
Concept explainers
A wild
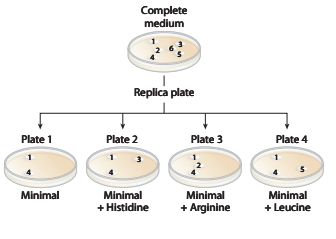
a. Identify the colonies that are prototrophic (wild type). What growth information leads to your answer?
b. Identify the colonies that are auxotrophic (mutant). What growth information leads to your answer?
c. Identify any colonies that are
d. For colonies
e. Are there any colonies for which genotype information cannot be determined? If so, which colony or colonies?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (2nd Edition)
- 0.2 mL of YGM was added to 1.8 mL of 0.2% YGM. What is the % concentration of yeast in this sample?arrow_forwardIn a nutrient medium that lacks histidine, a thin layer of agar containing ~109 Salmonella typhimurium histidine auxotrophs (mutant cells that require histidine to survive) produces ~13 colonies over a two-day incubation period at 37 ° C. How do these colonies arise in the absence of histidine? The experiment is repeated in the presence of 0.4 μg of 2-aminoanthracene. The number of colonies produced over two days exceeds 10,000.What does this indicate about 2-aminoanthracene? What can you surmise about its carcinogenicity?arrow_forwardFifteen bacterial colonies growing on a complete medium (that means that they have all of nutrients that they need supplied in the dish, and they don't actually need to synthesize these compounds to survive) are transferred to minimal medium. Twelve of the colonies grow on minimal medium. Three colonies do not grow on minimal medium. But, if these three colonies are put on a plate that has minimal medium supplemented with the amino acid serine (min + Ser), they all What does this suggest about the three bacterial colonies (pick all that apply)? grow. They lack the ability to synthesize their own serine. O They are probably wild-type. They probably have a mutation that causes them to lack a certain protein. They probably have a mutation that causes them to be unable to perform translation. O They probably have a mutation that causes them to be unable to perform transcription. O They are able to synthesize everything that they need to grow except for serine.arrow_forward
- Using one of the graphs obtained with the medium II, name the different phases of the bacterial growth and indicate the starting and ending time points of these phases as well as the physiological characteristics of the bacteria during each phasearrow_forwardin a clean, non-sterile 15 mL centrifuge tube, prepare a 2.0% yeast suspension by adding 0.06 g Saccharomyces cerevisiae to 3 mL yeast growing medium (56 mM glucose, 20 mM HEPES, pH 6.8). What percent of yeast suspension is left after a 1:10 dilution?arrow_forwardWhich of the colonies are leucine auxotrophs? GMSA is the negative control, with no additional nutrients added. I selected 5 and 7, but this answer is incorrect. Please help.arrow_forward
- A bacterial strain has a generation time of 30 min, how long would it take an exponentially growing culture to increase from a titre of 5 x 103 cells per ml to 4 x 109 cells per ml? How many generations would have elapsed? Show all of your calculations. G = t/n to calculate generation time (i.e. for population to double) During the growth of the culture, periodic observations of the cells under the microscope have revealed the occurrence of typical rod-shaped cells. However, after further incubation, they appeared to change their morphology to form small oval or spherical-shaped structures. What do these structures likely represent? And what are the likely factors contributing to this observation? Explain what growth phase this culture will be in.arrow_forwardOne of the early results shows that the post-centrifugation pellet of encapsulated cells also contains EA1 and/or Sap. Why is this not proof that Bacillus anthracis cells have both an S-layer and a capsule simultaneously? I need help finding the answer in the article and explain in short answer link to article: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC106848/arrow_forwardOne of the early results shows that the post-centrifugation pellet of encapsulated cells also contains EA1 and/or Sap. Why is this not proof that Bacillus anthracis cells have both an S-layer and a capsule simultaneously? I need help finding the answer in the article and explain in short answer link to article: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC106848/arrow_forward
- For the study of alanine production by a recombinant strain of E. coli, cultivation was carried out in a benchtop bioreactor with 4.5 L of culture medium, using glucose as a limiting substrate. During the cultivation, there was no lag phase and the cells showed exponential growth for 5 hours. The following table presents the results of the analysis of ammonia and glucose consumption, and alanine accumulation throughout the cultivation. Knowing that 500 mL of a cell suspension at a concentration of 5.0 g/L (inoculum) was added to the 4.5 L of medium in the reactor and that the YX/NH3 previously determined was 7.5, calculate:a) the maximum specific growth rateb) YX/S and YP/S yield factorsc) How long would it take to reach Cx = 30 g/L if the cells continued with the exponential growth profile until the end of the culture (without nutrient deprivation or any type of inhibition)?d) Describe how the mathematical treatment of the data should be done to determine the type of product formation…arrow_forwardA serial dilution of overnight E.coli culture was performed by pipetting 1ml of a bacterial culture into a 9 ml LB medium. After this, from 10-4 and 10-5 dilution tubes 100µl were plated onto LB agar plates. Upon overnight incubation at 37°C, 200 colonies were counted in 10-4 and 22 colonies were present on 10-5 plates. How many colony-forming units were present per ml of the original culture? If the formula for CFU/ml =no. Of colonies/dilution factor*volume of culture platearrow_forwardTo determine the number of cells in a pure culture of Klebsiella pneumoniae, you have performed a serial dilution using three tubes of sterile saline (9.9 ml each). A sample of 0.1 ml from the culture was added to tube 1. Similarly, 0.1 ml from tube 1 was used to inoculate tube 2, and tube 3 was inoculated using 0.1 ml from tube 2. A nutrient agar plate was then inoculated using 0.1 ml from tube 3 and incubated overnight. The next day, 92 colonies were observed on the plate. How many cfu/ml were in the original culture? Using a Petroff-Hauser counting chamber, the number of cells in the same culture was estimated to be 8.5 • 109 cells/ml. How can you explain these results?arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





