
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780131495081
Author: Douglas C. Giancoli
Publisher: Addison-Wesley
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 12, Problem 85GP
Two identical, uniform beams are symmetrically set up against each other (Fig. 12–92) on a floor with which they have a coefficient of friction μs = 0.50. What is the minimum angle the beams can make with the floor and still not fall?
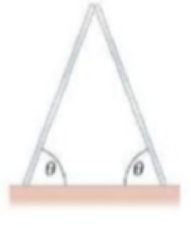
FIGURE 12–92
Problem 85.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Two identical, uniform beams are symmetrically set up
against each other (Fig. 9–87) on a floor
with which they have a coefficient of fric-
tion µs = 0.50. What is the minimum
angle the beams can make with the
floor and still not fall?
FIGURE 9-87
Problem 71.
-
5. Two identical, uniform beams of length 3 m and weighing 260 N each are
connected at one end by a frictionless hinge. A light horizontal crossbar, attached at the
midpoints of the beams maintains an angle 50° between the beams. The beams are
suspended from the ceiling by vertical wires so they form a V. See figure. (a) What force
does the crossbar exert on each beam? (b) Is the crossbar under compression or tension,
i.e. are the ends of the crossbar being pushed together or stretched farther apart? (c) What
force (magnitude and direction) does the hinge exert on each beam?
Crossbar
Hinge
(III) A uniform ladder of mass m and length l
leans at an angle 0 against a frictionless wall,
Fig. 9–70. If the coefficient of static friction
between the ladder and the ground is µs,
determine a formula for the minimum
angle at which the ladder will not slip.
FIGURE 9-70
Problem 30.
Chapter 12 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
Ch. 12.1 - For simplicity, we wrote the equation in Example...Ch. 12.2 - We did not need to use the force equation to solve...Ch. 12.2 - CHAPTER-OPENING QUESTIONGuess Now! The diving...Ch. 12.2 - Why is it reasonable to ignore friction along the...Ch. 12.4 - Two steel wires have the same length and are under...Ch. 12 - Describe several situations in which an object is...Ch. 12 - A bungee jumper momentarily comes to rest at the...Ch. 12 - Prob. 3QCh. 12 - Your doctors scale has arms on which weights slide...Ch. 12 - A ground retaining wall is shown in Fig. 1240a....
Ch. 12 - Can the sum of the torques on an object be zero...Ch. 12 - A ladder, leaning against a wall, makes a 60 angle...Ch. 12 - A uniform meter stick supported at the 25-cm mark...Ch. 12 - Prob. 9QCh. 12 - Prob. 10QCh. 12 - Place yourself facing the edge of an open door....Ch. 12 - Prob. 12QCh. 12 - Prob. 13QCh. 12 - Which of the configurations of brick, (a) or (b)...Ch. 12 - Name the type of equilibrium for each position of...Ch. 12 - Is the Youngs modulus for a bungee cord smaller or...Ch. 12 - Examine how a pair of scissors or shears cuts...Ch. 12 - Materials such as ordinary concrete and stone are...Ch. 12 - (I) Three forces are applied to a tree sapling, as...Ch. 12 - (I) Approximately what magnitude force, FM, must...Ch. 12 - Prob. 3PCh. 12 - (I) A tower crane (Fig. 1248a) must always be...Ch. 12 - (II) Calculate the forces FA and FB that the...Ch. 12 - Prob. 6PCh. 12 - (II) The two trees in Fig. 1250 are 6.6 m apart. A...Ch. 12 - Prob. 8PCh. 12 - Prob. 9PCh. 12 - Prob. 10PCh. 12 - (II) Find the tension in the two cords shown in...Ch. 12 - (II) Find the tension in the two wires supporting...Ch. 12 - Prob. 13PCh. 12 - (II) The force required to pull the cork out of...Ch. 12 - (II) Calculate and FA and FB for the beam shown in...Ch. 12 - Prob. 16PCh. 12 - Prob. 17PCh. 12 - (II) Three children are trying to balance on a...Ch. 12 - (II) The Achilles tendon is attached to the rear...Ch. 12 - (II) A shop sign weighing 215 N is supported by a...Ch. 12 - (II) A traffic light hangs from a pole as shown in...Ch. 12 - (II) A uniform steel beam has a mass of 940 kg. On...Ch. 12 - (II) Two wires run from the top of a pole 2.6 m...Ch. 12 - (II) A large 62.0-kg board is propped at a 45...Ch. 12 - (II) Repeat Problem 24 assuming the coefficient of...Ch. 12 - (II) A 0.75-kg sheet hangs from a massless...Ch. 12 - (II) A uniform rod AB of length 5.0 m and mass M =...Ch. 12 - (III) A 56.0-kg person stands 2.0 m from the...Ch. 12 - (III) A door 2.30 m high and 1.30 m wide has a...Ch. 12 - (III) A cubic crate of side s = 2.0 m is...Ch. 12 - (III) A refrigerator is approximately a uniform...Ch. 12 - (III) A uniform ladder of mass m and length leans...Ch. 12 - Prob. 33PCh. 12 - (I) A nylon string on a tennis racket is under a...Ch. 12 - (I) A marble column of cross-sectional area 1.4 m2...Ch. 12 - (I) By how much is the column in Problem 35...Ch. 12 - (I) A sign (mass 1700 kg) hangs from the end of a...Ch. 12 - (II) How much pressure is needed to compress the...Ch. 12 - Prob. 39PCh. 12 - (II) At depths of 2000 m in the sea, the pressure...Ch. 12 - (III) A pole projects horizontally from the front...Ch. 12 - (I) The femur bone in the human leg has a minimum...Ch. 12 - (II) (a) What is the maximum tension possible in a...Ch. 12 - (II) If a compressive force of 3.3 104 N is...Ch. 12 - (II) (a) What is the minimum cross-sectional area...Ch. 12 - (II) Assume the supports of the uniform cantilever...Ch. 12 - (II) An iron bolt is used to connect two iron...Ch. 12 - (II) A steel cable is to support an elevator whose...Ch. 12 - (II) A heavy load Mg = 66.0 kN hangs at point E of...Ch. 12 - (II) Figure 1271 shows a simple truss that carries...Ch. 12 - (II) (a) What minimum cross-sectional area must...Ch. 12 - (II) onsider again Example 1211 but this time...Ch. 12 - (III) The truss shown in Fig. 1272 supports a...Ch. 12 - (III) Suppose in Example 1211, a 23-ton truck (m =...Ch. 12 - (III) For the Pratt truss shown in Fig. 1273,...Ch. 12 - (II) How high must a pointed arch be if it is to...Ch. 12 - The mobile in Fig. 1274 is in equilibrium. Object...Ch. 12 - A tightly stretched high wire is 36 m long. It...Ch. 12 - What minimum horizontal force F is needed to pull...Ch. 12 - A 28-kg round table is supported by three legs...Ch. 12 - When a wood shelf of mass 6.6 kg is fastened...Ch. 12 - Prob. 62GPCh. 12 - The center of gravity of a loaded truck depends on...Ch. 12 - In Fig. 1279, consider the right-hand...Ch. 12 - Assume that a single-span suspension bridge such...Ch. 12 - When a mass of 25 kg is hung from the middle of a...Ch. 12 - The forces acting on a 77,000-kg aircraft flying...Ch. 12 - A uniform flexible steel cable of weight mg is...Ch. 12 - A 20.0-m-long uniform beam weighing 650 N rests on...Ch. 12 - A cube of side l rests on a rough floor. It is...Ch. 12 - A 65.0-kg painter is on a uniform 25-kg scaffold...Ch. 12 - A man doing push-ups pauses in the position shown...Ch. 12 - A 23-kg sphere rests between two smooth planes as...Ch. 12 - A 15.0-kg ball is supported from the ceiling by...Ch. 12 - Parachutists whose chutes have failed to open have...Ch. 12 - A steel wire 2.3 mm in diameter stretches by...Ch. 12 - A 2500-kg trailer is attached to a stationary...Ch. 12 - Prob. 78GPCh. 12 - A 25-kg object is being lifted by pulling on the...Ch. 12 - A uniform 6.0-m-long ladder of mass 16.0 kg leans...Ch. 12 - There is a maximum height of a uniform vertical...Ch. 12 - A 95,000-kg train locomotive starts across a...Ch. 12 - A 23.0-kg backpack is suspended midway between two...Ch. 12 - A uniform beam of mass M and length l is mounted...Ch. 12 - Two identical, uniform beams are symmetrically set...Ch. 12 - If 35 kg is the maximum mass m that a person can...Ch. 12 - (a) Estimate the magnitude of the force FM the...Ch. 12 - One rod of the square frame shown in Fig. 1295...Ch. 12 - A steel rod of radius R = 15 cm and length 0,...Ch. 12 - A home mechanic wants to raise the 280-kg engine...Ch. 12 - A 2.0-m-high box with a 1.0-m-squarc base is moved...Ch. 12 - You are on a pirate ship and being forced to walk...Ch. 12 - A uniform sphere of weight mg and radius r0 is...Ch. 12 - Use the method of joints to determine the force in...Ch. 12 - A uniform ladder of mass m and length leans at an...Ch. 12 - In a mountain-climbing technique called the...Ch. 12 - (III) A metal cylinder has an original diameter of...Ch. 12 - (III) Two springs, attached by a rope, are...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Explain all answers clearly, with complete sentences and proper essay structure if needed. An asterisk (*) desi...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Q1. What is the empirical formula of a compound with the molecular formula
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
If someone at the other end of a room smokes a cigarette, you may breathe in some smoke. The movement of smoke ...
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
5. When the phenotype of heterozygotes is intermediate between the phenotypes of the two homozygotes, this patt...
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Look at the relative positions of each pair of atoms listed here in the periodic table. How many core electrons...
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
The following results were obtained from a broth dilution test for microbial susceptibility. Antibiotic Concent...
Microbiology: An Introduction
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- It is a sad day in Oman: 11-01-2020. The flag poles around the country are lowered. One end of horizontal flagpoles of mass 23 kg is hinged to the wall; the other side is hanging by a wire that makes angles 0 = 40° with both the flag pole and the wall. What is the tension in the wire (a) tinge the horizontal component of the force of the hinge on the pole (b) the vertical components of the force of the hinge on the pole (c)arrow_forwardIt is a sad day in Oman: 11-01-2020. The flag poles around the country are lowered One end of horizontal flagpoles of mass 26 kg is hinged to the wall; the other side is hanging by a wire that makes angles 0 = 40 *with both the flag pole and the wall. What is: (a) the tension in the wire (b) the horizontal component of the force of the hinge on the pole (c) the vertical components of the force of the hinge on the polearrow_forwardProblem 19 A uniform ladder is 10 m long and weighs 200 N. The ladder leans against a vertical, frictionless wall at heighth 8.0 m above the ground. A horizontal force Fis applied to the ladder at distance d = 2.0m from its base (measured along the ladder). أ (a) If the force magnitude is F = 50 N, what is the necessary friction (magnitude and direction) on the floor to keep the ladder stable? (b) Suppose the coefficient of static friction between the floor and the ladder is 0.5, find the maximum magnitude of force F just before the ladder starts to move.arrow_forward
- It is a sad day in Oman: 11-01-2020. The flag poles around the country are loWered. flagpoles of mass 35 kg is hinged to the wall; the otherside is hanging by a wire that makes angles 0= 25 with both the flag pole and the wall. What is: (a) the tension in the wire Hing (b) the horizontal component of the force of the hinge on the pole (C) the vertical components of the force of the hinge on the polearrow_forwardIt is a sad day in Oman: 11-01-2020. The flag poles around the country are lowered. One end of horizontal flagpoles of mass 25 kg is hinged to the wall, the other side is hanging by a wire that makes angles 0= 30° with both the flag pole and the wall. What is. (a) the tension in the wire thnge (b) the horizontal component of the force of the hinge on the pole N. (c) the vertical components of the force of the hinge on the polearrow_forwardA uniform ladder rests against a smooth vertical wall and on a rough horizontal ground. The weight of the ladder is 10N and it is just about to slip when inclined 30 degrees to the vertical. Calculate the coefficient of friction Friesarrow_forward
- A heavy ball suspended by a cable is pulled to the side by a horizontal force F as shown in Fig. 9-43. If angle 0 is small, the magnitude of the force F can be less than the weight of the ball because: (a) the force holds up only part of the ball's weight. (b) even though the ball is stationary, it is not really in equilibrium. (c) F is equal to only the x component of the tension in the cable. (d) the original statement is not true. To move the ball, F must be at least equal to the ball's weight. FIGURE 9–43 MisConceptual Question 4.arrow_forwardA 1.2-m plank of mass 3 kg rests on two joists. Knowing that the coefficient of static friction between the plank and the joists is 0.30,determine the magnitude of the horizontal force required to move the plank when (a) a= 750 mm, (b) a = 900 mm.arrow_forward1. (1) Three forces are applied to a tree sapling, as shown in Fig. 12-45, to stabilize it. If FA = 385 N and FB = 475 N, find Fe in magnitude and direction. FB FIGURE 12-45 FC Problem 1. FIGURE 12-46 Problem 2. 2. (1) Approximately what magnitude force, FM, must the extensor muscle in the upper arm exert on the lower arm to hold a 7.3-kg shot put (Fig. 12-46)? Assume the lower arm has a mass of 2.3 kg and its CG is 12.0 cm from the elbow-joint pivot. 2.5 cm FM -30.0 cm- 105° Elbow joint FAarrow_forward
- (a) A uniform steel beam of mass 200.00 kg is held up by a steel cable that is connected to the beam a distance L 6.00 m from the wall, at an angle 0=30.00° as shown Figure 1. The beam is bolted to the wall with an unknown force F exerted by the wall on the beam. An object of mass 600.00 kg, resting on top of the beam, is placed a distance d 2.00 m from the wall. Solve this problem fully, by finding the tension in the cable, the horizontal and vertical components of the force that the wall exerts on the beam and its magnitude and its direction. Figure 1arrow_forward11-30 Two blocks are suspended on a continuous inex- tensible cord as shown in Fig. P11-30. Determine the angle O for equilibrium if the masses of blocks A and B are 50 and 40 kg, respectively. Fig. P11-30arrow_forwardA uniform ladder 10.0 m long and weighing 50.0 N rests against a smooth vertical wall. (a) If the ladder is just on the verge of slipping when it makes a 50.0° with the ground, find the coefficient of static friction between the ladder and ground. (b) If the coefficient of static friction is 0.360, and the same ladder makes a angle with respect to the horizontal, how far along the length of 60.0° the ladder can a 65-kg painter climb before the ladder begins to slip?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON
Static Equilibrium: concept; Author: Jennifer Cash;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0BIgFKVnlBU;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY