
Concept explainers
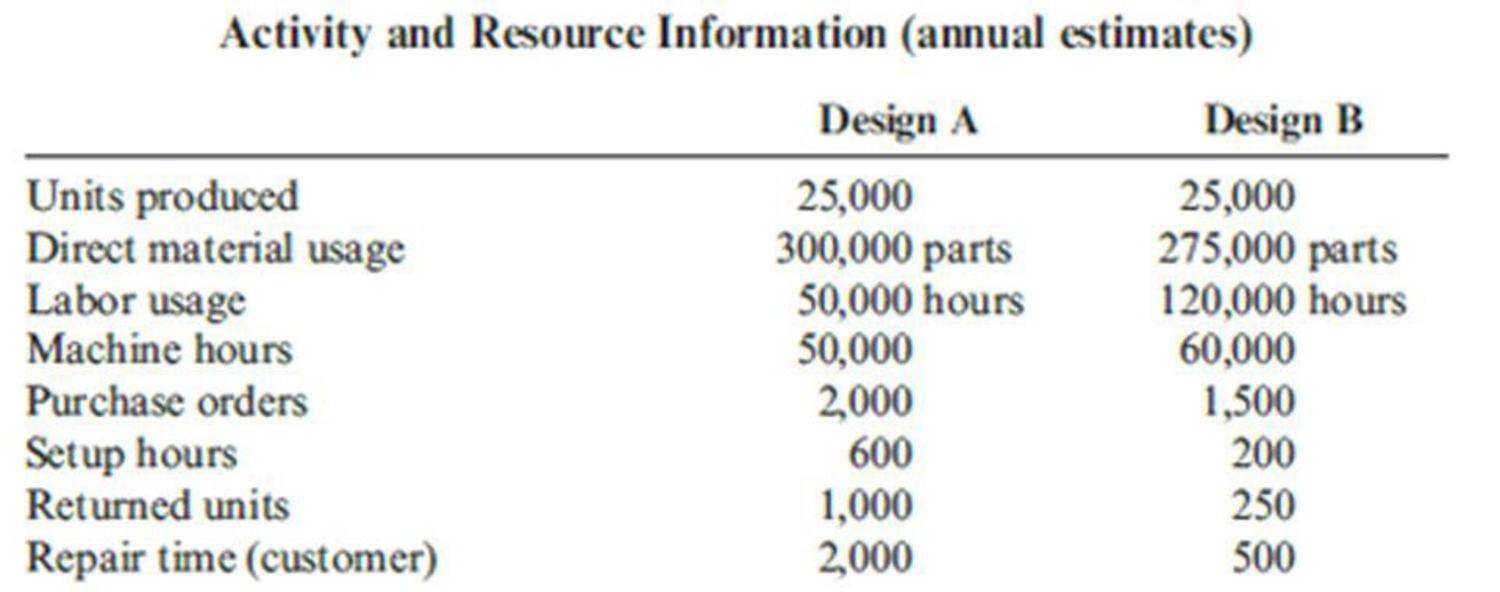
Kagle design engineers are in the process of developing a new “green” product, one that will significantly reduce impact on the environment and yet still provide the desired customer functionality. Currently, two designs are being considered. The manager of Kagle has told the engineers that the cost for the new product cannot exceed $550 per unit (target cost). In the past, the Cost Accounting Department has given estimated costs using a unit-based system. At the request of the Engineering Department, Cost Accounting is providing both unit-and activity-based accounting information (made possible by a recent pilot study producing the activity-based data).
Unit-based system:
Variable conversion activity rate: $100 per direct labor hour
Material usage rate: $20 per part
ABC system:
Labor usage: $15 per direct labor hour
Material usage (direct materials): $20 per part
Machining: $75 per machine hour
Purchasing activity: $150 per purchase order
Setup activity: $3,000 per setup hour
Warranty activity: $500 per returned unit (usually requires extensive rework)
Customer repair cost: $25 per repair hour (average)
Required:
- 1. Select the lower-cost design using unit-based costing. Are logistical and post-purchase activities considered in this analysis?
- 2. Select the lower-cost design using ABC analysis. Explain why the analysis differs from the unit-based analysis.
- 3. What if the post-purchase cost was an environmental contaminant and amounted to $10 per unit for Design A and $40 per unit for Design B? Assume that the environmental cost is borne by society. Now which is the better design?
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 11 Solutions
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Series)
- Solve clearly with correct dataarrow_forwardPROBLEM E Mulles, the owner of a successful fertilizer business, felt that it is time to expand operations. Mulles offered to form a partnership with Lucena, the owner of a nearby warehouse. The partnership would be called Mulles & Lucena Storage and Sales. Lucena accepted Mulles' offer and the partnership was formed on July 1,2024. Presented below is the trial balance for Mulles Fertilizer Supply on June 30, 2024: Cash Accounts Receivable Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts. Inventory Prepaid Rent Store Equipment Accumulated Depreciation Notes Payable Accounts Payable Mulles, Capital Total P 229,500 2,103,000 P 117,000 1,012,500 29,250 390,000 P3,764,250 97,500 330,000 505,500 2,714,250 P3,764,250 The partners agreed to share profits and losses equally and decided to invest an equal amount in the partnership. Lucena and Mulles agreed that Lucena's land is worth P500,000 and his building P1,450,000. Lucena is to contribute cash in an amount sufficient to make his capital account…arrow_forwardPLEASE HELP. ALL RED CELLS ARE INCORRECT. NOTICE, REVENUE ACCOUNTS ARE IN THE DROPDOWN!arrow_forward
- Journalize these transactions, also post the transcations to T-accounts and determine month-end balances. Finally prepare a trail balance.arrow_forwardSuppose during 2023, BlueStar Shipping reported the following financial information (in millions): Net Sales: $40,000 Net Income: $150 Total Assets at Beginning of Year: $26,000 • Total Assets at End of Year: $24,800 Calculate the following: (a) Asset Turnover (b) Return on Assets (ROA) as a percentagearrow_forwardPlease fill all cells! I need helparrow_forward
- Hilary owns a fruit smoothie shop at the local mall. Each smoothie requires 1/2 pound of mixed berries, which are expected to cost $5.50 per pound during the summer months. Shop employees are paid $7.00 per hour. Variable overhead consists of utilities and supplies, with a variable overhead rate of $0.12 per minute of direct labor time. Each smoothie should require 4 minutes of direct labor time. Determine the following standard costs per smoothie: Direct materials cost Direct labor cost Variable overhead costarrow_forwardgeneral accountingarrow_forwardThe following financial information is provided for Brightstar Corp.: Net Income (2023): $500 million Total Assets on January 1, 2023: $3,500 million Total Assets on December 31, 2023: $4,500 million What is Brightstar Corp. _ s return on assets (ROA) for 2023? A. 11.80% B. 12.50% C. 13.20% D. 14.00%arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage Learning

