
Concept explainers
To identify and summarize:
The steps of the cycle in the given figure
Introduction:
Organisms obtain energy through a process called
Answer to Problem 18STP
The cycle in the given figure is of Krebs cycle. The steps of the cycle can be summarized as follows:
- AcetylCoA combines with a 4- carbon compound to form a 6- carbon compound known as citric acid.
- Citric acid is then broken down in a series of steps releasing carbon dioxide and generates one ATP, 3 NADH and 1 FADH2.
- Finally acetyl CoA and citric acid are regenerated and the cycle continues.
Explanation of Solution
The following figure is given:
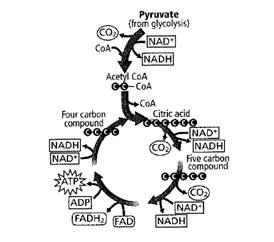
The end products of glycolysis are two ATP molecules and two pyruvate molecules. Most of the energy from the glucose is still present in pyruvate. In the presence of oxygen, pyruvate is transported into the mitochondrial matrix, where it is finally converted to carbon dioxide. The series of reactions involved in breaking down pyruvate to carbon dioxide is called Krebs cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. It is also called citric acid cycle.
Just before Krebs cycle starts, pyruvate reacts with coenzyme CoA to form a two carbon intermediate called acetyl CoA. Carbondioxide is released and NAD+ is converted to NADH. AcetylCoA then moves to mitochondrial matrix. The reaction produces two CO2 molecules and two NADH.
The Krebs cycle starts with acetyl CoA combining with a 4- carbon compound to form a 6- carbon compound known as citric acid. Citric acid then breaks down in a series of steps releasing carbon dioxide and generating one ATP, 3 NADH and 1 FADH2. FAD and NAD+ are electron carriers.
Finally acetyl CoA and citric acid are regenerated and the cycle continues. Two turns of Krebs cycle occurs for one glucose molecule. The net yield of Krebs cycle is 6CO2 molecules, 2 ATP, 8NADH and 2FADH2.
Chapter 11 Solutions
Biology Illinois Edition (Glencoe Science)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues
Microbiology: An Introduction
Campbell Essential Biology (6th Edition) - standalone book
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology Plus Mastering A&P with eText - Access Card Package (10th Edition) (New A&P Titles by Ric Martini and Judi Nath)
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





