
Concept explainers
The chromosome constitution number of this individual is

This drawing represents:
a. mitotic metaphase.
b. meiotic metaphase I.
c. meiotic metaphase II.
d. a gamete.
e. sixnonhomologous chromosomes.
Introduction:
The cell cycle consists of two main divisions known as mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis is the first division during the cell cycle in which the number of chromosomes remains same as the number of chromosomes in the parent cell; on the contrary, in meiosis, the number of chromosomes gets reduced to half.
Answer to Problem 1TYK
Correct answer:
Metaphase 1 of meiosis.
Explanation of Solution
Justification for the correct answer:
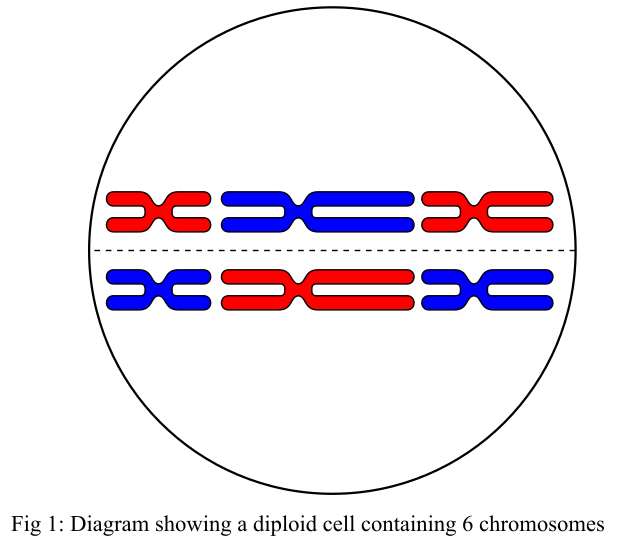
Option (b) is meiotic metaphase 1. There are two meiotic divisions after mitosis, namely, meiosis 1 and meiosis 2. During the meiosis 1, the paired chromosomes, also known as bivalent, arrange themselves on the metaphase plate. These paired chromosomes align at the middle of the plate and get attached to the meiotic spindle. The spindle is formed from the structure of the protein, which is responsible for dividing the genetic material in the cell. Hence, option (b) is correct.
Explanation for the incorrect answer:
Option (a) is metaphase in mitosis. Mitosis is the first part of the cell cycle that takes place before the meiosis. Metaphase stage in mitosis involves the arrangement of most condensed chromosomes and these chromosomes then get coiled at this stage. During the metaphase stage of meiosis, the chromosomes are not paired. So, it is an incorrect option.
Option (c) is metaphase 2 phase of meiosis 2. The chromosomes in the meiosis 2 are similar to the chromosomes found in the metaphase stage of mitosis. During the meiosis 2, the chromosomes get condensed and attach themselves to the spindles arising from the centromere present at the opposite poles. These condensed chromosomes are aligned on a metaphase plate but they are in a condensed form. So, it is an incorrect option.
Option (d) is a gamete. During fertilization fusion of one haploid gamete with another haploid gamete results in the formation of a diploid zygote. Number of chromosomes in a haploid cell is 23, two haploid cells fuse together to form a diploid cell. During meiosis number of chromosomes are reduced to 23 from 46 chromosomes. So, it is an incorrect option.
Option (e) states that number of non-homologous chromosomes is 6. Paired chromosomes are the one in which one chromosome is a homolog to another chromosome. These paired chromosomes have the same gene content and possess the same morphology as well. Non-homologous chromosomes are paired chromosomes in which both the chromosomes possess a different gene content. So, it is an incorrect option.
Hence, options (a), (c), (d), and (e) are incorrect.
Therefore, it may be concluded that in the metaphase division of meiosis 1 alignment of paired chromosomes on the metaphase plate takes place. These paired chromosomes get attached to the spindle fibers during this (metaphase 1) stage.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
- Artificial Selection: Explain how artificial selection is like natural selection and whether the experimental procedure shown in the video could be used to alter other traits. Why are quail eggs useful for this experiment on selection?arrow_forwardDon't give AI generated solution otherwise I will give you downwardarrow_forwardHello, Can tou please help me to develope the next topic (in a esquematic format) please?: Function and Benefits of Compound Microscopes Thank you in advance!arrow_forward
- Identify the AMA CPT assistant that you have chosen. Explain your interpretation of the AMA CPT assistant. Explain how this AMA CPT assistant will help you in the future.arrow_forwardwhat is the difference between drug education programs and drug prevention programsarrow_forwardWhat is the formula of Evolution? Define each item.arrow_forward
- Define the following concepts from Genetic Algorithms: Mutation of an organism and mutation probabilityarrow_forwardFitness 6. The primary theory to explain the evolution of cooperation among relatives is Kin Selection. The graph below shows how Kin Selection theory can be used to explain cooperative displays in male wild turkeys. B When paired, subordinant males increase the reproductive success of their solo, dominant brothers. 0.9 C 0 Dominant Solo EVOLUTION Se, Box 13.2 © 2023 Oxford University Press rB rB-C Direct Indirect Fitness fitness fitness gain Subordinate 19 Fitness After A. H. Krakauer. 2005. Nature 434: 69-72 r = 0.42 Subordinant Dominant a) Use Hamilton's Rule to show how Kin Selection can support the evolution of cooperation in this system. Show the math. (4 b) Assume that the average relatedness among male turkeys in displaying pairs was instead r = 0.10. Could kin selection still explain the cooperative display behavior (show math)? In this case, what alternative explanation could you give for the behavior? (4 pts) 7. In vampire bats (pictured below), group members that have fed…arrow_forwardExamine the following mechanism and classify the role of each labeled species in the table below. Check all the boxes that applyarrow_forward
- 1. Define and explain the two primary evolutionary consequences of interspecific competitionarrow_forward2 A linear fragment of DNA containing the Insulin receptor gene is shown below, where boxes represent exons and lines represent introns. Assume transcription initiates at the leftmost EcoRI site. Sizes in kb are indicated below each segment. Vertical arrows indicate restriction enzyme recognition sites for Xbal and EcoRI in the Insulin receptor gene. Horizontal arrows indicate positions of forward and reverse PCR primers. The Horizontal line indicates sequences in probe A. Probe A EcoRI Xbal t + XbaI + 0.5kb | 0.5 kb | 0.5 kb | 0.5kb | 0.5 kb | 0.5 kb | 1.0 kb EcoRI On the gel below, indicate the patterns of bands expected for each DNA sample Lane 1: EcoRI digest of the insulin receptor gene Lane 2: EcoRI + Xbal digest of the insulin receptor gene Lane 3: Southern blot of the EcoRI + Xbal digest insulin receptor gene probed with probe A Lane 4: PCR of the insulin receptor cDNA using the primers indicated Markers 6 5 4 1 0.5 1 2 3 4arrow_forward4. (10 points) woman. If both disease traits are X-linked recessive what is the probability A man hemizygous for both hemophilia A and color blindness mates with a normal hemophilia A nor colorblindness if the two disease genes show complete that a mating between their children will produce a grandson with neither a. linkage? (5 points) that a mating between their children will produce a grandson with both hemophilia A and colorblindness if the two disease genes map 40 cM apart? (5 points)arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





