
Concept explainers
To label: The components of skeletal muscle fibres in Fig 12.1 (a).
Introduction: A complete skeletal muscle is regarded as one of the organs of the muscular system. Muscles are the largest cylindrical structure that composes of the fascicle, muscle fiber, myofibrils, and filaments.
Answer to Problem 1.1BGL
Pictorial representation:
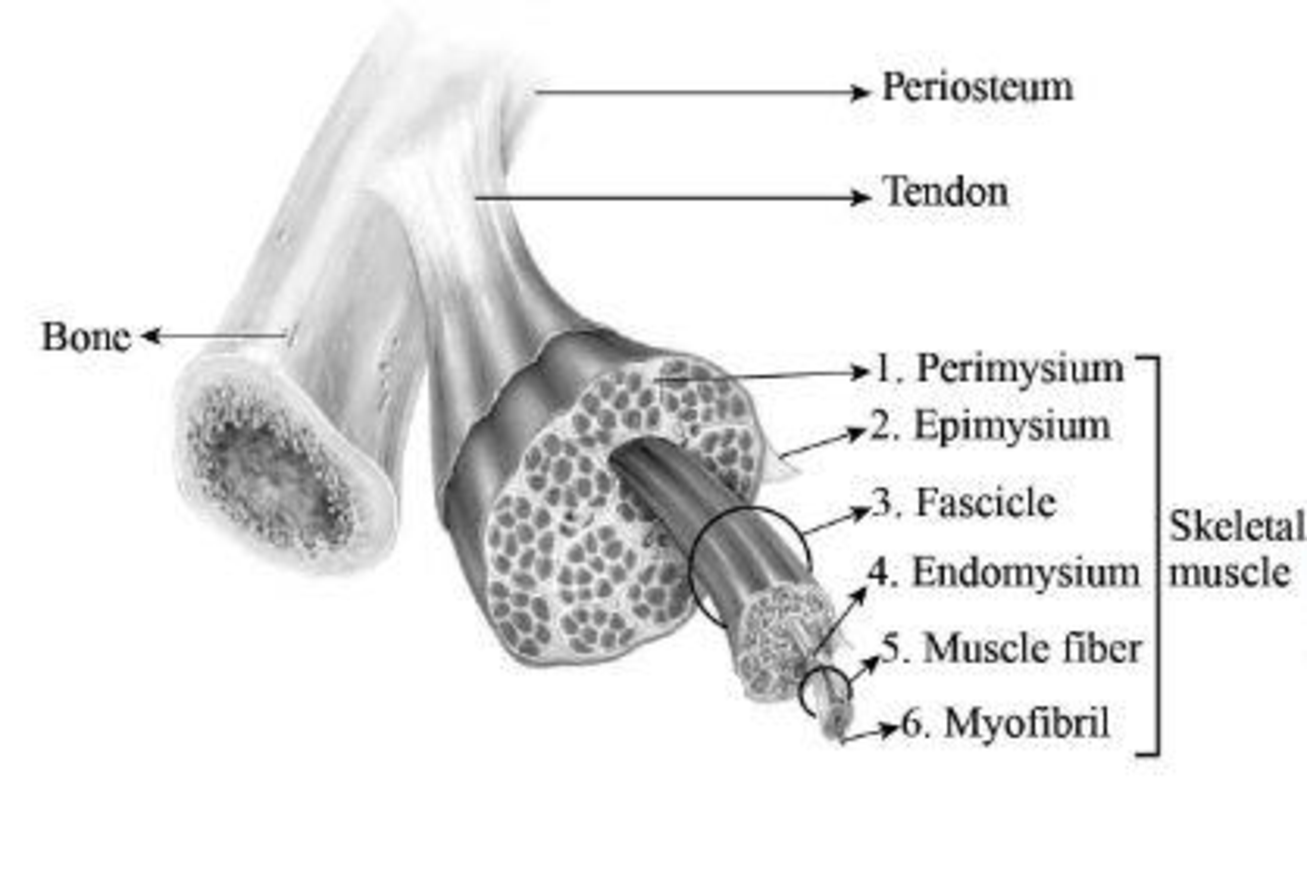
Fig 1: Components of skeletal muscle fibre
Explanation of Solution
The fascicles are bundles of skeletal muscles that are enveloped by connective tissues, which is termed as perimysium. The epimysium is a type of connective tissue that envelops every muscle. The areolar connective tissue that is present inside the muscle is termed as endomysium. This structure composes of nerves as well as capillaries and overlies the sarcolemma. Muscle fibers are smaller in size and they are present inside the fascicle. Myofibrils are rod-like structures and form the basic unit of muscle. They are made of thick and thin filaments.
To label: The components of the fascicle in Fig 12.1 (b).
Introduction: Predominant role played by muscles in the human body is contraction. Muscles that are connected with bones, organs, and blood vessels play a significant role in movements. Muscles are also significant for stability of joints, heat production, and posture.
Answer to Problem 1.1BGL
Pictorial representation:
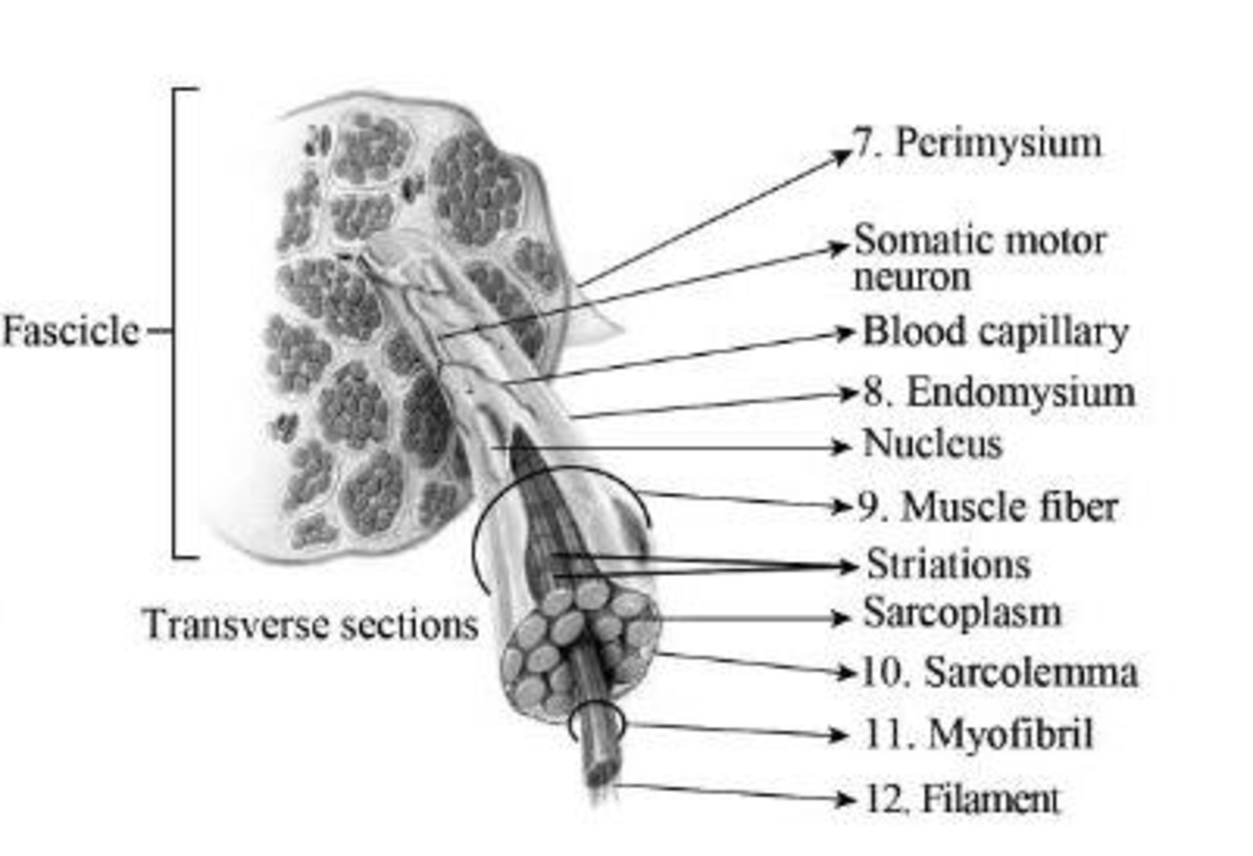
Fig 2: Components of the fascicle
Explanation of Solution
A muscle fascicle is formed of a bunch of skeletal muscle fibers. These fibers are enveloped by connective tissues known as perimysium. The areolar connective tissue that is present inside the muscle is termed as endomysium. Muscle fibers are smaller structures that are present inside the fascicle. The sarcolemma is a fine, tube-like structure that surrounds the fibres in skeletal muscles. Myofibrils are rod-like structures and form the basic unit of muscle. They are made of thick and thin filaments.
To label: The cross-section of a fascicle in a muscle in Fig 12.2 (a).
Introduction: The force that can be generated by a muscle fiber is determined by the muscle fascicle. Tendons are structures that connect the muscle with the bones. This junction is highly prone to injuries.
Answer to Problem 1.1BGL
Pictorial representation:
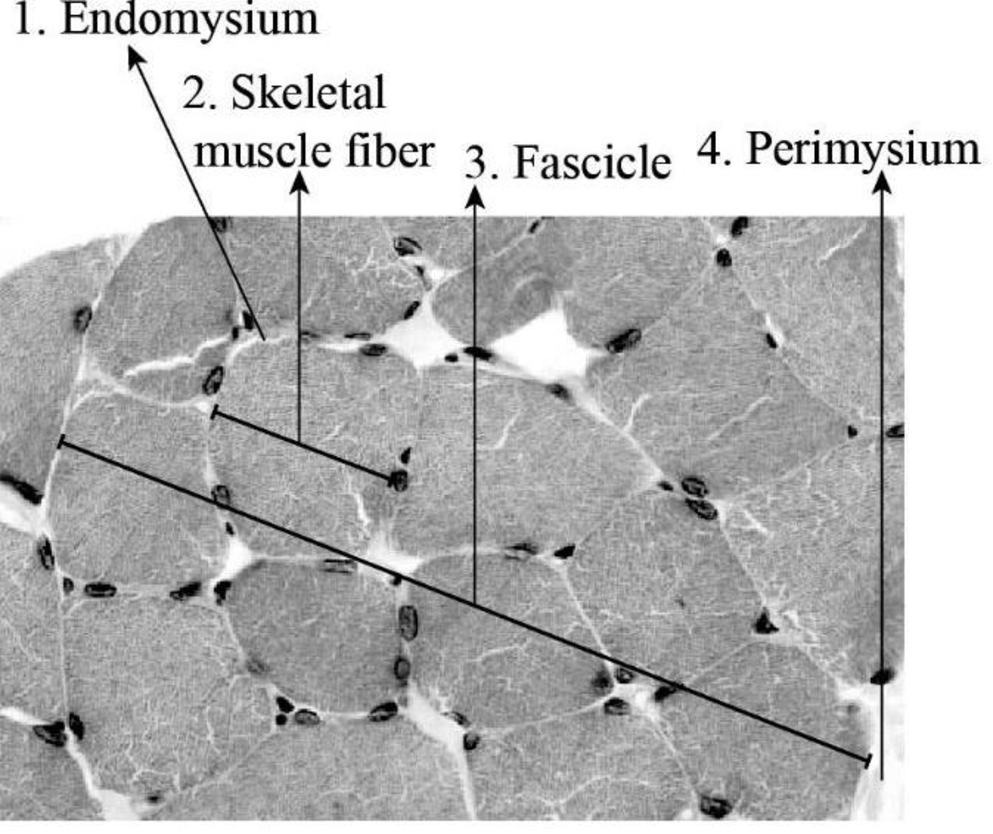
Fig 3: Cross-section of a muscle fascicle
Explanation of Solution
Skeletal muscle cells appear as long, cylindrical structures; therefore, they are generally referred to as muscle fibers. They are structured into a cluster known as fascicles. The epimysium spreads between fascicles internally, forming septa, which are called perimysium. The perimysium further stretches into thinner strands known as endomysium.
To label: The longitudinal section of muscle fibers in Fig 12.2 (b).
Introduction: Skeletal muscle fibers present in humans are large in size. The plasma membrane of the skeletal muscle fiber is known as sarcolemma. This membrane surrounds the sarcoplasm, which is the cytoplasm of the muscle fiber.
Answer to Problem 1.1BGL
Pictorial representation:
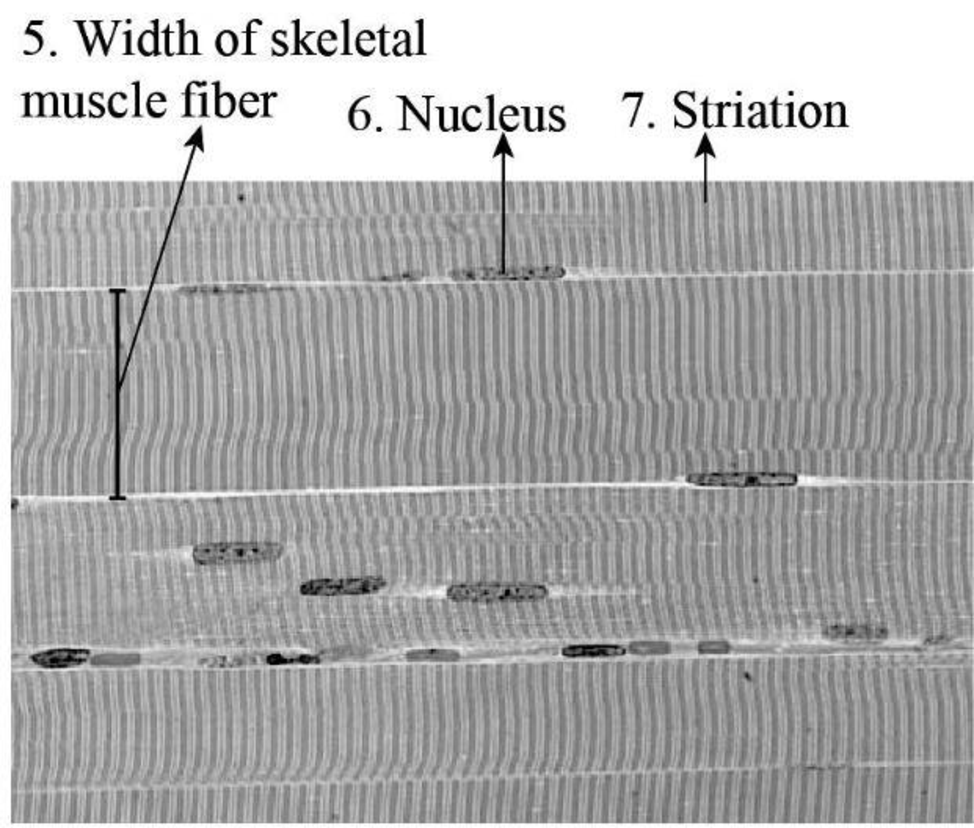
Fig 4: Longitudinal-section of muscle fibers
Explanation of Solution
The skeletal muscle fibers display striated appearance (striation) that is due to the organisation of myofilaments. These fibers are cylindrical shaped and possess more than one nucleus or multinucleated. The width of a typical muscle fiber is 10-50 μm.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Laboratory Manual for Anatomy and Physiology, 6e Loose-Leaf Print Companion
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





