
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:The complete Lewis structure of lisinopril needs to be drawn.
Concept Introduction: The complete Lewis structure of a molecule can be drawn using the total number of valence electrons present in it. It shows distribution of total number of valence electrons between the atoms of molecules. The bonded electrons are those electrons which are involved in bonding and they are represented as bonds or lines between the bonded atoms. The lone pair of electrons are those electrons which are not involved in bonding they are represented as dots (in pair) on the symbol of the atom.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is as follows:
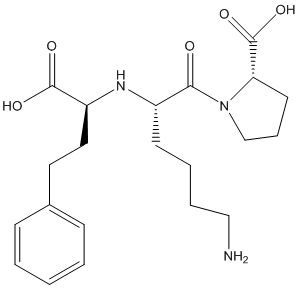
Here, O can have maximum of 2 lone pairs of electrons, N can have 1 lone pair of electrons and there is no lone pair of electrons on C and H atoms.
The valence electrons of C, H, N and O is 4, 1, 5 and 6 respectively.
The complete Lewis structure will be as follows:
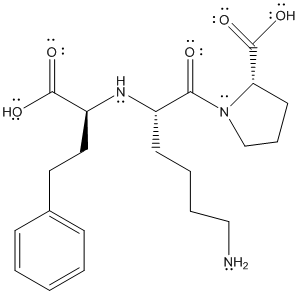
(b)
Interpretation:All the bond angles in lisinopril needs to be identified using the valence shell electron-pair repulsion model.
Concept Introduction: Hybridization is defined as mixing of orbital. The geometry of a central atom depends on its hybridization. The shape will be different from geometry if there are lone pair of electrons present on the central atom. The bond angles of central atom can be determined from its hybridization and geometry.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The complete Lewis structure of lisinopril is as follows:
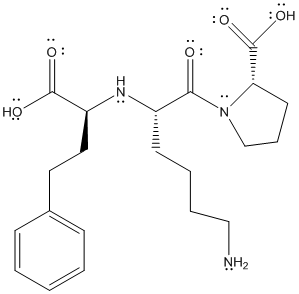
The valence electrons of C, H, N and O atom is 4, 1, 5 and 6 respectively. The C atom with 4 single bonds will have
The central atom with
(c)
Interpretation: The most polar bond in lisinopril needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction: A bond is said to be polar if there is electronegativity difference between the atoms. The most polar bond will be the one with maximum electronegativity difference between the bonded atoms.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The structure is given as follows:
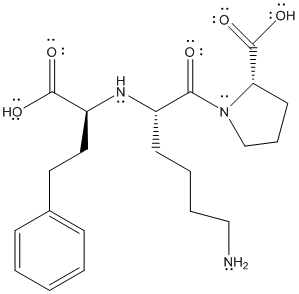
Here, C and H have comparable electronegativity thus, C-H bond is non-polar. The difference in electronegativity can be observed if C or H are bonded with O and N atoms.
Here, H is more electropositive than C thus, the electronegativity difference will be more in case of O-H or N-H bond as compared to O-C or N-C bonds.
Comparing O-H and N-H bond, O atom is more electronegative thus, electronegativity difference will be more in O-H and it is most polar bond in lisinopril.
(d)
Interpretation: Whether the given molecule is polar or non-polar needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction: If there are polar bonds present in a molecule then it is considered as a polar molecule.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Due to the presence of polar O-H, N-H, C-O and C-N bonds, lisinopril is considered as a polar molecule.
(e)
Interpretation: This is to be explained whether lisinopril possess resonance or not.
Concept Introduction: Resonance is possessed by a molecule if there is possibility of delocalization of electrons. This can be positive if there is intercation between alternate lone pairs and pi bonds present in a molecule.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
The complete structure of lisinopril is as follows:
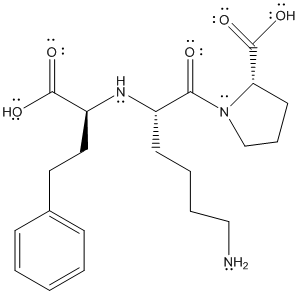
The above structure shows resonance as lone pair of electrons on oxygen atom is in conjugation with double bond. Similarly, lone pair of electrons on N atom is in conjugation with double bonded oxygen atom.
This is represented as follows:
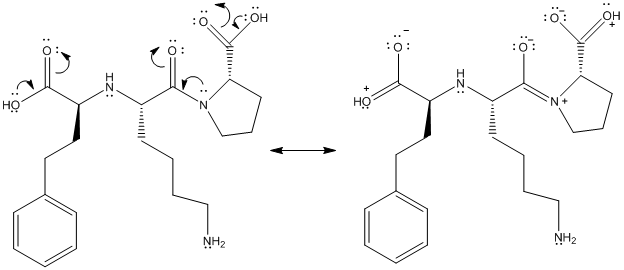
(f)
Interpretation: The
Concept Introduction: The functional groups are identity groups of the molecules. Functional groups define the types of
(f)
Explanation of Solution
The complete structure of lisinopril is as follows:
Here, -COOH, NH-, -NH2, CON- and benzene or
Functional groups are labelled as follows:
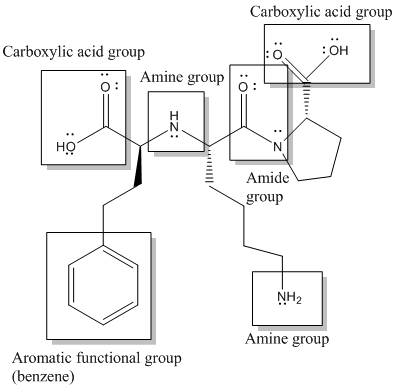
(g)
Interpretation: The molecular formula of lisinopril needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction: Molecular formula of any compound can be determined by calculating the total number of atoms of each element present in it.
(g)
Explanation of Solution
The complete structure of lisinopril is as follows:
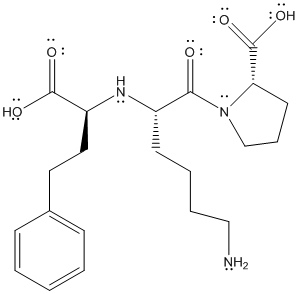
There are 4 types of atoms present in the above molecule namely carbon atom, oxygen atom, hydrogen atom and nitrogen atom.
From the above structure, the molecular formula will be
(h)
Interpretation: The types of intermolecular forces present in the lisinopril molecules needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction: Intermolecular forces are defined as type of forces present between the two molecules when they come in contact of each other. The type of forces depends on the physical and chemical properties of atoms present in the molecule.
(h)
Explanation of Solution
The complete structure is represented as follows:
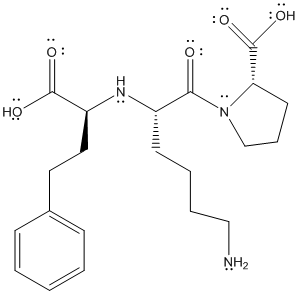
All the type of molecules containing non-polar bonds exhibits London dispersion forces. Due to the non-polar bonds (C-C and C-H) in the molecule. London dispersion forces are present.
Due to the presence of O-H bond, it also exhibits hydrogen bonding.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
- Hi, I need help on my practice final, If you could offer strategies and dumb it down for me with an explanation on how to solve that would be amazing and beneficial.arrow_forwardHi I need help with my practice final, it would be really helpful to offer strategies on how to solve it, dumb it down, and a detailed explanation on how to approach future similar problems like this. The devil is in the details and this would be extremely helpfularrow_forwardIn alpha-NbI4, Nb4+ should have the d1 configuration (bond with paired electrons: paramagnetic). Please comment.arrow_forward
- Hi, I need help on my practice final, if you could explain how to solve it offer strategies and dumb it down that would be amazing. Detail helpsarrow_forwardBriefly explain the following paragraph: both the distortion of symmetry and the fact that the solid is diamagnetic indicate the existence of a Nb-Nb bond.arrow_forwardHi I need help on my practice final, If you could explain how to solve it, offer strategies, and dumb it down that would be amazing.arrow_forward
- -1 2 3 4 5 7 8 At a certain temperature this reaction follows first-order kinetics with a rate constant of 0.0635 s 2C1,0, (g) →2C1, (g)+50, (g) Suppose a vessel contains C1,0, at a concentration of 1.03 M. Calculate how long it takes for the concentration of C1,0, to decrease by 86.0%. You may assume no other reaction is important. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. e х th Earrow_forwardASAP....arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
