
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780134319650
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 12.2, Problem 12.11P
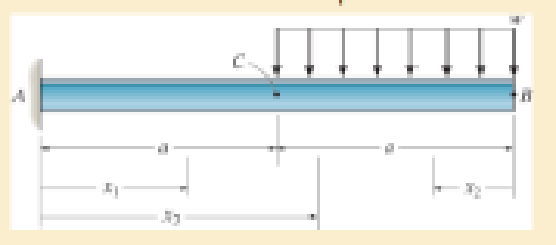
Determine the equations of the elastic curve using the coordinates x1 and x3. What is the slope at B and deflection at C? El is constant.
Probs. 12–10/11
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule19:59
Students have asked these similar questions
B:
Find the numerical solution for the 2D equation below and calculate the temperature values for
each grid point shown in Fig. 2 (show all steps).
(Do only one trail using following initial values and show the final matrix)
T₂
0
T3
0
loc
Show all work. Indicate the origin that is used for each plane.
Identify the Miller indices for the following planes.
N
23
1
A)
X
B)
y
the following table gives weight gain time data for the oxidation of some metal at an elevated temperature
W(mg/cm2). Time (min)
4.66 20
11.7 50
41.1 175
a) determin whether the oxidation kinetics obey a linear, parabolic, or logarithmic rate expression.
b) Now compute W after a time of 1000 min
Chapter 12 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Ch. 12.2 - In each case, determine the internal bending...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the slope and deflection of end A of the...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the slope and deflection of end A of the...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the slope of end A of the cantilevered...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the maximum deflection of the simply...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the maximum deflection of the simply...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the slope of the simply supported beam...Ch. 12.2 - An L2 steel strap having a thickness of 0.125 in....Ch. 12.2 - The L2 steel blade of the band saw wraps around...Ch. 12.2 - A picture is taken of a man performing a pole...
Ch. 12.2 - El is constant. Prob. 124Ch. 12.2 - Determine the deflection of end C of the...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the elastic curve for the cantilevered...Ch. 12.2 - The A-36 steel beam has a depth of 10 in. and is...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the equations of the elastic curve using...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the equations of the elastic curve for...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the equations of the elastic curve using...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the equations of the elastic curve using...Ch. 12.2 - Draw the bending-moment diagram for the shaft and...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the maximum deflection of the beam and...Ch. 12.2 - The simply supported shaft has a moment of inertia...Ch. 12.2 - A torque wrench is used to tighten the nut on a...Ch. 12.2 - The pipe can be assumed roller supported at its...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the equations of the elastic curve for...Ch. 12.2 - The bar is supported by a roller constraint at B,...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the deflection at B of the bar in Prob....Ch. 12.2 - Determine the equations of the elastic curve using...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the maximum deflection of the solid...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the elastic curve for the cantilevered...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the equations of the elastic curve using...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the equations of the elastic curve using...Ch. 12.2 - The floor beam of the airplane is subjected to the...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the maximum deflection of the simply...Ch. 12.2 - The beam is made of a material having a specific...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the slope at end B and the maximum...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the equation of the elastic curve using...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the equations of the elastic curve using...Ch. 12.3 - The shaft is supported at A by a journal bearing...Ch. 12.3 - The shaft supports the two pulley loads shown....Ch. 12.3 - The beam is made of a ceramic material. If it is...Ch. 12.3 - Determine the equation of the elastic curve, the...Ch. 12.3 - The beam is subjected to the load shown. Determine...Ch. 12.3 - Determine the equation of the elastic curve, the...Ch. 12.3 - Determine the equation of the elastic curve and...Ch. 12.3 - The shaft supports the two pulley loads. Determine...Ch. 12.3 - Determine the maximum deflection of the...Ch. 12.3 - Determine the slope at A and the deflection of end...Ch. 12.3 - Determine the maximum deflection in region AB of...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.42PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.43PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.44PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.45PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.46PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.47PCh. 12.3 - Determine the value of a so that the displacement...Ch. 12.3 - Determine the displacement at C and the slope at...Ch. 12.3 - Determine the equations of the slope and elastic...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the slope and deflection of end A of the...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the slope and deflection of end A of the...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the slope and deflection of end A of the...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the slope and deflection at A of the...Ch. 12.4 - Prob. 12.11FPCh. 12.4 - Determine the maximum deflection of the simply...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the slope and deflection at C. El is...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the slope and deflection at C. El is...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the deflection of end B of the...Ch. 12.4 - Prob. 12.54PCh. 12.4 - The composite simply supported steel shaft is...Ch. 12.4 - Prob. 12.56PCh. 12.4 - Prob. 12.57PCh. 12.4 - Determine the deflection at C and the slope of the...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the maximum deflection of the...Ch. 12.4 - Prob. 12.60PCh. 12.4 - Determine the position a of the roller support B...Ch. 12.4 - Prob. 12.62PCh. 12.4 - Determine the slope and the deflection of end B of...Ch. 12.4 - The two A-36 steel bars have a thickness of 1 in....Ch. 12.4 - Determine the slope at A and the displacement at...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the deflection at C and the slopes at...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the maximum deflection within region AB....Ch. 12.4 - Determine the slope at A and the maximum...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the slope at C and the deflection at B....Ch. 12.4 - Determine the slope at A and the maximum...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the displacement of the 20-mm-diameter...Ch. 12.4 - The two force components act on the tire of the...Ch. 12.4 - Prob. 12.73PCh. 12.4 - The rod is constructed from two shafts for which...Ch. 12.4 - Prob. 12.75PCh. 12.4 - Determine the slope at point A and the maximum...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the position a of roller support B in...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the slope at B and deflection at C. El...Ch. 12.4 - Prob. 12.79PCh. 12.4 - Prob. 12.80PCh. 12.4 - Prob. 12.81PCh. 12.4 - Determine the maximum deflection of the beam. El...Ch. 12.5 - The W10 15 cantilevered beam is made of A-36...Ch. 12.5 - The W10 15 cantilevered beam is made of A-36...Ch. 12.5 - The W14 43 simply supported beam is made of A992...Ch. 12.5 - The W14 43 simply supported beam is made of A992...Ch. 12.5 - The W14 43 simply supported beam is made of A-36...Ch. 12.5 - The W14 43 simply supported beam is made of A-36...Ch. 12.5 - The W8 48 cantilevered beam is made of A-36 steel...Ch. 12.5 - The beam supports the loading shown. Code...Ch. 12.5 - The W24 104 A-36 steel beam is used to support...Ch. 12.5 - The W8 48 cantilevered beam is made of A-36 steel...Ch. 12.5 - The rod is pinned at its end A and attached to a...Ch. 12.5 - Prob. 12.94PCh. 12.5 - The pipe assembly consists of three equal-sized...Ch. 12.5 - The assembly consists of a cantilevered beam CS...Ch. 12.5 - Determine the smallest force F required to attract...Ch. 12.5 - Prob. 12.98PCh. 12.7 - Determine the reactions at the supports A and B,...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the reactions at the supports, then draw...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the reactions at the supports A, B, and...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the reactions at the supports A and B,...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the reactions at the supports A and B,...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the moment reactions at the supports A...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the reactions at the supports A and B,...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the reactions at the support A and B. EI...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the reactions at roller support A and...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the moment reactions at the supports A...Ch. 12.7 - The beam has a constant E1I1 and is supported by...Ch. 12.7 - The beam is supported by a pin at A, a roller at...Ch. 12.8 - Determine the moment reactions at the supports A...Ch. 12.8 - Determine the reaction at the supports, then draw...Ch. 12.8 - Determine the vertical reaction at the journal...Ch. 12.8 - Determine the reactions at the supports A and B,...Ch. 12.8 - Determine the reactions at the supports. EI is...Ch. 12.8 - Determine the vertical reaction at the journal...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reactions at the fixed support A and...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reactions at the fixed support A and...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reactions at the fixed support A and...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reaction at the roller B. EI is...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reaction at the roller B. EI is...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reaction at the roller support B if...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reactions at the journal bearing...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reactions at the supports, then draw...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reactions at the supports, then draw...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reactions at the supports A and B....Ch. 12.9 - The beam is used to support the 20-kip load....Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reactions at the supports A and B....Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reactions at the supports A and B....Ch. 12.9 - Before the uniform distributed load is applied to...Ch. 12.9 - The fixed supported beam AB is strengthened using...Ch. 12.9 - The beam has a constant E1I1, and is supported by...Ch. 12.9 - The beam is supported by the bolted supports at...Ch. 12.9 - Each of the two members is made from 6061-T6...Ch. 12.9 - The beam is made from a soft linear elastic...Ch. 12.9 - The beam AB has a moment of inertia I = 475 in4...Ch. 12.9 - The rim on the flywheel has a thickness t, width...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the moment developed in each corner....Ch. 12 - Determine the equation of the elastic curve. Use...Ch. 12 - Draw the bending-moment diagram for the shaft and...Ch. 12 - Determine the moment reactions at the supports A...Ch. 12 - Specify the slope at A and the maximum deflection....Ch. 12 - Determine the maximum deflection between the...Ch. 12 - Determine the slope at B and the deflection at C....Ch. 12 - Determine the reactions, then draw the shear and...Ch. 12 - El is constant.Ch. 12 - Using the method of superposition, determine the...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
7.13* For a bearing
DE = NUS 5 53’56 ”WT and angles to the right, compute the bearing of PG if angle
DEF 2 88°...
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
Determine the slope and deflection of end A of the cantilevered beam. E = 200 GPa and I = 65.0(106) mm4. F122
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
The keywordindicates that a method does not return a value.
Java How to Program, Early Objects (11th Edition) (Deitel: How to Program)
In the following exercises, write a program to carry out the task. The program should use variables for each of...
Introduction To Programming Using Visual Basic (11th Edition)
Assume the following variables are defined: int age; double pay; char section; Write a single cin statement tha...
Starting Out with C++ from Control Structures to Objects (9th Edition)
Under what circumstances does an object become a candidate for garbage collection?
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A cylindrical specimen of aluminum is pulled in tension. Use the stress v. strain plot below for this specimen of Al to answer parts (a) - (f). Hint: Each strain increment is 0.004. Be sure to include your engineering problem solving method per the class rubric. 400 350 300 250 Stress (MPa) 200 150 100 50 Aluminum (Stress v. Strain) 0 0 0.02 0.04 0.06 0.08 Strain 0.1 0.12 0.14 0.16 a. Compute the modulus of elasticity. b. Determine the yield strength at a strain offset of 0.002. c. Determine the tensile strength of this metal. d. Compute the ductility in percent elongation. e. Compute the modulus of resilience. f. Determine the elastic strain recovery for an unloaded stress of 340 MPa.arrow_forwardConsider a single crystal of silver oriented such that a tensile stress is applied along a [112] direction. If slip occurs on a (011) plane and in a [111] direction and is initiated at an applied tensile stress of 15.9 MPa, compute the critical resolved shear stress.arrow_forwardA hypothetical component must not fail when a tensile stress of 15.25 MPa is applied. Determine the maximum allowable internal crack length if the surface energy of the component is 1.50 J/m2. Assume a modulus of elasticity of 350 GPa.arrow_forward
- Fresh air at 21.1 C in which partial pressure of water vapor is 0.018 atmosphere is blown at the rate of 214 m3/h first through a preheater and then adiabatically saturated in spray chambers to 100% saturation and again reheated this reheated air has humidity of 0.024 kg water vapor per kg dry air. It is assumed that the fresh air and the air leaving the re-heater have the same percentage humidity. Determine:- a- The temperature of preheater, spray-chamber and re-heater b- Heat requirement for preheating and re-heating 11:39 مarrow_forwardThe answer to the problem is 7.24 N. Please show me how to get the final answerarrow_forwardThe answer to the problem is 17.9N. Please show me how to get the final answerarrow_forward
- The answer to the problem is 2.93 ft/s. Please show me how to get the final answerarrow_forwardExample(3): 0.15 kg/s steam at atmospheric pressure and superheated to 400 K is bled into an air stream at 320 K and 20 per cent relative humidity. What is the temperature, enthalpy, and relative humidity of the mixed stream if the air is flowing at 5 kg/ s? How much steam would be required to provide an exit temperature of 330 K and what would be the humidity of this mixture? 11:39 مarrow_forwardThe answer to the problem is 31.3rad/s. Please show me how to get the final answerarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Solids: Lesson 53 - Slope and Deflection of Beams Intro; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I7lTq68JRmY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY