
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780134110684
Author: Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus)
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 12, Problem 62EAP
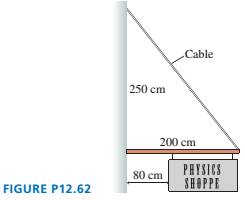
A 120-cm-wide sign hangs from a 5.0 kg, 200-cm-long pole. A cable of negligible mass supports the end of the rod as shown in FIGURE P12.62. What is the maximum mass of the sign if the maximum tension in the cable without breaking is 300 N?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
Chapter 12 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Ch. 12 - Prob. 1CQCh. 12 - If the angular velocity w is held constant, by...Ch. 12 - FIGURE Q12.3 shows three rotating disks, all of...Ch. 12 - 4. Must an object be rotating to have a moment of...Ch. 12 - 5. The moment of inertia of a uniform rod about an...Ch. 12 - 6. You have two solid steel spheres. Sphere 2 has...Ch. 12 - The professor hands you two spheres. They have the...Ch. 12 - Six forces are applied to the door in FIGURE...Ch. 12 - Prob. 9CQCh. 12 - Rank in order, from largest to smallest, the...
Ch. 12 - The solid cylinder and cylindrical shell in FIGURE...Ch. 12 - A diver in the pike position (legs straight, hands...Ch. 12 - Prob. 13CQCh. 12 - A high-speed drill reaches 2000 rpm in 0.50 s. a....Ch. 12 - A skater holds her arms outstretched as she spins...Ch. 12 - A ceiling fan with 80-cm-diameter blades is...Ch. 12 - An 18-cm-long bicycle crank arm, with a pedal at...Ch. 12 - Prob. 5EAPCh. 12 - The three masses shown in FIGURE EX12.6 are...Ch. 12 - The three masses shown in FIGURE EX12.7 are...Ch. 12 - A 100 g ball and a 200 g ball are connected by a...Ch. 12 - A thin, 100 g disk with a diameter of 8.0 cm...Ch. 12 - What is the rotational kinetic energy of the...Ch. 12 - The three200g masses in FIGURE EX12.11 are...Ch. 12 - A drum major twirls a 96-cm-long, 400 g baton...Ch. 12 - The four masses shown in FIGURE EX12.13 are...Ch. 12 - The four masses shown in FIGURE EXI2.13 are...Ch. 12 - The three masses shown in FIGURE EXI2.15 are...Ch. 12 - A 12-cm-diameter CD has a mass of 21 g. What is...Ch. 12 - A 25 kg solid door is 220 cm tall, 91 cm wide....Ch. 12 - Prob. 18EAPCh. 12 - In FIGURE EX12.19, what magnitude force provides...Ch. 12 - The 20-cm-diameter disk in FIGURE EX12.20 can...Ch. 12 - The axle in FIGURE EXI2.21 is half the distance...Ch. 12 - A 4.0-rn-long, 500 kg steel beam extends...Ch. 12 - An athlete at the gym holds a 3.0 kg steel ball in...Ch. 12 - An object’s moment of inertia is 2.0 kg m2. Its...Ch. 12 - An object whose moment of inertia is 4.0 kg m2...Ch. 12 - A 1.0 kg ball and a 2.0 kg ball are connected by a...Ch. 12 - Starting from rest, a 12-cm-diameter compact disk...Ch. 12 - A 4.0 kg, 36-cm-diameter metal disk, initially at...Ch. 12 - The two objects in FIGURE EXI2.29 are balanced on...Ch. 12 - Prob. 30EAPCh. 12 - The 3.0-rn-long, 100 kg rigid beam of FIGURE...Ch. 12 - A 5.0 kg cat and a 2.0 kg bowl of tuna fish are at...Ch. 12 - A car tire is 60cm in diameter. The car is...Ch. 12 - A 500 g, 8.0-cm-diameter can is filled with...Ch. 12 - Prob. 35EAPCh. 12 - A solid sphere of radius R is placed at a height...Ch. 12 - Prob. 37EAPCh. 12 - Evaluate the cross products AB and CD .Ch. 12 - Prob. 39EAPCh. 12 - Force F=10j N is exerted on a particle at 5i+5j m....Ch. 12 - A 1.3 kg ball on the end of a lightweight rod is...Ch. 12 - What are the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 12 - What is the angular momentum vector of the 2.0 kg,...Ch. 12 - Prob. 44EAPCh. 12 - Prob. 45EAPCh. 12 - A 2.0 kg, 20-cm-diameter turntable rotates at 100...Ch. 12 - Prob. 47EAPCh. 12 - A toy gyroscope has a ring of mass M and radius R...Ch. 12 - Prob. 49EAPCh. 12 - Prob. 50EAPCh. 12 - Determine the moment of inertia about the axis of...Ch. 12 - What is the moment of inertia of a 2.0 kg,...Ch. 12 - Calculate by direct integration the moment of...Ch. 12 - Calculate the moment of inertia of the rectangular...Ch. 12 - a. A disk of mass M and radius R has a hole of...Ch. 12 - Consider a solid cone of radius R, height H, and...Ch. 12 - Prob. 57EAPCh. 12 - A 3.0-m-long ladder, as shown in Figure 12.35....Ch. 12 - In FIGURE P12.59, an 80 kg construction worker...Ch. 12 - Prob. 60EAPCh. 12 - Prob. 61EAPCh. 12 - A 120-cm-wide sign hangs from a 5.0 kg,...Ch. 12 - Prob. 63EAPCh. 12 - Flywheels are large, massive wheels used to store...Ch. 12 - of mass m1and m2are connected by a massless string...Ch. 12 - The 2.0 kg, 30-cm-diameter disk in FIGURE P12.66...Ch. 12 - A 30-cm-diameter, 1.2 kg solid turntable rotates...Ch. 12 - Your engineering team has been assigned the task...Ch. 12 - A hollow sphere is rolling along a horizontal...Ch. 12 - A 750 g disk and a 760 g ring, both 15 cm in...Ch. 12 - A cylinder of radius R, length L. and mass M is...Ch. 12 - The 5.0 kg, 60-cm-diameter disk in FIGURE P12.72...Ch. 12 - A thin, uniform rod of length L and mass M is...Ch. 12 - A long, thin rod of mass M and length L is...Ch. 12 - The marble rolls down the track shown in FIGURE...Ch. 12 - sThe sphere of mass M and radius R in FIGURE...Ch. 12 - A satellite follows the elliptical orbit shown in...Ch. 12 - A 10 g bullet traveling at 400 m/s strikes a 10...Ch. 12 - A 200 g, 40-cm-diameter turntable rotates on...Ch. 12 - Luc, who is 1.80 m tall and weighs 950 N, is...Ch. 12 - A merry-go-round is a common piece of playground...Ch. 12 - A 45 kg figure skater is spinning on the toes of...Ch. 12 - Prob. 83EAPCh. 12 - The earth’s rotation axis, which is tilted 23.5...Ch. 12 - sThe bunchberry flower has the fastest-moving...Ch. 12 - The two blocks in FIGURE CP12.86 are connected by...Ch. 12 - A rod of length L and mass M has a nonuniform mass...Ch. 12 - In FIGURE CP12.88, a 200 g toy car is placed on a...Ch. 12 - Prob. 89EAPCh. 12 - A 75 g, 30-cm-long rod hangs vertically on a...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- air is pushed steadily though a forced air pipe at a steady speed of 4.0 m/s. the pipe measures 56 cm by 22 cm. how fast will air move though a narrower portion of the pipe that is also rectangular and measures 32 cm by 22 cmarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward13.87 ... Interplanetary Navigation. The most efficient way to send a spacecraft from the earth to another planet is by using a Hohmann transfer orbit (Fig. P13.87). If the orbits of the departure and destination planets are circular, the Hohmann transfer orbit is an elliptical orbit whose perihelion and aphelion are tangent to the orbits of the two planets. The rockets are fired briefly at the depar- ture planet to put the spacecraft into the transfer orbit; the spacecraft then coasts until it reaches the destination planet. The rockets are then fired again to put the spacecraft into the same orbit about the sun as the destination planet. (a) For a flight from earth to Mars, in what direction must the rockets be fired at the earth and at Mars: in the direction of motion, or opposite the direction of motion? What about for a flight from Mars to the earth? (b) How long does a one- way trip from the the earth to Mars take, between the firings of the rockets? (c) To reach Mars from the…arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwarda cubic foot of argon at 20 degrees celsius is isentropically compressed from 1 atm to 425 KPa. What is the new temperature and density?arrow_forwardCalculate the variance of the calculated accelerations. The free fall height was 1753 mm. The measured release and catch times were: 222.22 800.00 61.11 641.67 0.00 588.89 11.11 588.89 8.33 588.89 11.11 588.89 5.56 586.11 2.78 583.33 Give in the answer window the calculated repeated experiment variance in m/s2.arrow_forward
- How can i solve this if n1 (refractive index of gas) and n2 (refractive index of plastic) is not known. And the brewsters angle isn't knownarrow_forward2. Consider the situation described in problem 1 where light emerges horizontally from ground level. Take k = 0.0020 m' and no = 1.0001 and find at which horizontal distance, x, the ray reaches a height of y = 1.5 m.arrow_forward2-3. Consider the situation of the reflection of a pulse at the interface of two string described in the previous problem. In addition to the net disturbances being equal at the junction, the slope of the net disturbances must also be equal at the junction at all times. Given that p1 = 4.0 g/m, H2 = 9.0 g/m and Aj = 0.50 cm find 2. A, (Answer: -0.10 cm) and 3. Ay. (Answer: 0.40 cm)please I need to show all work step by step problems 2 and 3arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION (Physics Animation); Author: EarthPen;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XjkUcJkGd3Y;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY