
Concept explainers
To Analyze: Phase of meiosis I and meiosis II
Introduction: Meiosis is a specialized form of cell division in which number of chromosomes is reduced to half. The reduction in chromosomes number is achieved by one round of
Explanation of Solution
| Meiosis I | Prophase I | Metaphase I | Anaphase I | Telophase I |
| Description | Nuclear envelope breaks down, crossing over occurs, and chromosomes condensed. | Homologous pairs move together along the metaphase plate. | Homologous chromosomes are separated and move to opposite poles. | The chromosomes arrive at the poles and Each daughter cell has half the number of chromosome. |
| Sketch | 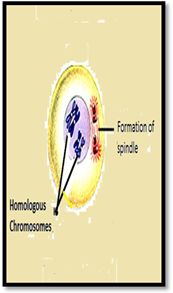 |  | 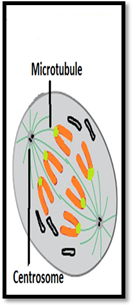 | 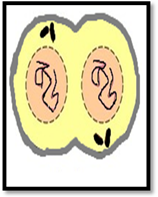 |
| Meiosis II | Prophase II | Metaphase II | Anaphase II | Telophase II |
| Description | The centrosomes are duplicated during interkinesis move away from opposite poles and new spindles are formed. | The sister chromatids are condensed and aligned at the metaphase of the cell. | The chromatids are pulled apart and move opposite poles. | The chromatids are arrived at opposite poles and start to decondensed. Nuclear envelopes reform around the chromosomes |
| Sketch | 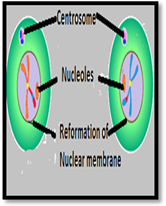 | 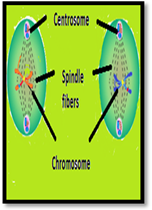 | 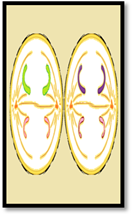 | 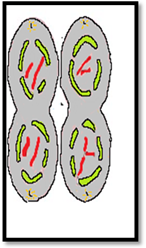 |
Hence, in meiosis I, homologous chromosomes are separates and produced two haploids daughter cells. In meiosis II, sister chromatids are separated and produced four haploid daughter cells.
Chapter 10 Solutions
Biology Science Notebook
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth
Concepts of Genetics (11th Edition)
Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition)
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





