2 - Prob. 1bTCh. 12.2 - Imagine that you were to release the block from...Ch. 12.2 - In general, does the buoyant force on an object...Ch. 12.2 - By how much does the volume reading increase when...Ch. 12.2 - Does the volume of water displaced by a completely...Ch. 12.2 - Consider the following statement made by a...Ch. 12.2 - A rectangular block, A, is released from rest at...Ch. 12.2 - A second block, B,of the same size and shape as A...Ch. 12.2 - A third block, C, of the same size and shape as A...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
The data were obtained from a use-dilution test comparing four disinfectants against Salmonella choleraesuis. G...
Microbiology: An Introduction
Why is it necessary to be in a pressurized cabin when flying at 30,000 feet?
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Name the components (including muscles) of the thoracic cage. List the contents of the thorax.
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
15.1 What purpose do the bla and lacZ genes serve in the plasmid vector ?
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
The following results were obtained from a broth dilution test for microbial susceptibility. Antibiotic Concent...
Microbiology: An Introduction
28. As the earth mates, what is the speed of (a) a physics student in Miami. Florida. at latitude 26°, and (b) ...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 2. Consider the situation described in problem 1 where light emerges horizontally from ground level. Take k = 0.0020 m' and no = 1.0001 and find at which horizontal distance, x, the ray reaches a height of y = 1.5 m.arrow_forward2-3. Consider the situation of the reflection of a pulse at the interface of two string described in the previous problem. In addition to the net disturbances being equal at the junction, the slope of the net disturbances must also be equal at the junction at all times. Given that p1 = 4.0 g/m, H2 = 9.0 g/m and Aj = 0.50 cm find 2. A, (Answer: -0.10 cm) and 3. Ay. (Answer: 0.40 cm)please I need to show all work step by step problems 2 and 3arrow_forwardFrom number 2 and 3 I just want to show all problems step by step please do not short cut look for formulaarrow_forward
- Look at the answer and please show all work step by steparrow_forward3. As a woman, who's eyes are h = 1.5 m above the ground, looks down the road sees a tree with height H = 9.0 m. Below the tree is what appears to be a reflection of the tree. The observation of this apparent reflection gives the illusion of water on the roadway. This effect is commonly called a mirage. Use the results of questions 1 and 2 and the principle of ray reversibility to analyze the diagram below. Assume that light leaving the top of the tree bends toward the horizontal until it just grazes ground level. After that, the ray bends upward eventually reaching the woman's eyes. The woman interprets this incoming light as if it came from an image of the tree. Determine the size, H', of the image. (Answer 8.8 m) please show all work step by steparrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON
The Laws of Thermodynamics, Entropy, and Gibbs Free Energy; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8N1BxHgsoOw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY