
Concept explainers
Find the force representing the reaction at A using the virtual work method.
Find the couple representing the reaction at A using the virtual work method.
Answer to Problem 10.53P
The force representing the reaction at A is
The couple representing the reaction at A is
Explanation of Solution
Find the force at A;
Show the free-body diagram of the continuous beam as in Figure 1.
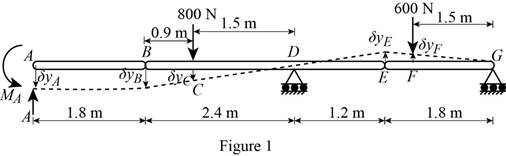
Consider the member AB is horizontal.
The vertical displacement at point A is
Find the vertical displacement
Find the vertical displacement
Find the vertical displacement
Find the vertical displacement
Use the concept of virtual work;
Substitute
Therefore, the force representing the reaction at A is
Find the couple at A;
Show the free-body diagram of the continuous beam as in Figure 2.
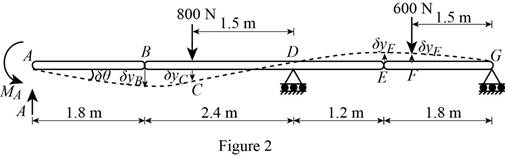
Rotate the member AB in the beam through
Find the vertical reaction
Find the vertical displacement
Find the vertical displacement
Find the vertical displacement
Use the concept of virtual work;
Substitute
Therefore, the couple representing the reaction at A is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
VECTOR MECH...,STAT.+DYNA.(LL)-W/ACCESS
- L (a) a) Using the method of joints, determine the force in each member of the truss shown if the force L is applied at (a) (on top of the truss). State А 4d В whether each member is in tension or compression. b) Using the method of joints, determine the force in each member of the truss shown if instead the force L is applied at (b) (on the bottom of the truss). State whether each member is in tension or compression. 3d C I(b) Larrow_forwardFor the shown frame and loads P=756 KN and Q=1512 KN, - 3 m 1.5 m 1 m 8 m 6 m magnitude of y-component of reaction at B (KN) a. 168 b. 210 C. 252 d. 262.5 e. 294 magnitude of x-component of reaction at B (KN) a. 6552 b. 4368 с. 5460 d. 2184 e. 7644 magnitude of x-component of reaction at C (KN) magnitude of y-component of reaction at C (KN) magnitude of y-component of reaction at A (KN)arrow_forward71 of 923 > Fig. 10.123 E 6.126 Solve Prob. 6.125 when (a) ẞ = 0, (b) f = 6°. 6.127 The press shown is used to emboss a small seal at E. Knowing that P = 250 N, determine (a) the vertical component of the force exerted on the seal, (b) the reaction at A. Answer Fig. P6.127 and P6.128 = 200 mm A B 60° D -20° 400 mm 15° Aa Carrow_forward
- Question 4: (a) (i) State the Principle of Moment (Varignon's Theorem). (ii) Prove that the moment of a couple is the same about any axis perpendicular to the plane of action of the couple. (b) A uniform rod Whose centre of gravity G divides it into the ratio AG : GB = a :b is in limiting equilibrium at an angle a with the horizontal with its upper end B resting against a smooth peg and its lower end A attached to a light cord, which is fastened to a point C on the same level as B. Prove that the angle B at which the cord is inclined to the horizontal is given by the equation a+b b tanß = tana cot a a a Question 5: (a) From Lesotho Bank tower an object was observed on the ground at a depression o below the horizon. A gun was fired at an elevation a, but the shot missing the object, stuck the ground at a point whose depression was y. Prove that the correct elevation 0 of the gun is given by sin(20 +0) + sin(o) sin(2a+0) + sin(o) sin y (1+ cos(20)) sin o (1+cos(2y))arrow_forward6.70 A uniform cable weighing 15 N/m is suspended from points A and B. The force in the cable at B is known to be 500 N. Using the result of Prob. 6.69, calculate (a) the force in the cable at A; and (b) the span L. B 8 m 4 m Fig. P6.70arrow_forwardThree cylinders are piled in a rectangular ditch as shown, neglecting friction. Wa=15lb, Wb=40lb and Wc=20lb. Determine reaction between cylinder A and the floor, reaction between cylinder A and wall, reaction between cylinder A and cylinder B, reaction between cylinder B and cylinder C, reaction between cylinder B and the wall, and reaction between cylinder C and the wall.arrow_forward
- The uniform 10 kg rod AB is supported by a ball and socket joint at A and by the cord CG that is attached to the midpoint G of the rod. Knowing that the rod leans against a frictionless vertical wall at B and that the tension in the cord CG, TCG=52.1 N, determine the following a.) Which of the following best shows the equivalent force-couple set at point A of the tension at cord CG, TCG? Choices: a F= -36.8 N i + 24.5 N j - 27.6 N k M = -7.36 Nm i - 11.03 Nm j b F= -36.8 N i + 24.5 N j - 27.6 N k M = -7.36 Nm i - 29.4 Nm k c F= 36.8 N i - 24.5 N j + 27.6 N k M = 7.36 Nm i + 11.03 Nm j d F= 36.8 N i - 24.5 N j + 27.6 N k M = 7.36 Nm i + 29.4 Nm k b.) Which of the following moments is equal to zero? Choices: The moment of the tension in cord CG, TCG about point OThe moment of the tension in cord CG, TCG about point AThe moment of the tension in cord CG, TCG about point BThe moment of the tension in cord CG, TCG about axis ABarrow_forwardA freight wagon is at rest on a track at an angle of 25o to the vertical. The gross weight of the wagon and its load is 36kN and acts at a point 750 mm from the track, in the middle between the two axles. The wagon is held by a cable 600 mm from the track. Determine the traction on the cable and the reaction on each pair of wheels.arrow_forwardThe bent rod in Fig. a is supported at A by a journal bearing, at D by a ball-and-socket joint, and at B by means of cable BC. Using only one equilibrium equation, obtain a direct solution for the tension in cable BC. The bearing at A is capable of exerting force components only in the z and y directions since it is properly aligned on the shaft. In other words, no couple moments are required at this support. 1 m B 0.5 m .Free-Body Diagram. As shown in Fig. b, there are six unknowns 0.5 m Equations of Equilibrium. The cable tension T, may be obtained directly by summing moments about an axis that passes through points D and A. Why? 100 kgarrow_forward
- The pin at C is attached to member BCD and can slide along a slot cut in the fixed plate shown. Neglecting the effect of friction, derive an expression for the magnitude of the couple M required to maintain equilibrium when the force P that acts at D is directed (a) as shown, (b) vertically downward, (c) horizontally to the right.Fig. P10.18arrow_forward7.34 The cylinder and the block are connected by a horizontal cord. Determine the largest couple C that can be applied to the cylinder without disturbing the equilibrium of the system. Assume that both bodies are homogeneous.arrow_forward4.7 When cars C and D stop on a two-lane bridge, the forces exerted by their tires on the bridge are as shown. Determine the total reactions at A and B when (a) a = 2.9 m, (b) a = 8.1 m. -12 m 3.9 kN 6.3 kN| 7.9 kN 7.3 kN C D\B A L-20m-| -2.6 m→ -2.8 marrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





